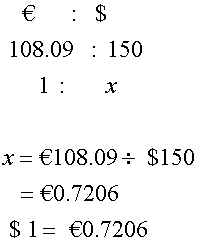Utility Bills
Telephone, gas and electricity bills usually include a standing charge plus a cost for each unit used. VAT is added to the whole bill.
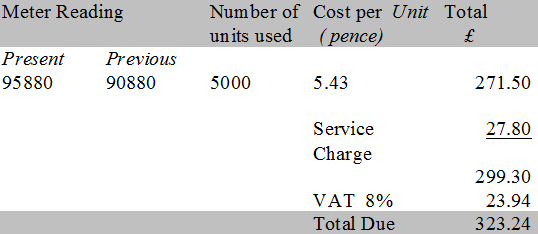
VAT is payable on the whole bill.
Loans
Secured Loans – Your house is at risk if you default.
Unsecured Loans – Goods are yours; house is safe.
Hire Purchase – Goods become yours after final payment.
Mortgages – Secured loans for houses, ships, etc.
Joe Bloggs wishes to borrow £10,000. Which option is cheapest?
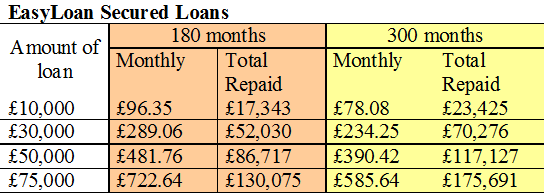
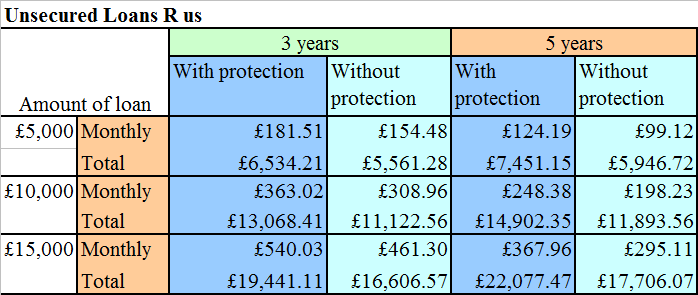

EasyLoan costs £17,343 over 15 years.
Loans R Us costs £11,122.56 over 3 years (unprotected).
Fred’s Finance:

Cheapest: Loans R Us (3 years, unprotected).
Hire Purchase (HP)
HP requires a deposit followed by fixed monthly payments. Goods become yours only after the final payment.
A TV costs £600 cash.
HP: 10% deposit + 36 × £15.75.
How much cheaper is cash?
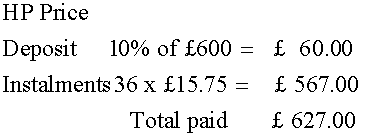
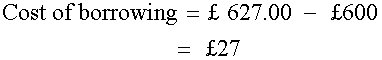
Cash is £27 cheaper.
Car Finance

Options when buying a car:
- Cash: Buy outright.
- Car Loan: Spread cost over time.
- HP: Own after final payment.
- PCP: Pay for depreciation; optional final payment.
- PCH / Leasing: Long‑term rental; never own.
Hire Purchase (HP)
Key Features
- Contracts up to 5 years.
- Flexible deposit.
- You own the car at the end.
- No mileage limits.
Risks
- You do not own the car until the final payment.
- Missed payments may lead to repossession.
Personal Contract Purchase (PCP)
Key Features
- Lower monthly payments.
- Options at end: return, upgrade, or buy.
Risks
- Mileage limits apply.
- Excess wear charges possible.
- You only own the car if you pay the final amount.
Leasing / PCH
Key Features
- 24–48 month contracts.
- Flexible initial rental.
Risks
- You never own the car.
- Charges for excess mileage or damage.
Insurance
Insurance premiums depend on the probability of an event happening. Higher risk → higher premium.
Bodgit Insurance charges £3.50 per £1000 of house value.
Cost to insure a £189,000 house?
