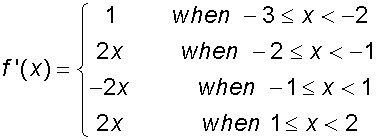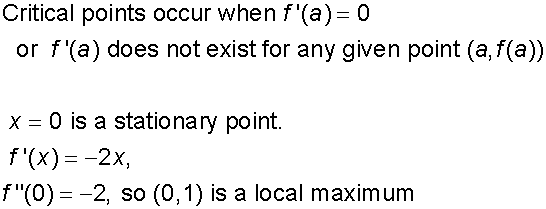Gradients of tangents to curves
The derivative of a function for some particular value
is also the gradient of the graph of the function at that point.
Example
A curve has equation 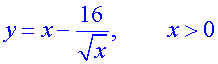
Find the gradient of the tangent at the point where x = 4.
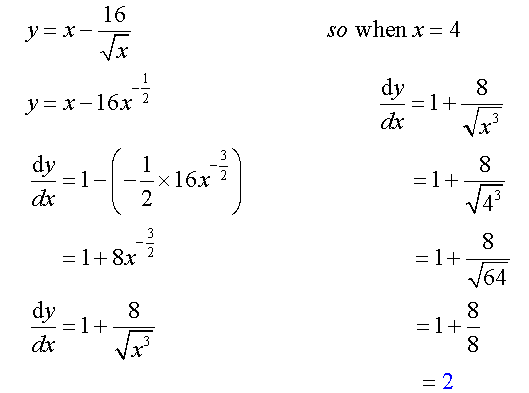
Finding the equation of a tangent
Example
The point A( -1,7) lies on the curve with equation ![]()
Find the equation of the tangent to the curve at point A.
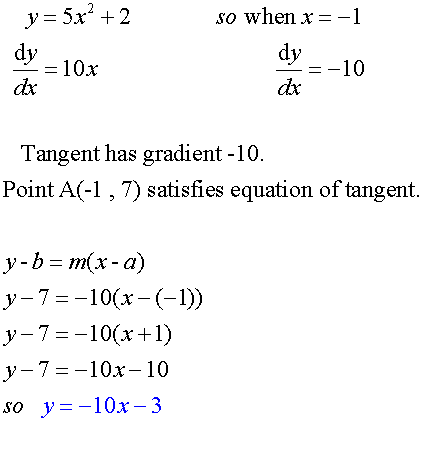
Increasing/ Decreasing functions
The graph below is decreasing when x is less than zero:-
- The value of the function is decreasing as x is increasing
- The gradient is negative
and increasing when x is greater than zero:-
- The value of the function is increasing as x is increasing
- The gradient is positive
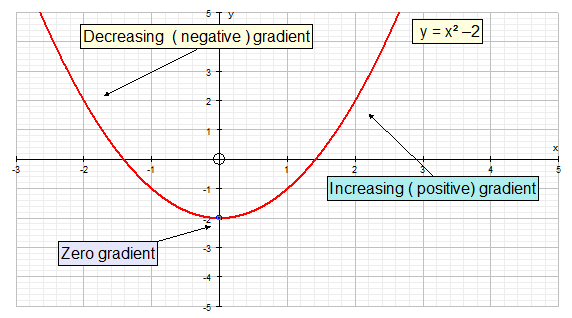
When x = 0, the gradient is zero and the graph changes from
a negative gradient to a positive gradient.
This turning point is called a stationary point.
