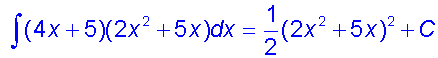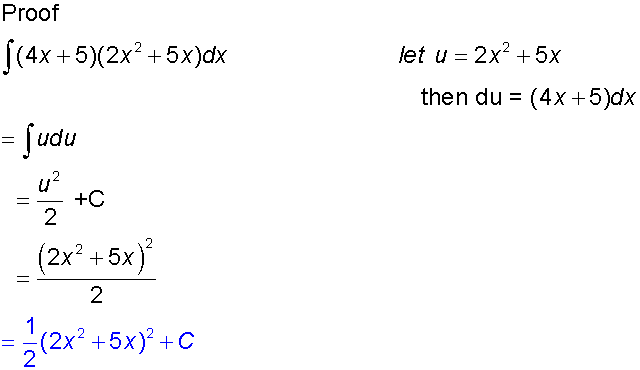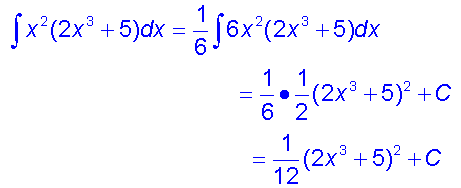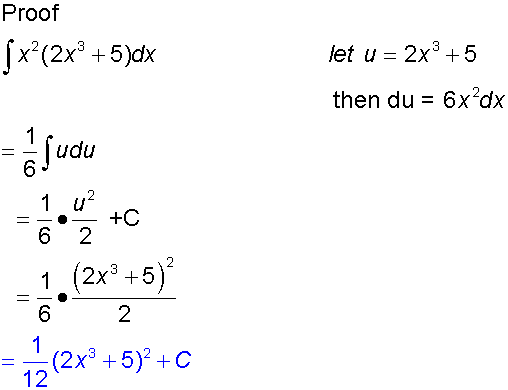Integral Calculus
![]()
Integral calculus is mainly concerned with summing the values of a function over a particular range, and is particularly useful for finding the area of an irregular shape.
Integration is the process of finding the anti-derivative.
![]() means the indefinite integral of the function
is to be calculated with respect to x.
means the indefinite integral of the function
is to be calculated with respect to x.
The anti-derivative F(x) is called the integral,
c is called the constant of integration.
![]()
so differentiating the integral results in the original function.
Basic Rules of Integration
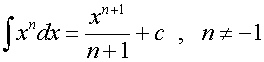
Examples
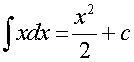
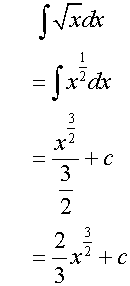
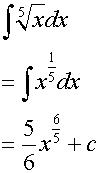
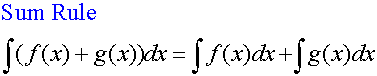
Examples
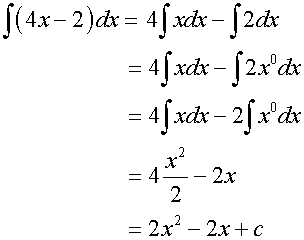
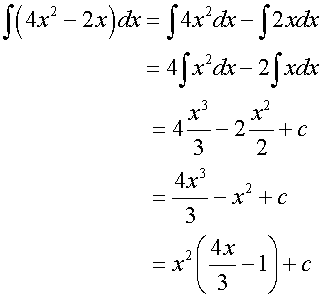
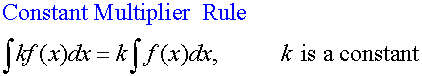
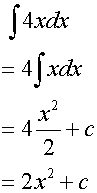
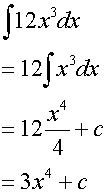
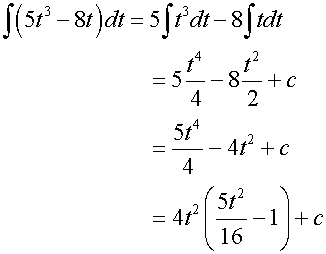
∫(ax +b)n
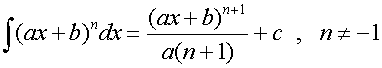
Example
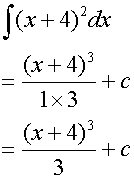
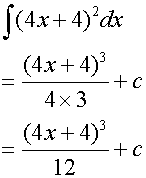
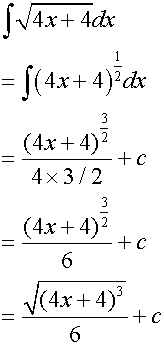
Integrating Trig Functions
![]()
![]()
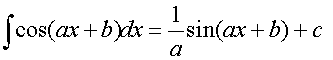
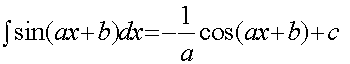
Remember to use Radians !!!
