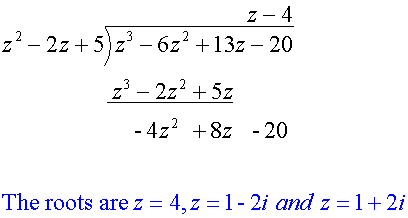Complex Numbers
Sets reminder
![]()
![]()
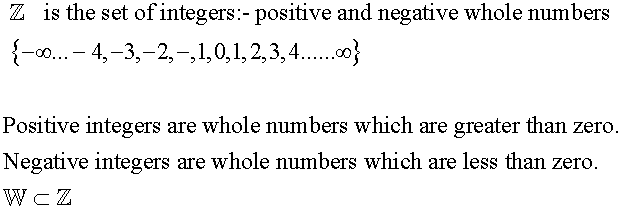


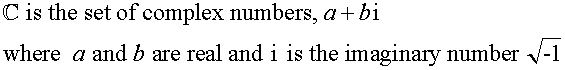
![]()
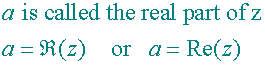
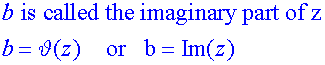
Complex conjugate
This is reflection in the real axis
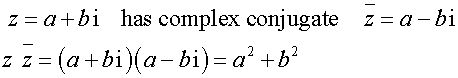
Example
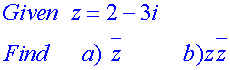
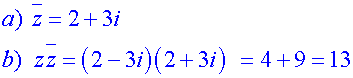
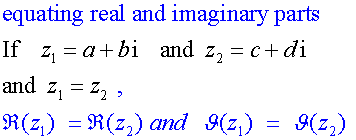
Arithmetic operations
![]()
![]()
![]()
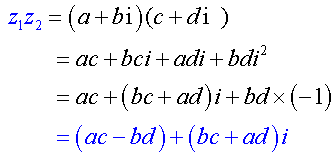
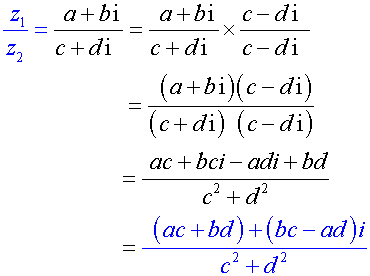
Example
Solve the equation x2- 2x + 5 = 0
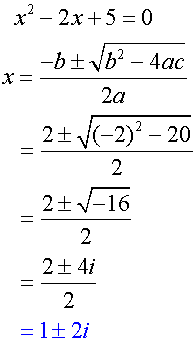
Example
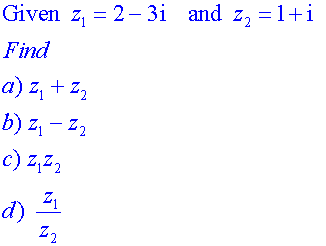
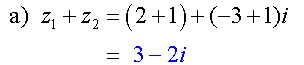
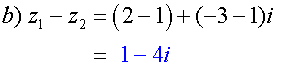
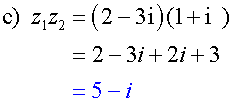
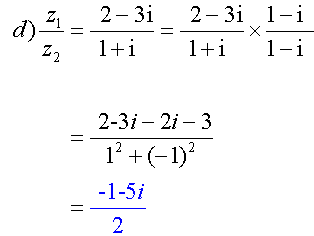
Alternatively,
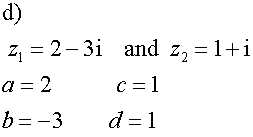
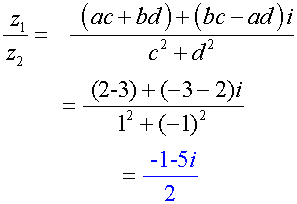
Inverse
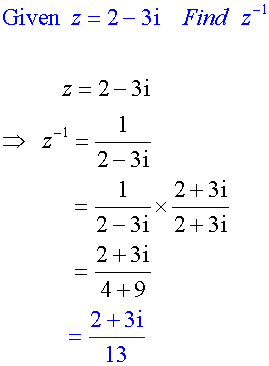
Argand diagrams
z = x + iy can be represented on the complex plane
by the point P(x,y)
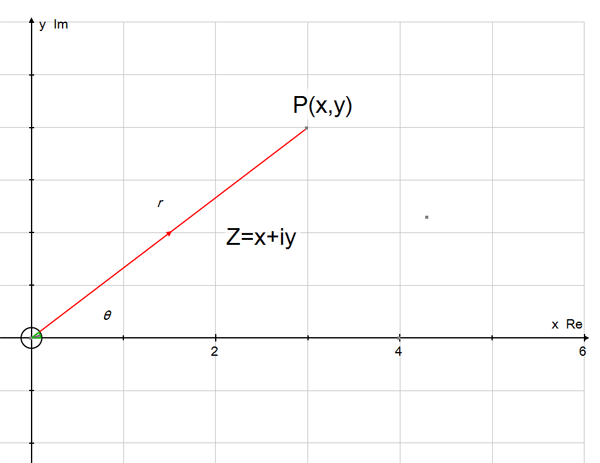