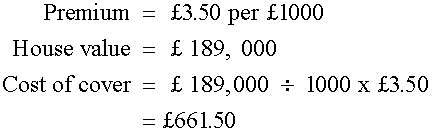
Bank Interest
Interest is a percentage of capital charged on loans or paid on savings.
Simple Interest
Simple interest is calculated only on the original capital.
Calculate simple interest on £500 for 3 years at 6%.
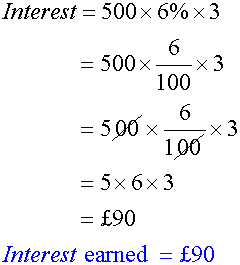
Compound Interest
Compound interest uses interest earned to increase capital.
Calculate compound interest on £500 for 3 years at 6%.
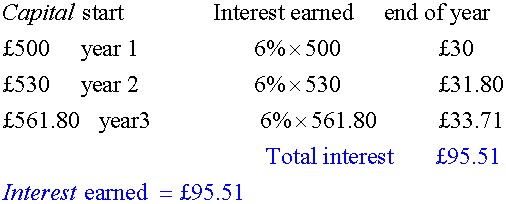
Using the CRy mnemonic:

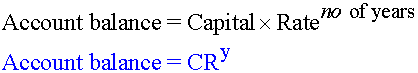

For monthly rates, convert years → months.

More than one interest period
CRy can be chained:
Capital × rate₁term₁ × rate₂term₂ × …
£5,000 placed in savings on 1 April 2022.
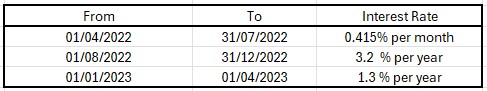
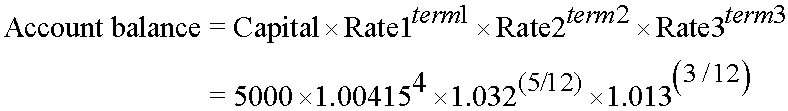
Balance = £5167.33
Effective Interest
Effective interest accounts for compounding.
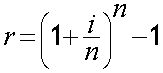
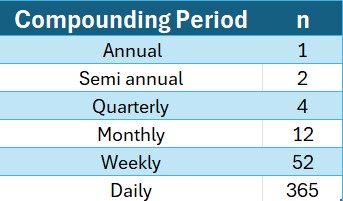
EAR (Effective Annual Rate) is used for loans.
AER (Annual Equivalent Rate) is used for savings.
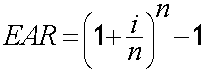
A loan has a nominal rate of 5%. Find EAR if compounded:
- Semi‑annually
- Monthly
- Daily
Changing between interest periods
Source: LibreTexts Mathematics
To convert annual effective → monthly effective:
Do NOT divide by 12!
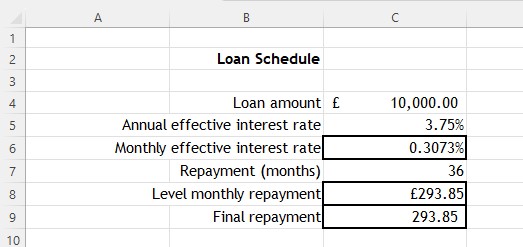
The monthly effective interest rate is 0.31% (1 d.p.).