Example
![]()
![]()
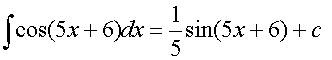
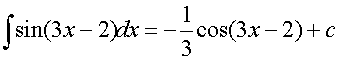
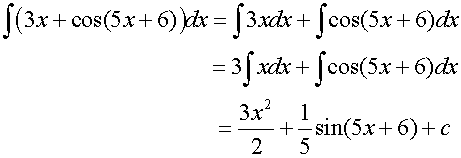
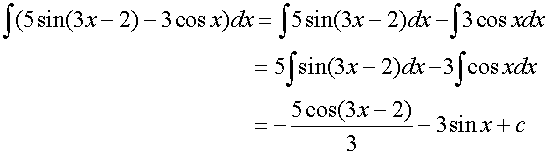
Integrating Logarithms and Exponentials
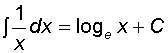
![]()
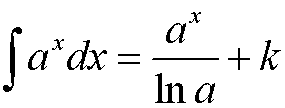
Don’t forget to apply the chain rule in reverse if necessary!
Examples
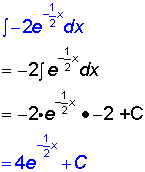
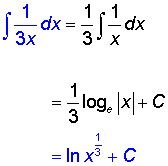
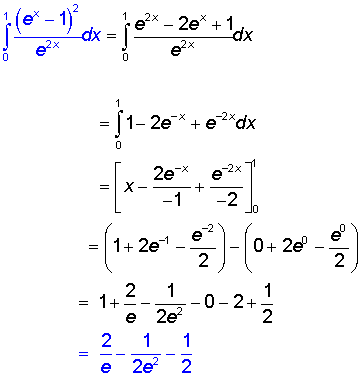
