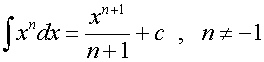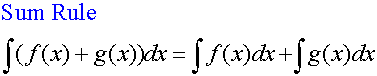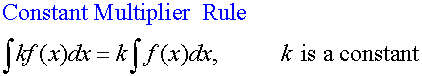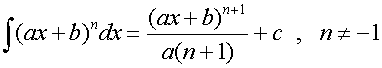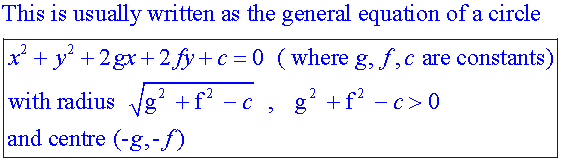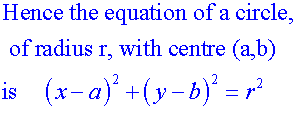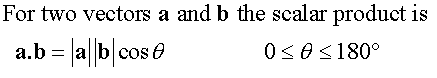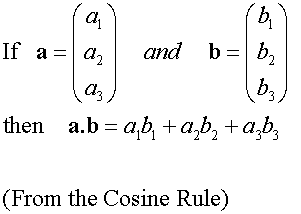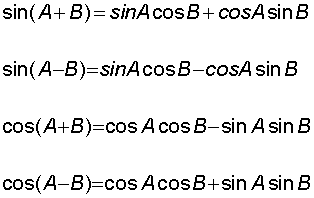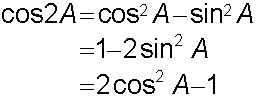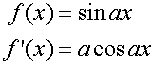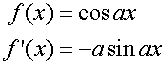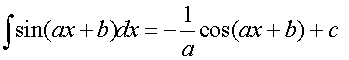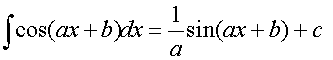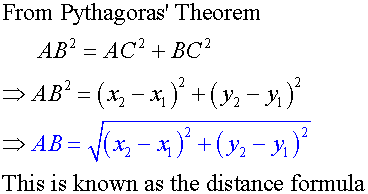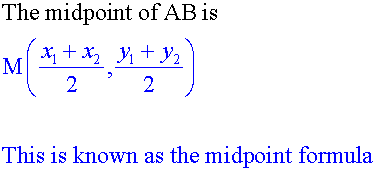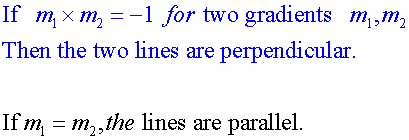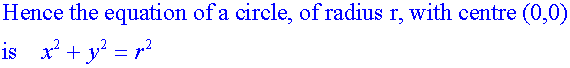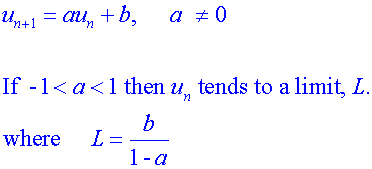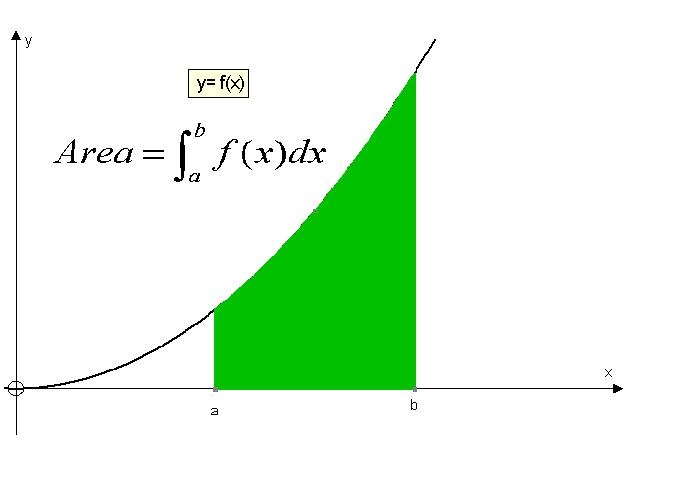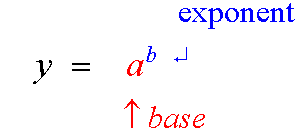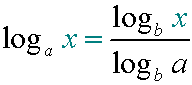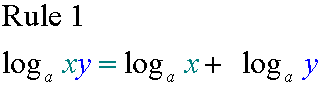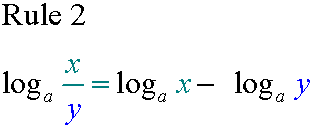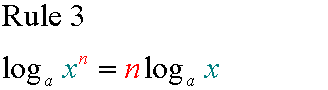