Use in Loan Schedules
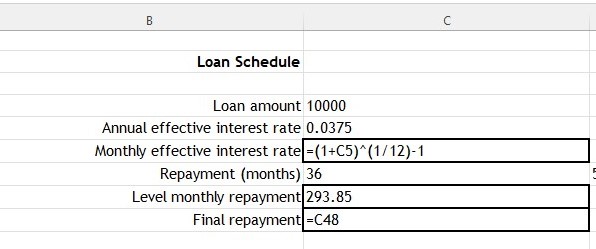
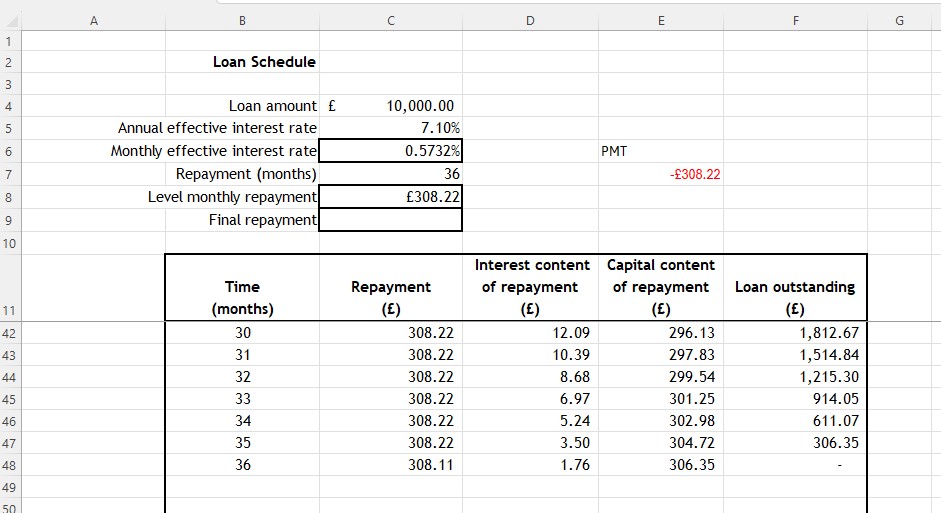
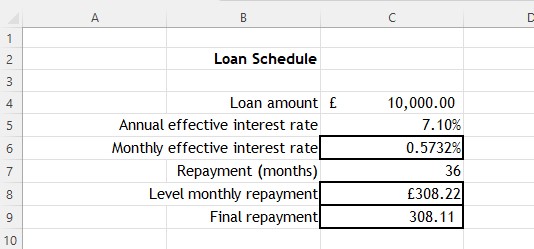
A loan of £10,000 is borrowed over 3 years. The annual effective interest rate is 7.1%.
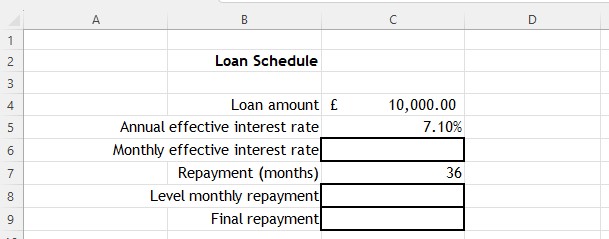
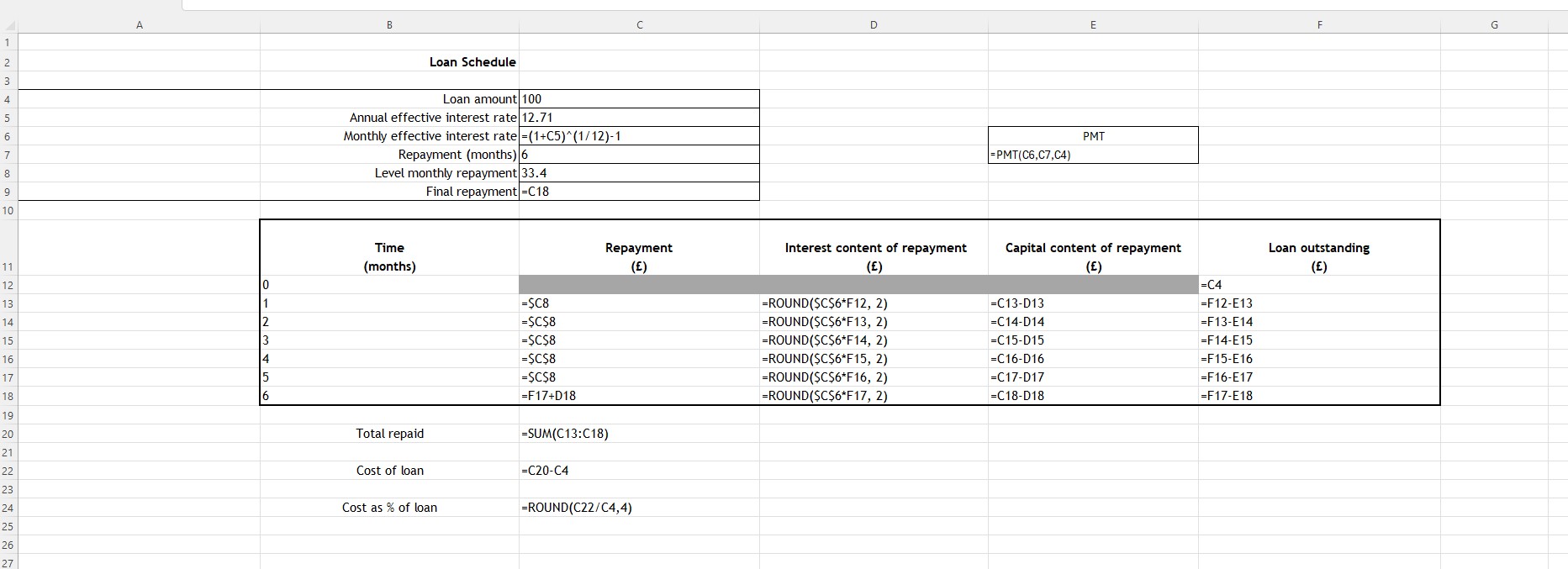
Enter the formula =(1+C5)^(1/12)-1 into cell C6 to calculate the monthly effective interest rate.
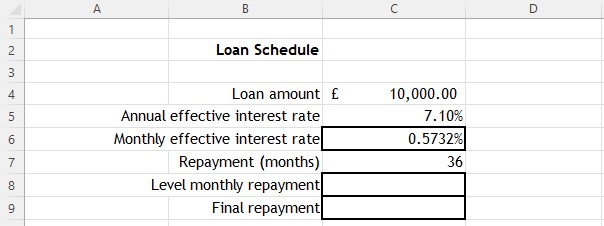