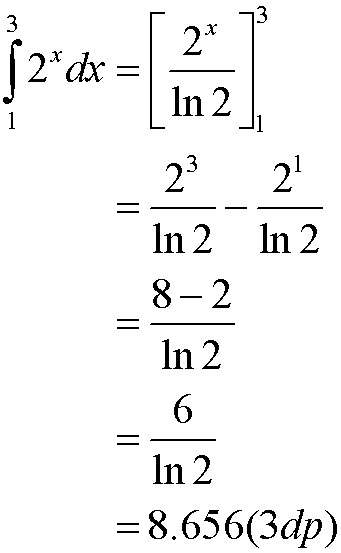
Integration by substitution
This can be used when the function to be integrated

Examples
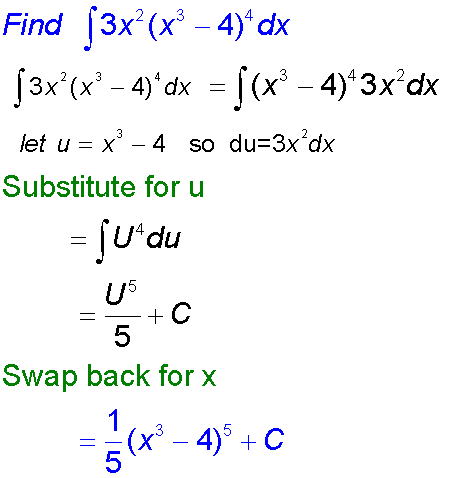
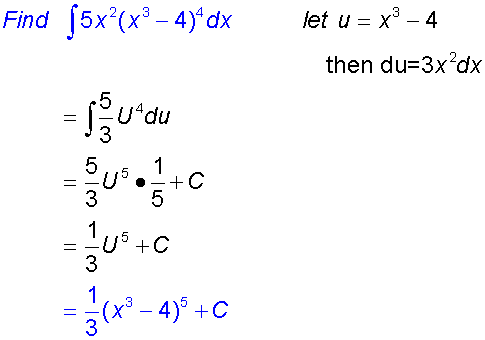
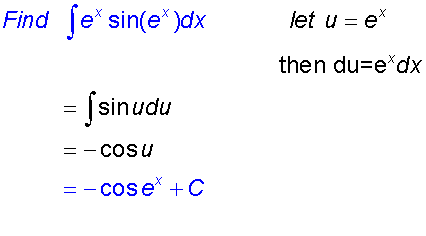
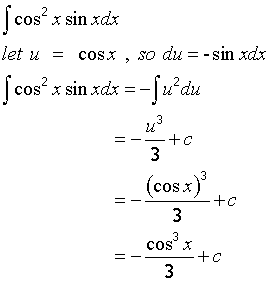
This is very useful for for finding integrals such as sin3xdx
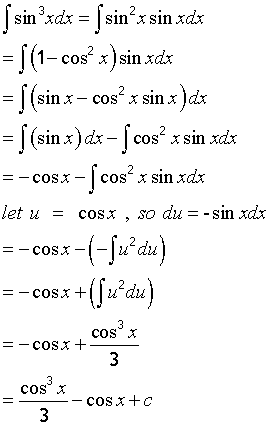
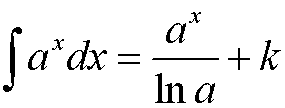
Proof
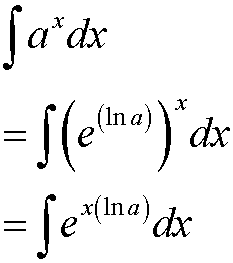