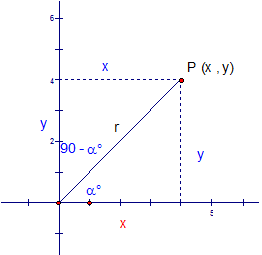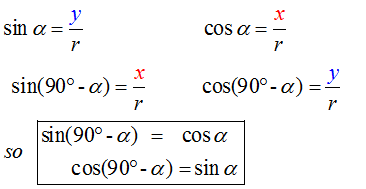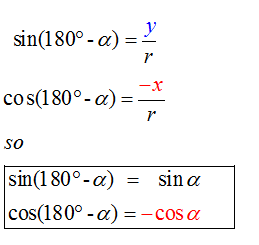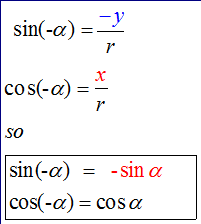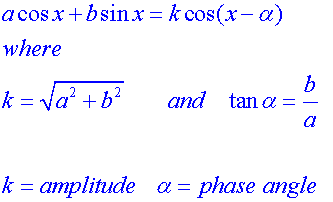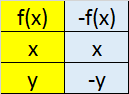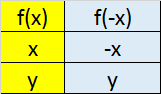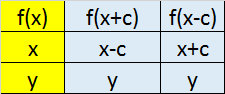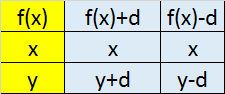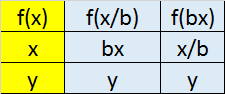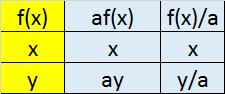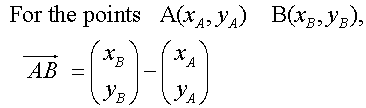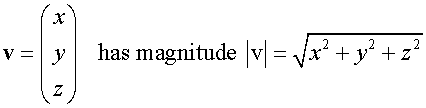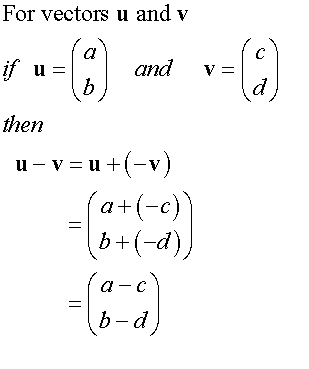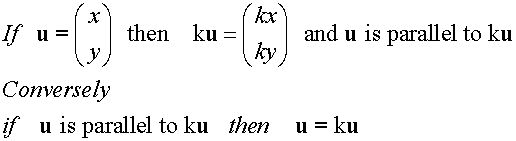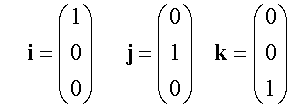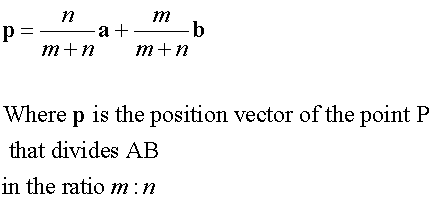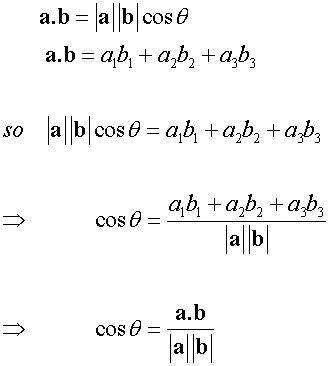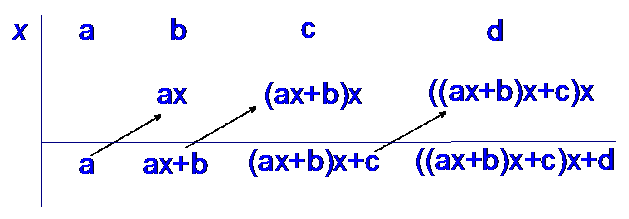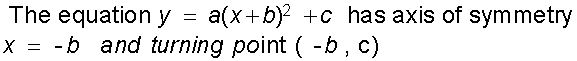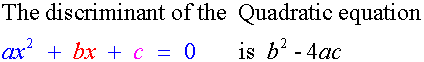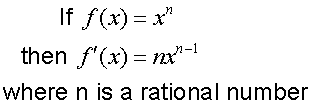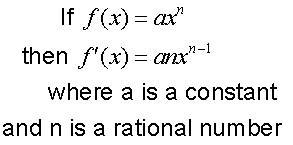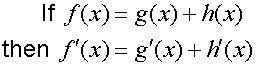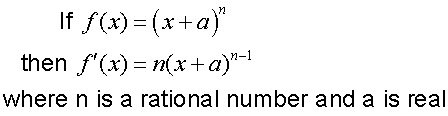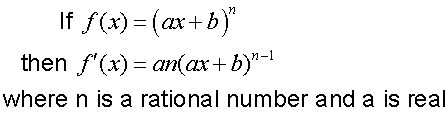