The Excel function PMT calculates payments based on a constant interest rate and number of periods.
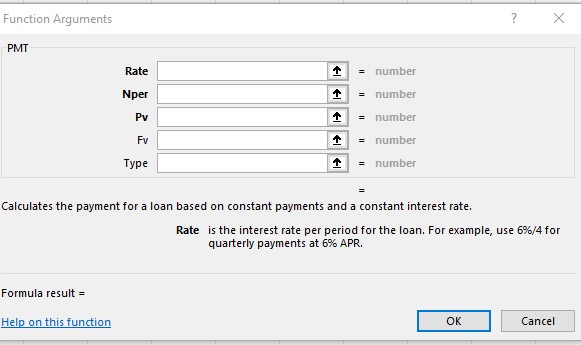
Here:
- Rate = effective monthly rate (C6)
- NPER = number of payments (C7)
- PV = loan value (C4)
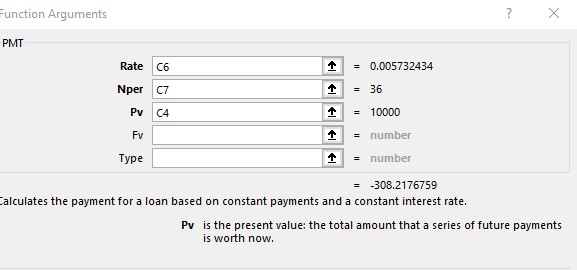
This gives a fixed monthly payment of £308.22.
Set up a loan schedule with these headings:

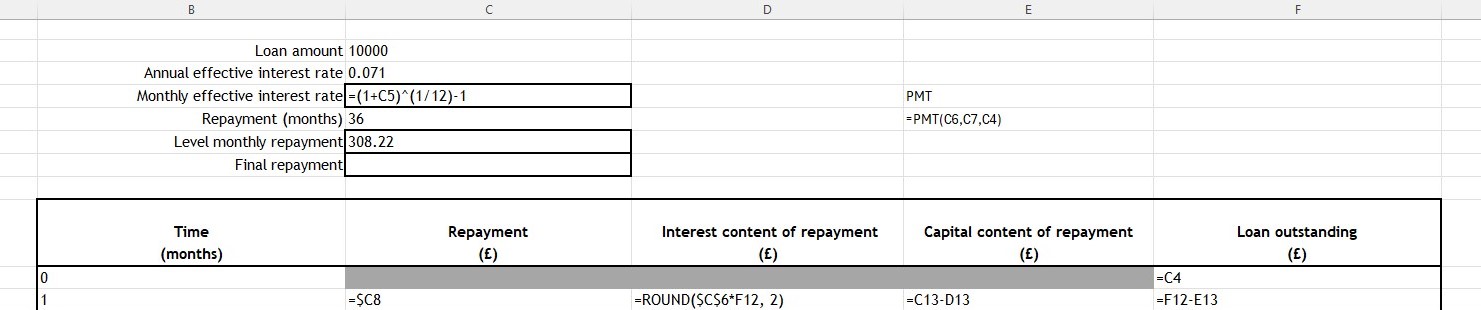
Enter =$C$4 into F12
(type =C4 then press F4).