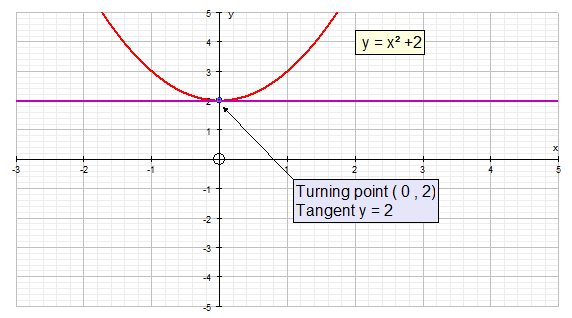
The stationary point can be a :-
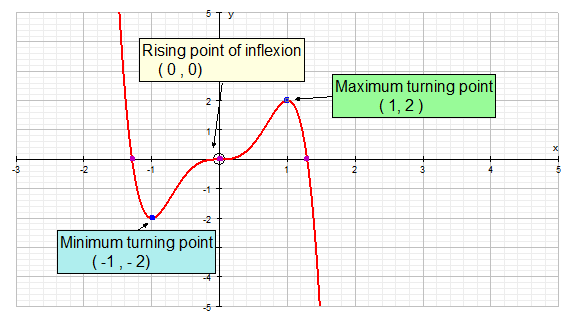
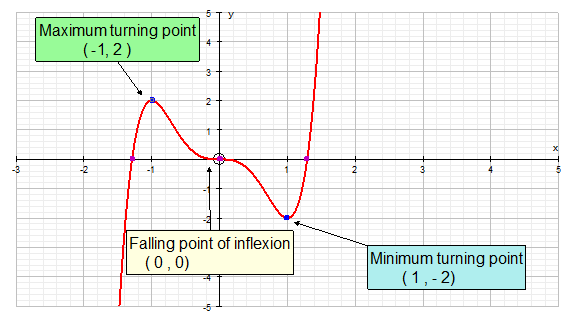
Maximum
Minimum
Rising point of inflection
Falling point of inflection
Finding Stationary Points
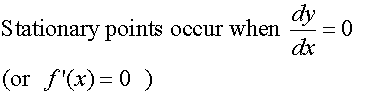
To find the stationary points, set the first derivative
of the function to zero, then factorise and solve.
Example
Find the stationary points of the graph ![]()
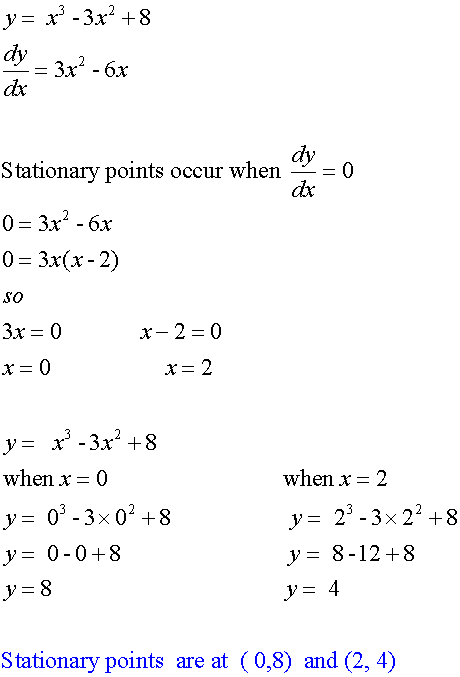
Nature Tables
To find out if the stationary point is a maximum,
minimum or point of inflection,
construct a nature table:-
- Put in the values of x for the stationary points.
- Copy these values, with a small minus and plus sign.
- Copy the first part of the factorised form of the derivative.
- Repeat for subsequent parts of the factorised form of the derivative.
- Write down the whole factorised form of the derivative.
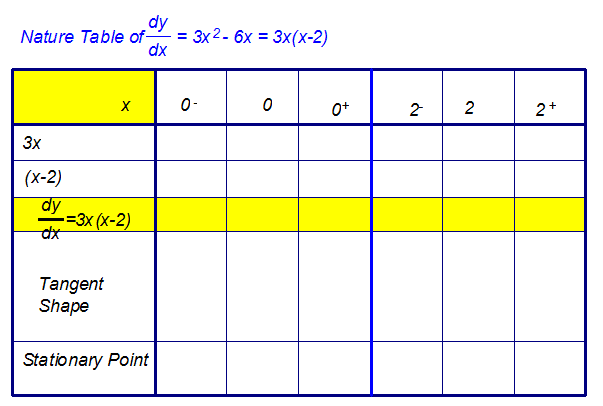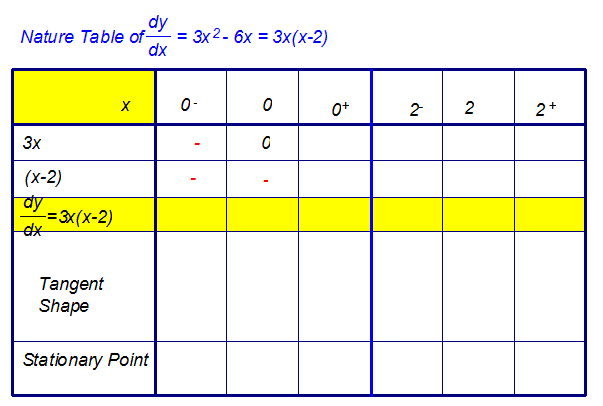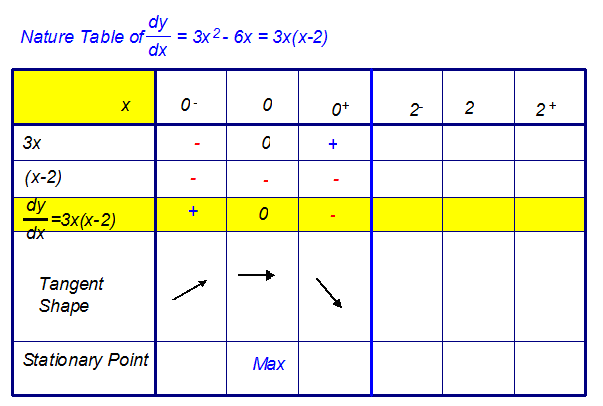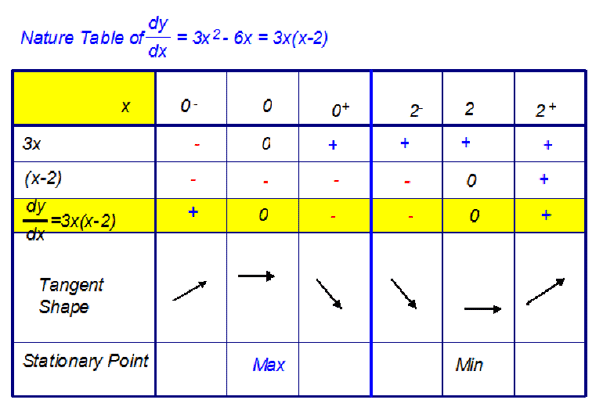