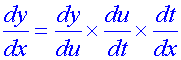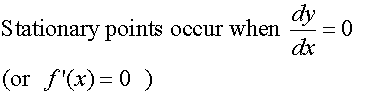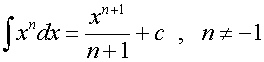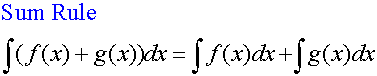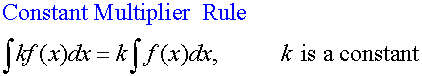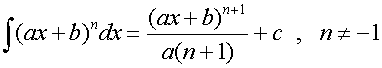SQA Higher Exam
The following formulae are on the exam question sheet.
These are given in the order in which they appear - but are not an exact reproduction of the exam formulae sheet, which is available here
Click on the formula for the relevant Maths Mutt page.
Apps 1.2 : Applying algebraic skills to circles
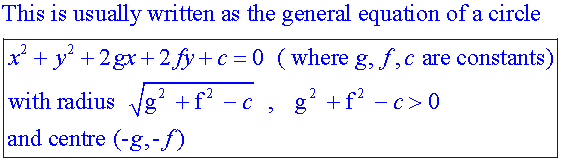
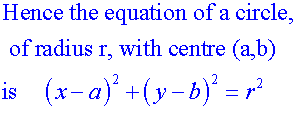
E&F 1.4: Applying geometric skills to vectors.
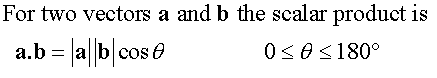
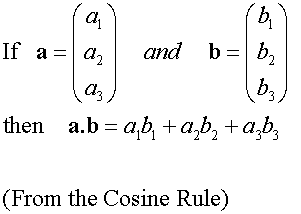
E&F 1.2 : Applying trigonometric skills to manipulating expressions.
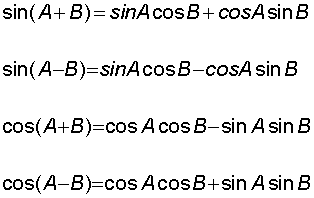
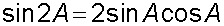
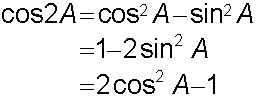
R&C 1.3 : Applying calculus skills of differentiation.