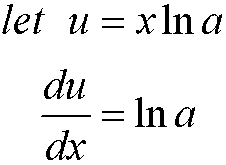
so
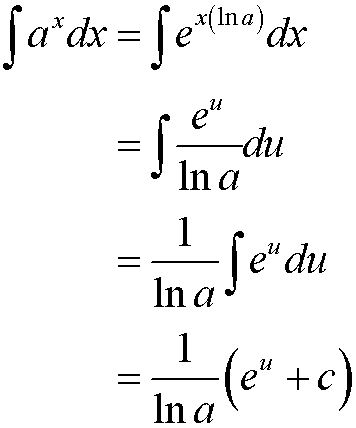
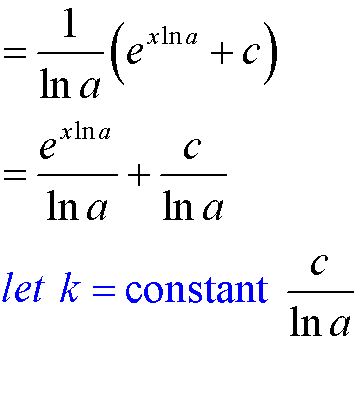
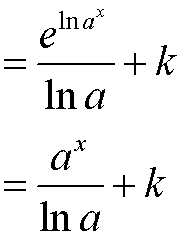
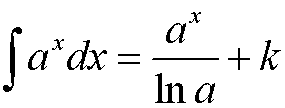
When finding definite integrals, remember to change the limits !
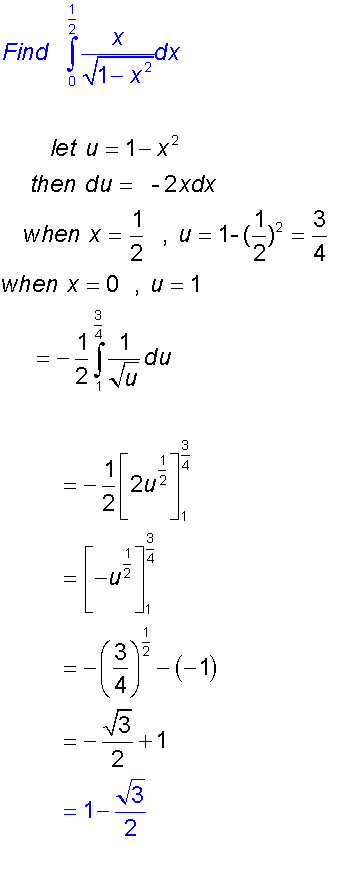
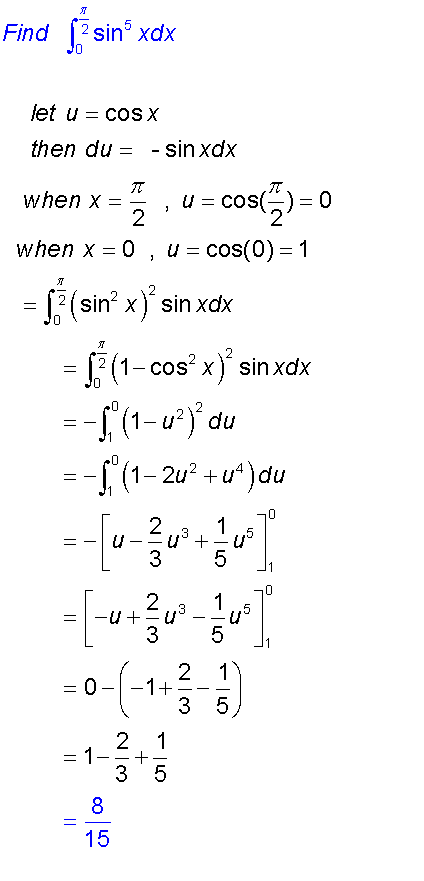
Sometimes it is easier to substitute dx
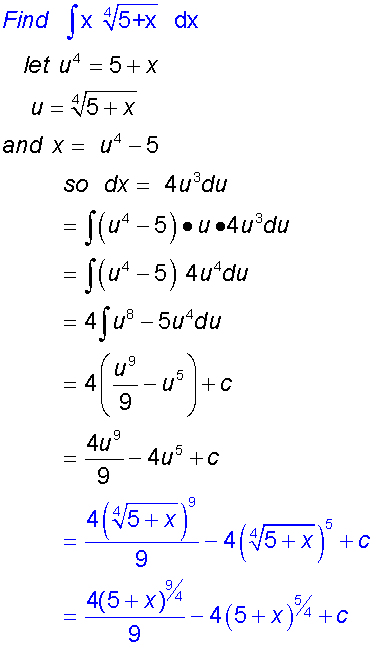
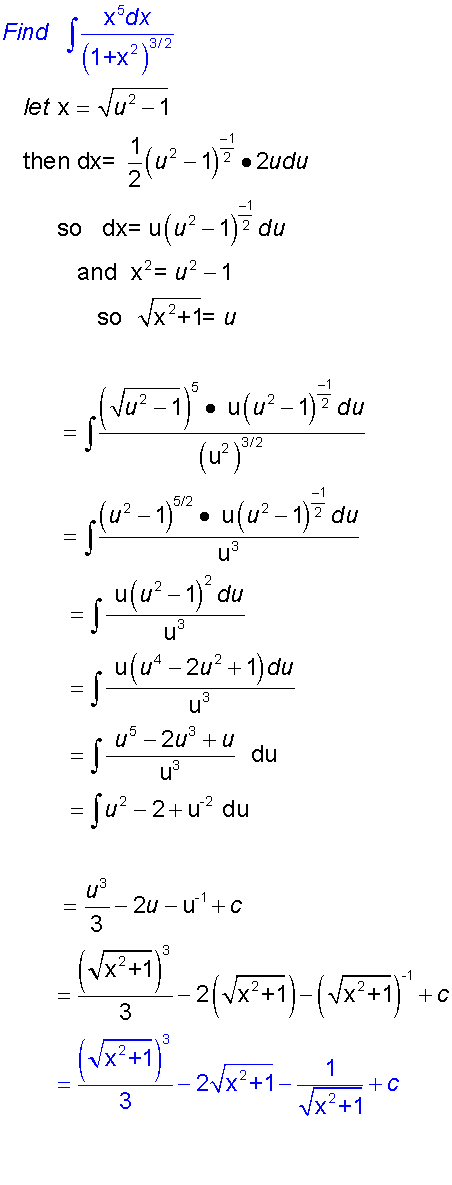
Common Forms