Starting with the first value,
- Replace x with the value. Do the calculation.
- Write in the sign of the answer that you get.
- Repeat for a number slightly smaller than x
Put your answer in the small minus box. - Repeat for a number slightly larger than x
Put your answer in the small plus box. - Multiply the signs together and put in the
factorised form of derivative box. - Now draw in the tangent shape.
- Repeat for other stationary points
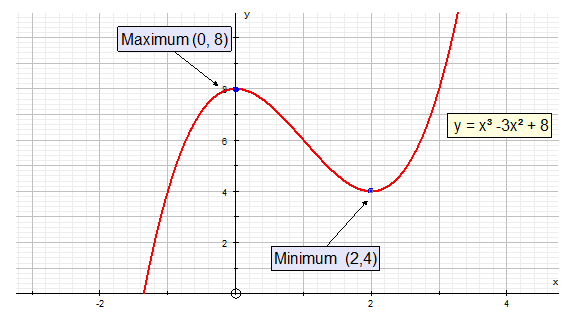
Second Derivative
The second derivative f’’(x) measures the gradient
with respect to x.
When this is positive, the curve is concave up – it is a
minimum turning point.
When f’’(x) is negative, the curve is concave down– it is a
maximum turning point.
When f’’(x) is zero, there may be a point of inflexion.
Draw a nature table to confirm.
Example
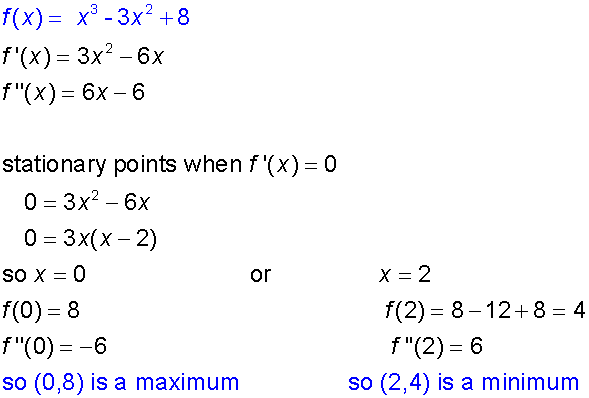
Closed Intervals
In a closed interval, the maximum and minimum values of the function
occur either at a stationary point or an end point.