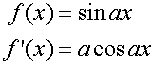
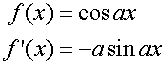
R&C 1.4 : Applying calculus skills of integration
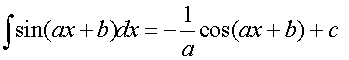
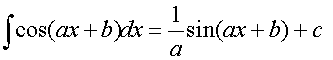
The following collection of formulae is not given in the exam and so must be learnt.
Applications (Apps)
Apps 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to rectilinear shapes.
y - b = m(x - a), where (a, b) are co-ordinates of a point on the line.
Gradient = tanθ where θ is measured anticlockwise.
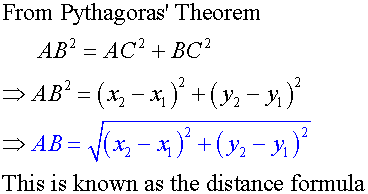
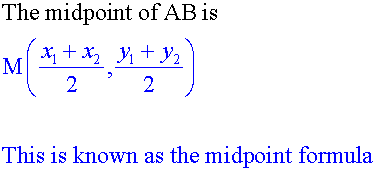
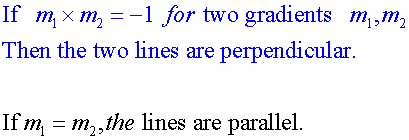
Apps 1.2 : Applying algebraic skills to circles
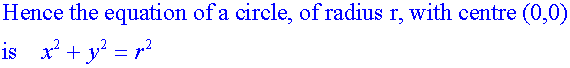
Touching circles :
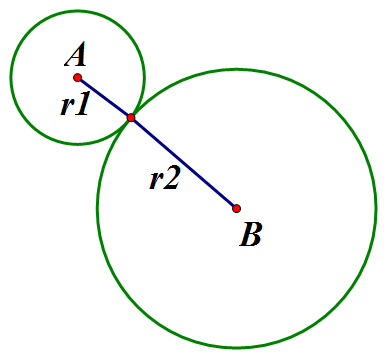
If AB = r1 +r2, the circles touch externally.
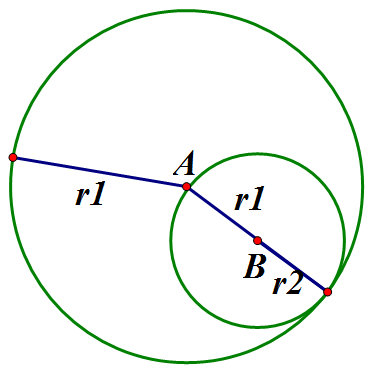
If AB = r1 - r2, the circles touch internally.
Apps 1.3 :Applying algebraic skills to sequences
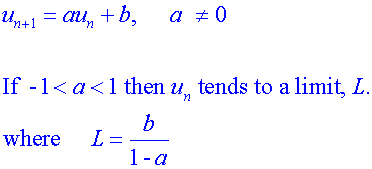
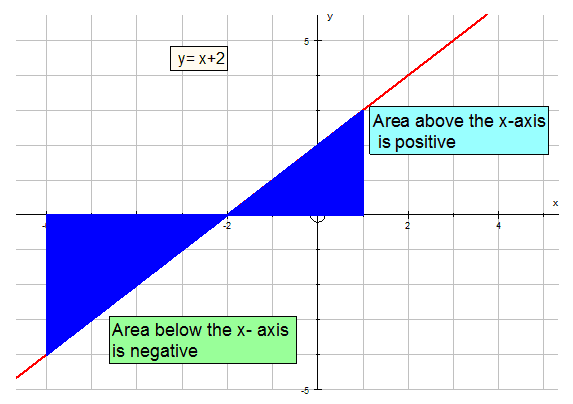
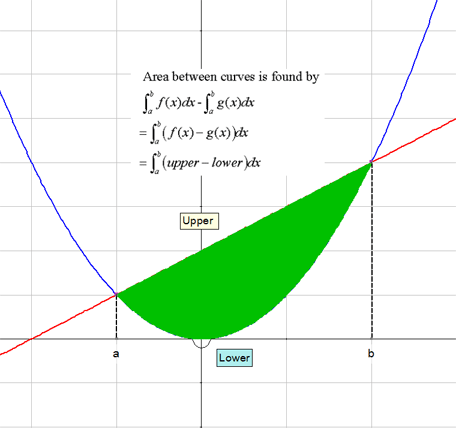
Apps 1.4 : Applying calculus skills to optimisation and area.