Points on the x axis are real.
Points on the y axis are imaginary.
z = x +iy can also be represented
by the vector ![]()
The length of ![]() , r, is called the modulus of z.
, r, is called the modulus of z.
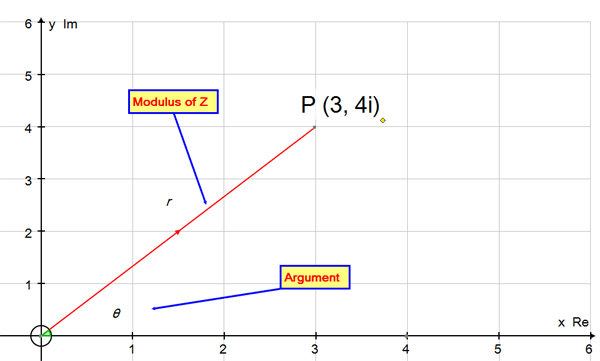
![]()
By Pythagoras’ Theorem
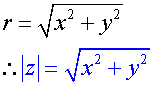
The size of the rotation is called the amplitude or
argument of z.
Arg z = θ + 2nπ
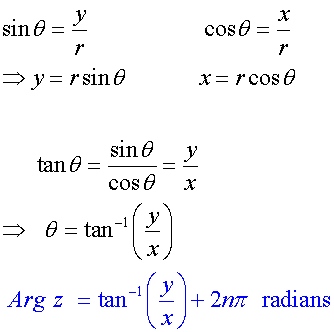
The principal argument is denoted arg z and lies
in the range –π< θ ≤ π
Example
Find the modulus and argument of the complex
number z = 3 + 4i
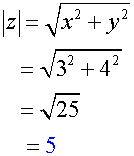
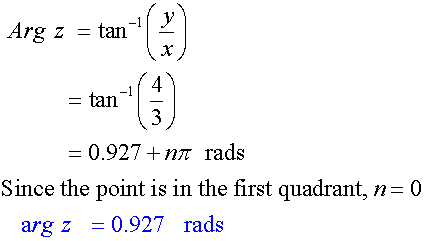
Loci
Given that z = x + iy, find the equation of the locus of the following :
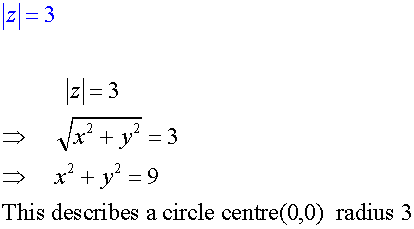
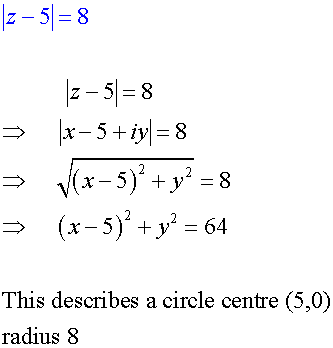
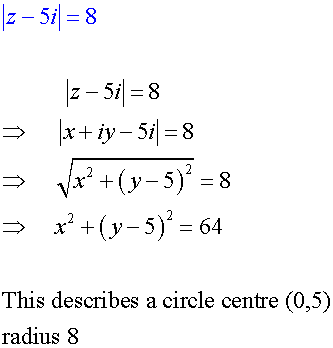
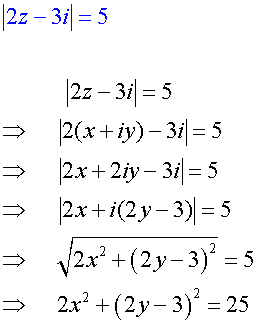
This describes an ellipse with centre (0,3/2)
Polar form
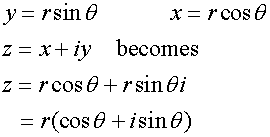
![]()
Example
Express z = 3 + 4i in polar form
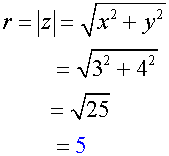
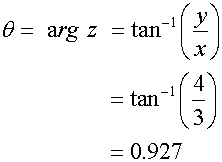
