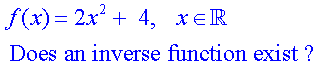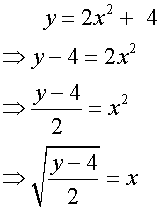One to One functions
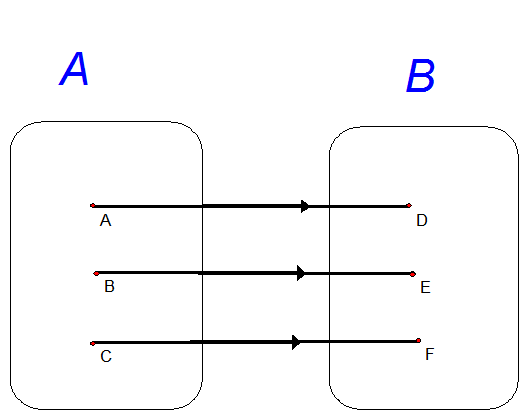
A one-to-one correspondence exists when all of the elements of set A
map to exactly one element of set B and vice versa.
This is a one-to-one correspondence.
This is a function, but not a one-to-one correspondence.
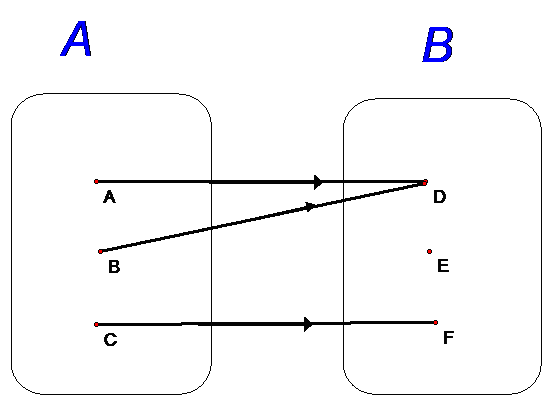
When a one-to-one correspondence exists,
the function that maps from set B to set A is called the inverse of f.
The inverse of a function f(x) is denoted f-1(x)
For each element, f(a) = b and f-1 (b) = a
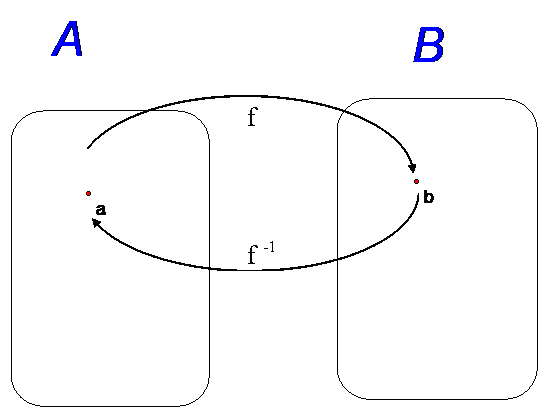
The domain of f is the range of f-1
The range of f is the domain of f-1
f-1 (f(x)) = f (f-1 (x)) = x
Inverse a function
To inverse a function ( which must be in a one – one correspondence)
reflect it in the line y = x.
Example
Find the inverse of the function f(x) = 2x + 2
f(x) = 2x + 2 has graph y = 2x + 2
f(0) = 0 + 2 = 2 so the point (0,2) is on the line y = 2x + 2.
f(-1) = -2 + 2 = 0 so the point (-1,0) is on the line y = 2x + 2.
If this function is reflected in the line y = x,
the values for x and y are swapped, since y = x and x = y.
So the point (0,2) becomes ( 2,0)
and the point ( -1,0) becomes ( 0,-1)
The equation of the reflected line can now be found:-
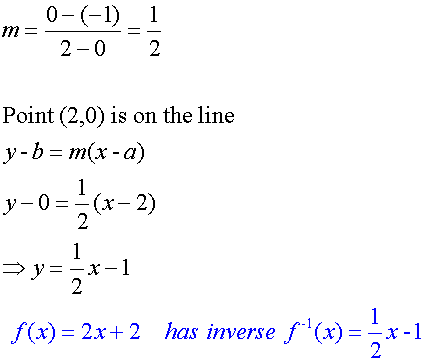
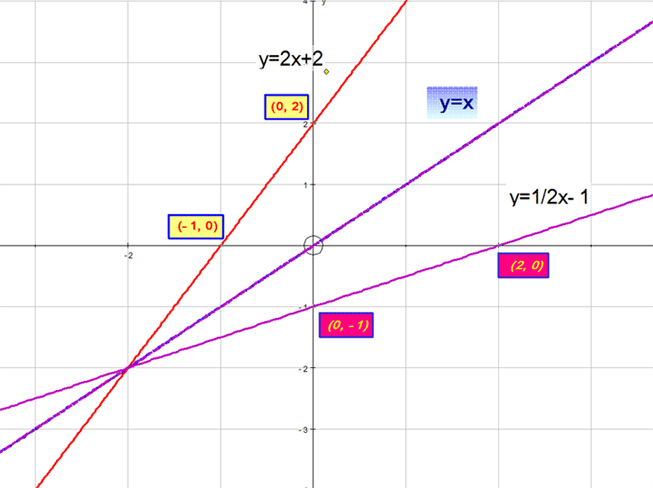
which looks like this:
Algebraic method
Example
Find the inverse of the function f(x) = 2x + 2
f-1 (f(x)) = f (f-1 (x)) = x
so , substituting for x into f(x) = 2x + 2
2(f-1 (x)) + 2 = x
Now just re-arrange to make f -1 (x) the subject of the formula
2(f-1 (x)) = x - 2
f-1 (x) =( x - 2)/2
so f -1 (x) = ½x – 1
Alternatively
f(x) = 2x + 2 has graph y = 2x + 2
Make x the subject of the formula y = 2x + 2
y = 2x + 2
y - 2 = 2x
½ (y - 2) = x
so x = ½ (y - 2)
Swap the letters (because of the reflection y = x)
y = ½ (x - 2)
y = ½x – 1
so f -1 (x) = ½x – 1
Example
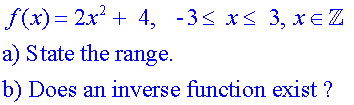
a)
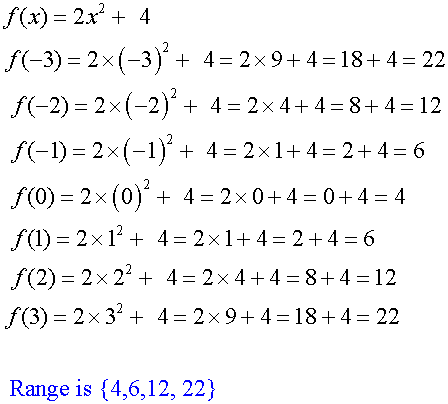
b)

Example