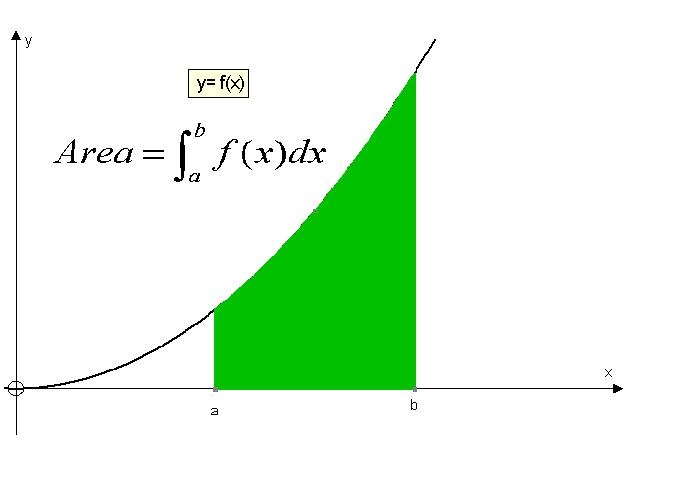
Expressions and Functions (E&F)
E&F 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to logarithms and exponentials
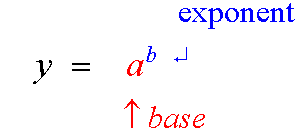
If y = ax
x = loga y
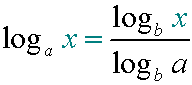
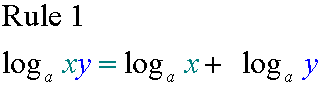
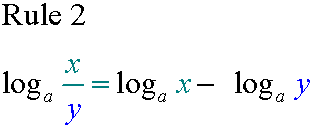
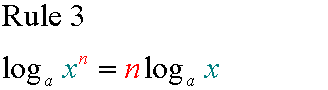
Rate of Decay
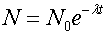
where N is the number of radioactive atoms present at time t , λ is the transformation decay constant and No is the original starting value.
E&F 1.2 : Applying trigonometric skills to manipulating expressions.
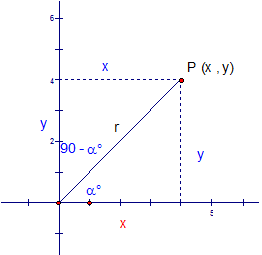
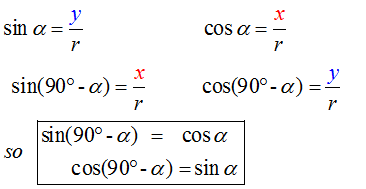
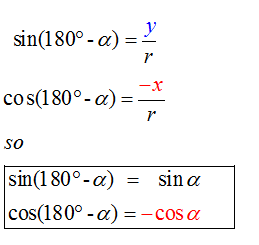
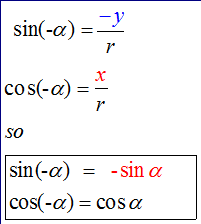
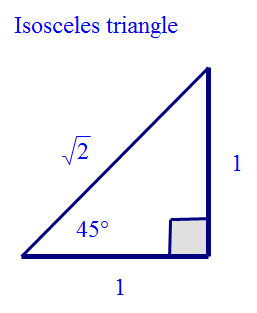
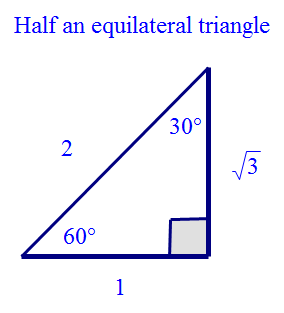
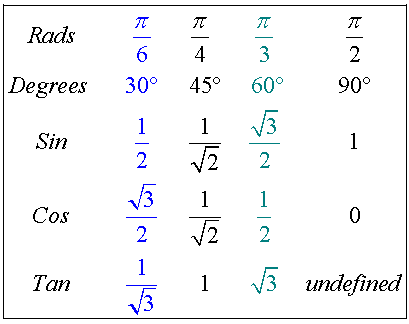
Exact values
Wave Theory
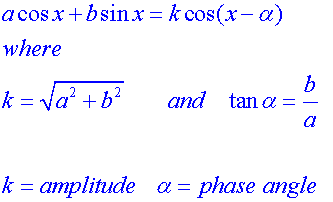
E&F 1.3 : Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions.