Extend the table down to 36 months.
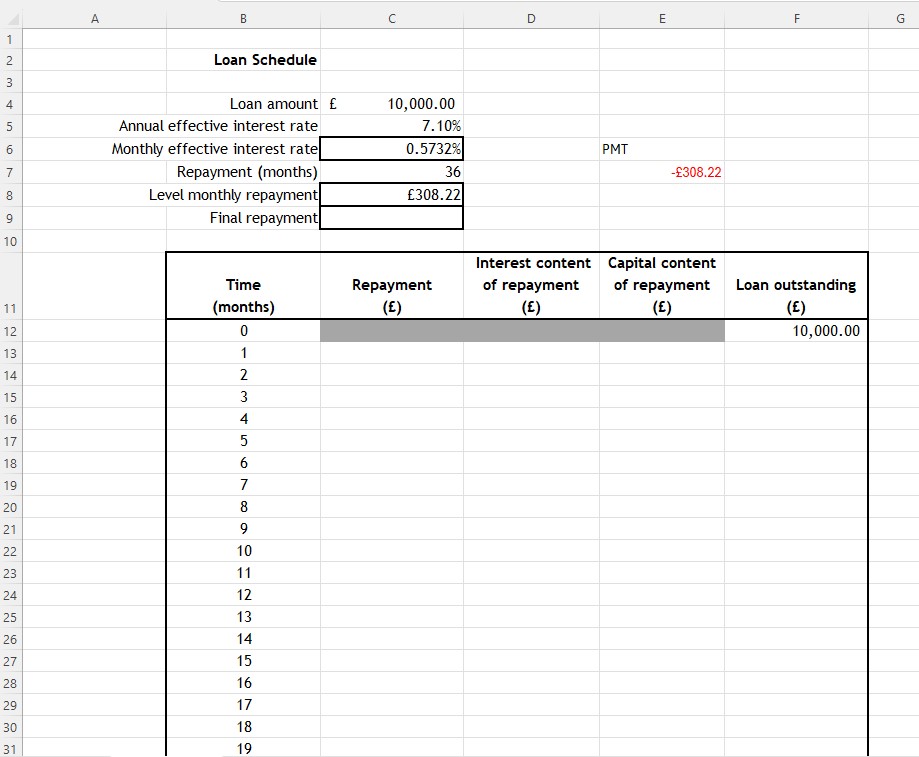
Repayment is C8, so enter =$C$8 in C13.
Interest content: =ROUND($C$6*F12,2)
Capital repaid: =C13-D13
New balance: =F12-E13
Copy down to the final row.