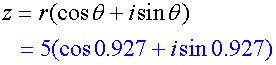
Note
![]()
![]()
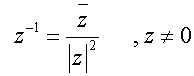
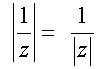
![]()
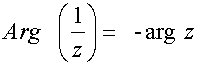
![]()
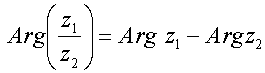
De moivre's theorem
![]()
Example
Given z = 3 + 4i , calculate z5
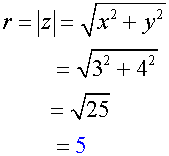
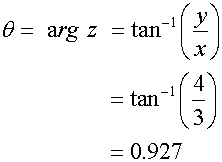
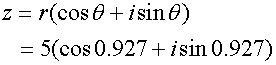

Roots of a complex number
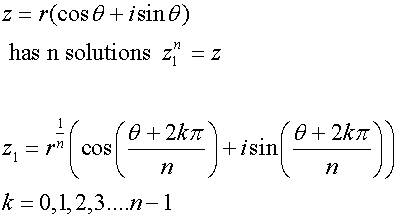
Example
Solve the equation
![]()
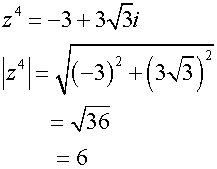
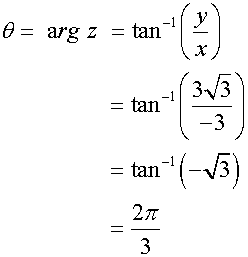
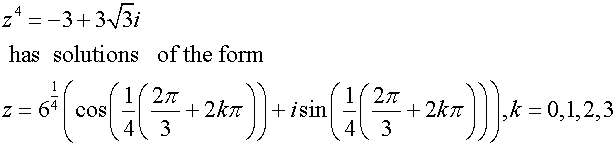
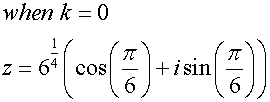
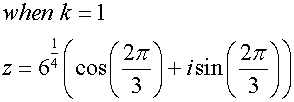
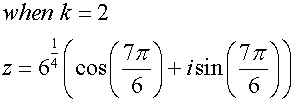
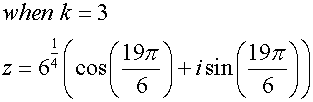
Complex roots
If the root of a polynomial is unreal,
it has complex roots
r(cosθ +isinθ) and r(cosθ -isinθ)
A polynomial of degree n will have n complex roots.
Example
Find the roots of the equation
z3- 6z2+ 13z - 20 = 0 , given z = 1 + 2i is a root
If z = 1 + 2i is a root , then so is its conjugate z = 1 - 2i
Factors are z -1 -2i and z -1+2i
![]()