The Domain is the set of input numbers,
the Codomain is the set of possible output numbers,
the Range is the set of actual output images.
Transformations
Reflection in
x axis y axis
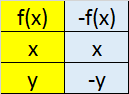
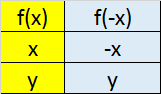
Translation in
x axis y axis
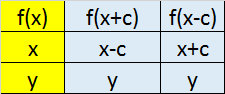
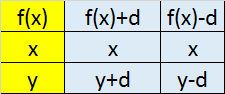
Scaling in
x axis y axis
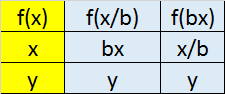
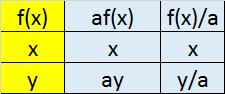
Inverse
The inverse of a function f(x) is denoted f-1(x)
f-1 (f(x)) = f (f-1 (x)) = x
To inverse a function ( which must be in a one – one correspondence)
reflect it in the line y = x.
Logarithms and exponential
An ordinary exponential function always has the points
(0, 1) , ( 1 , base) and (-1, 1/base )
since
a0 =1 , a1 = a and a-1 =1/a
The exponential function f(x) = ax has an inverse function
f-1(x) = logax upon reflection in the line y = x
If y = ax
x = loga y
An ordinary log function always has the points
(1, 0) and (base, 1)
since
loga1=0 and logaa=1
Log graphs
Log scale Y axis only
If y = abx then log y = log a + xlogb
Compare this to Y = mx + c
where Y = log y, m = log b and c = log a
Log scale both axis
If y = axb then log y = blog x + log a
Compare this to Y = mX + c
where Y = log y, X = logx and c = log a
E&F 1.4: Applying geometric skills to vectors.
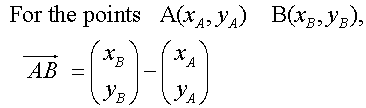

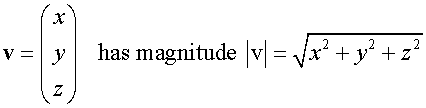
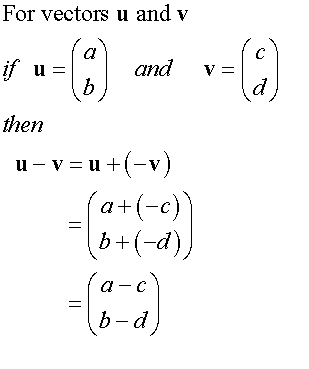
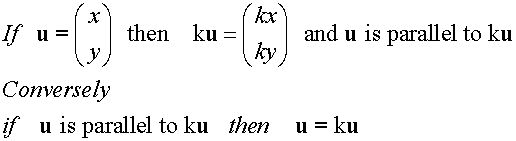

3D Vectors
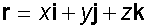
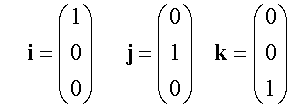
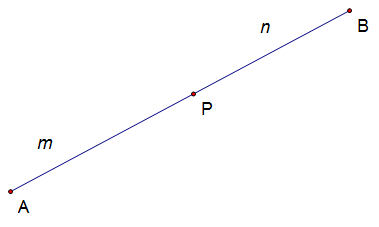
Section formula
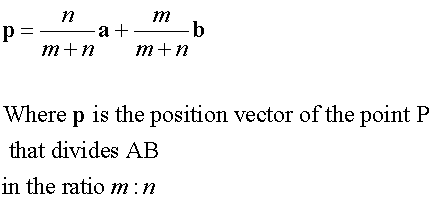
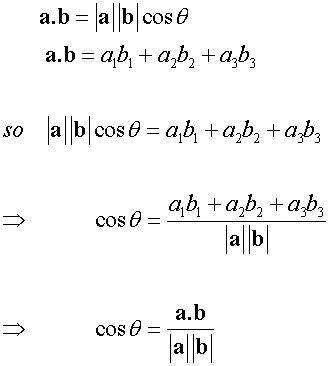
Relationships and Calculus (R&C)
R&C 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to solve equations.