Example
Find the maximum and minimum values of
![]()
Stationary points occur when f’(x)=0
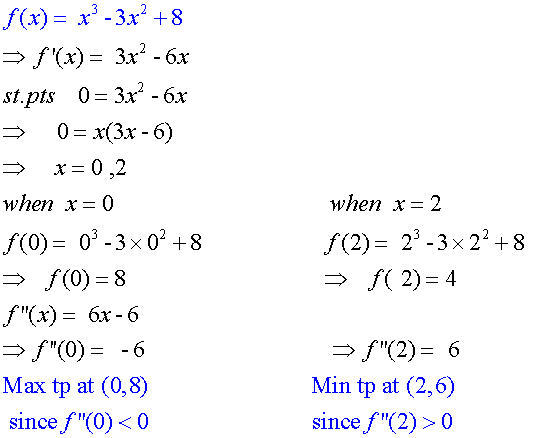
Now check end points
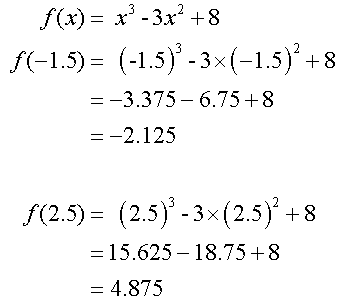
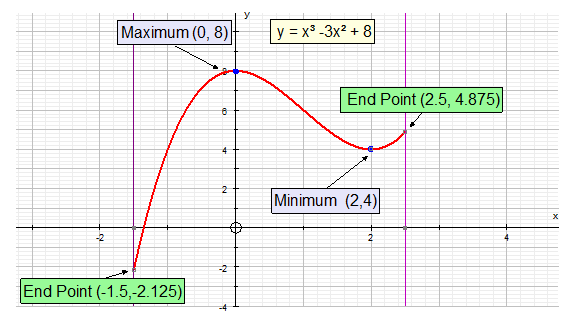
For the given interval, the maximum value is 8
and the minimum value is -2.125
Critical Points
Assuming a is in the domain of f

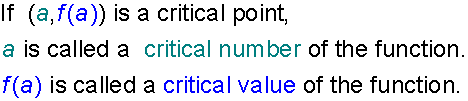

Endpoints
(These are also critical points)

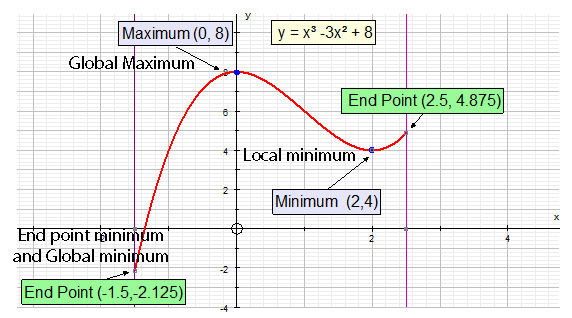
Global maxima and minima

A continuous function defined in a closed interval
must have both a global maximum and minimum.
They are found by examining the local extrema
and end points.
- Find the critical points
- List the endpoints under consideration
- Global maxima and minima must be one of these.
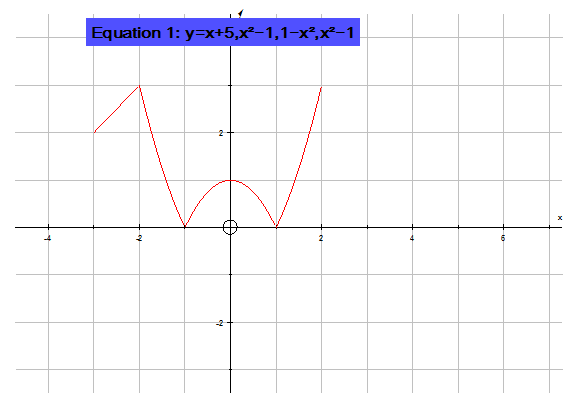
Looking at the example from above
![]()
Example
Find the global extrema of the following
piecewise function in the domain [-3,2].
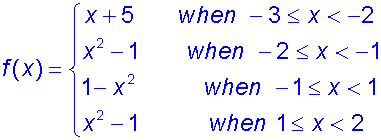
so