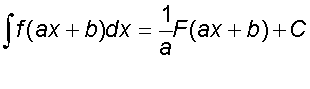
Examples
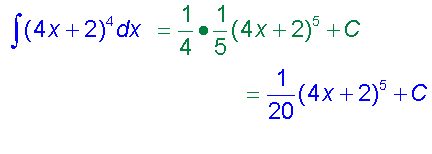
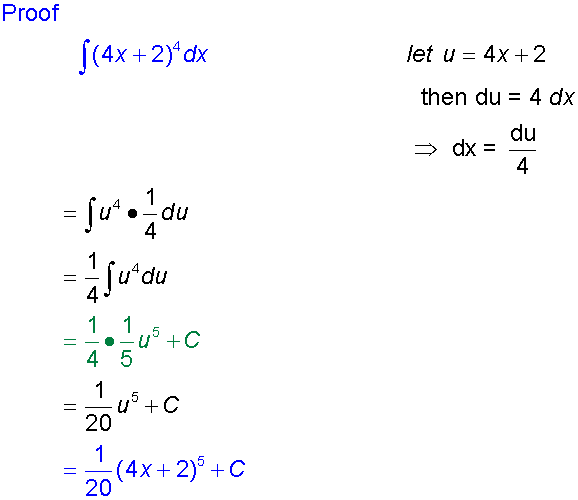
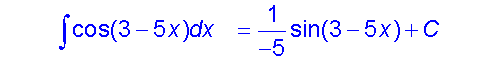
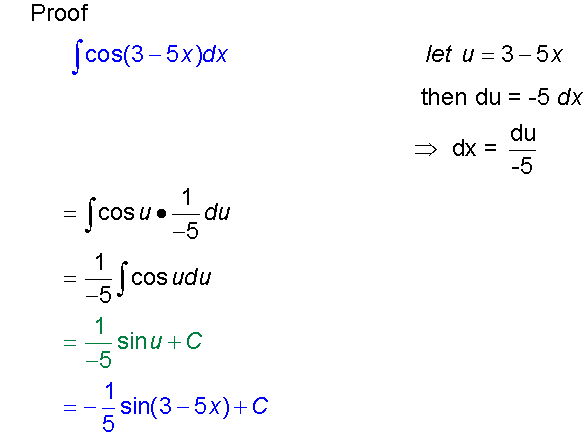
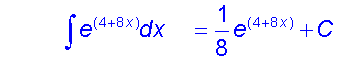
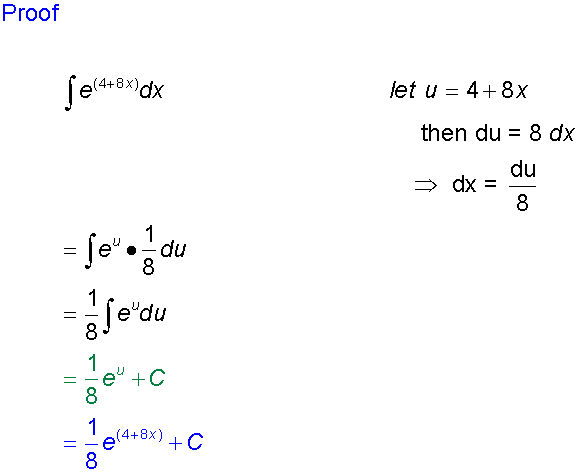
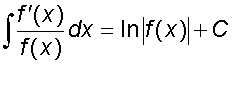
Examples
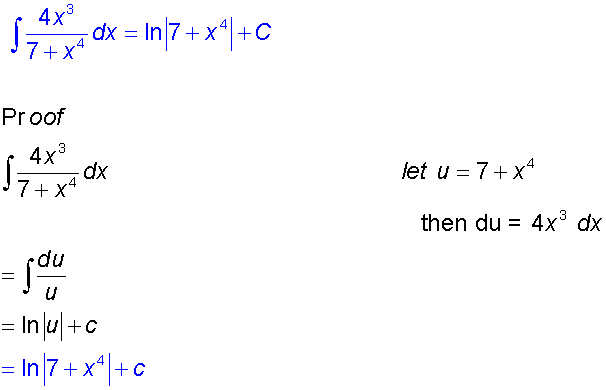
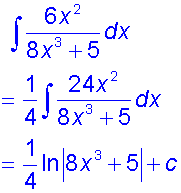
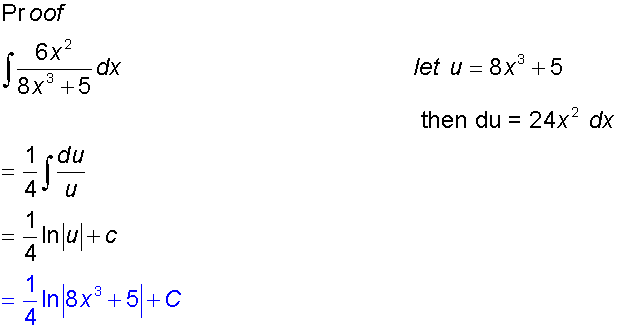
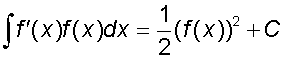
Example