Polynomial division
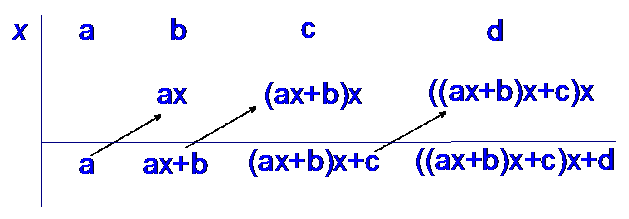
The Remainder Theorem
If a polynomial f(x) is divided by x-h, then the remainder is f(h).
( h may be a fraction)
The Factor Theorem
If f(x) is a polynomial , f(h) = 0<=> (x-h) is a factor of f(x)
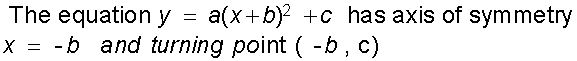
Quadratics
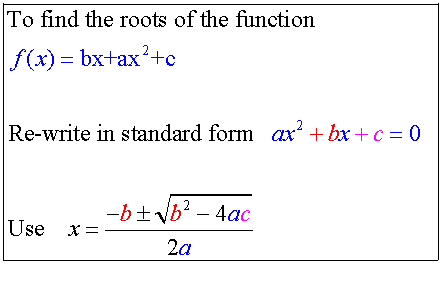
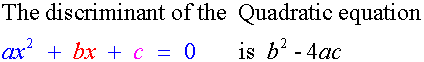



Tangency
If b2 – 4ac > 0 , the line cuts at two distinct points.
It is not a tangent.
If b2 – 4ac < 0 , the line does not touch the curve.
It is not a tangent.
If b2 – 4ac = 0 , the line touches the curve at only one point.
It is a tangent.
R&C 1.2 : Applying trigonometric skills to solve equations.


R&C 1.3 : Applying calculus skills of differentiation.
The derivative of a function for some particular value
is a measure of the rate at which the function is changing
at that particular value.
TThe derivative of a function for some particular value
is also the gradient of the graph of the function at that point.
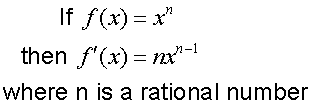
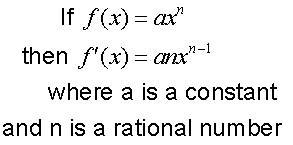
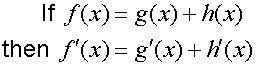
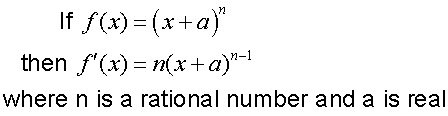
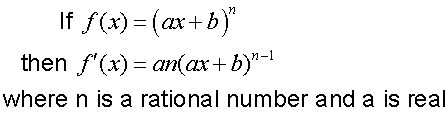
The chain rule
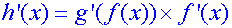
or in Leibnitz notation
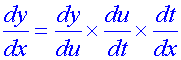
Graphing
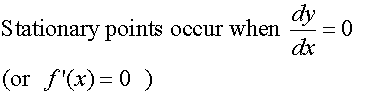
R&C 1.4 : Applying calculus skills of integration.