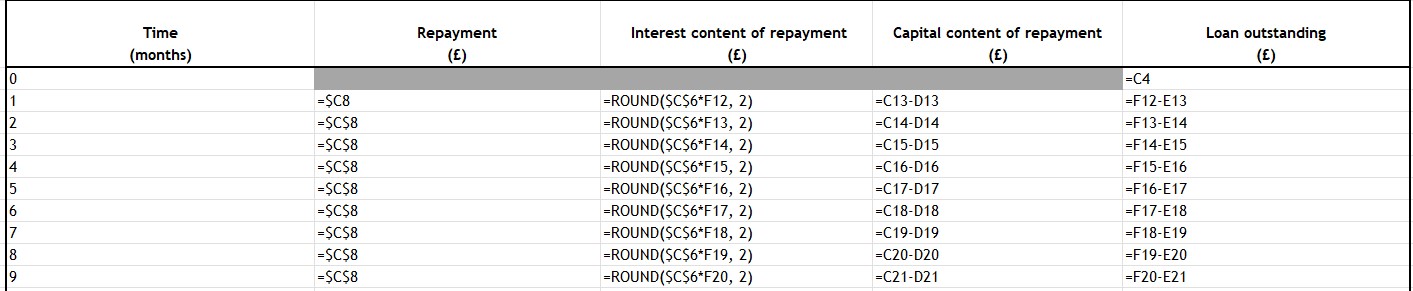
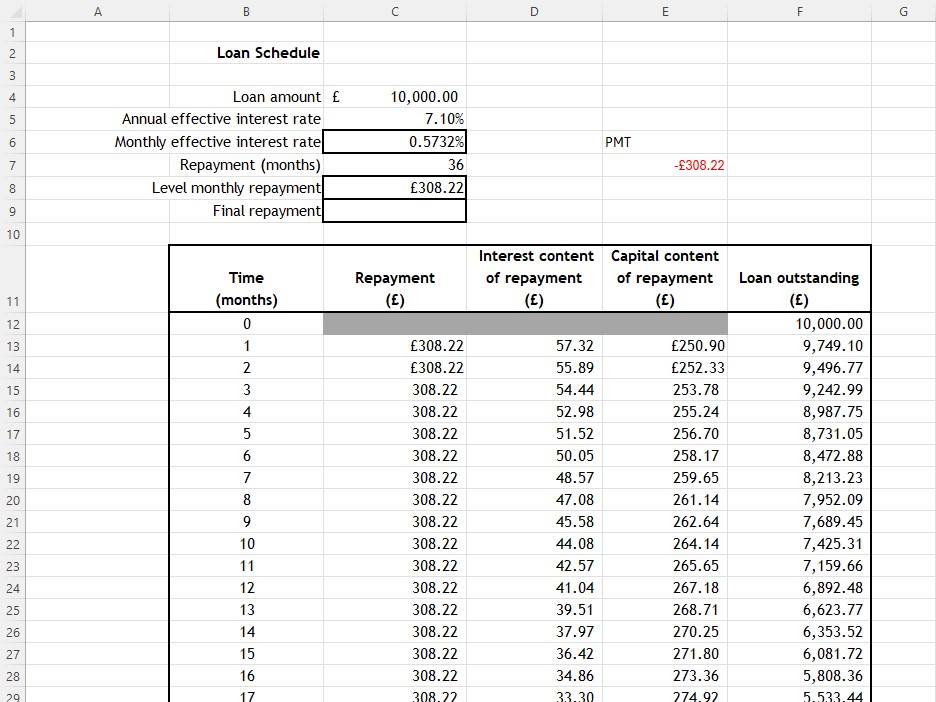
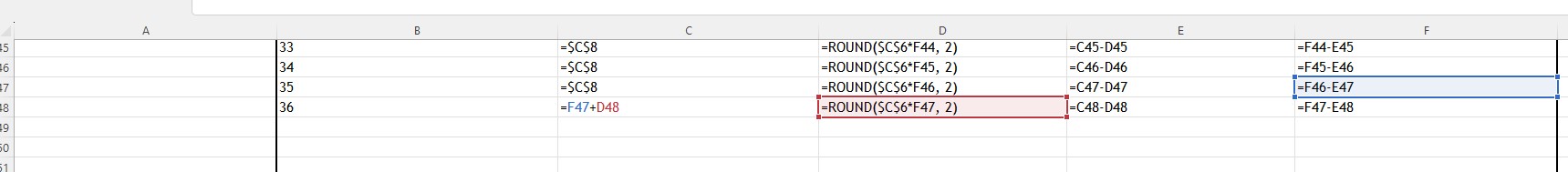
The final payment differs. Enter =F47 + D48 into C48.
Summary:
This can be represented by the recurrence relation:
\[
U_{n+1} = 1.0057U_n - 308.22
\]
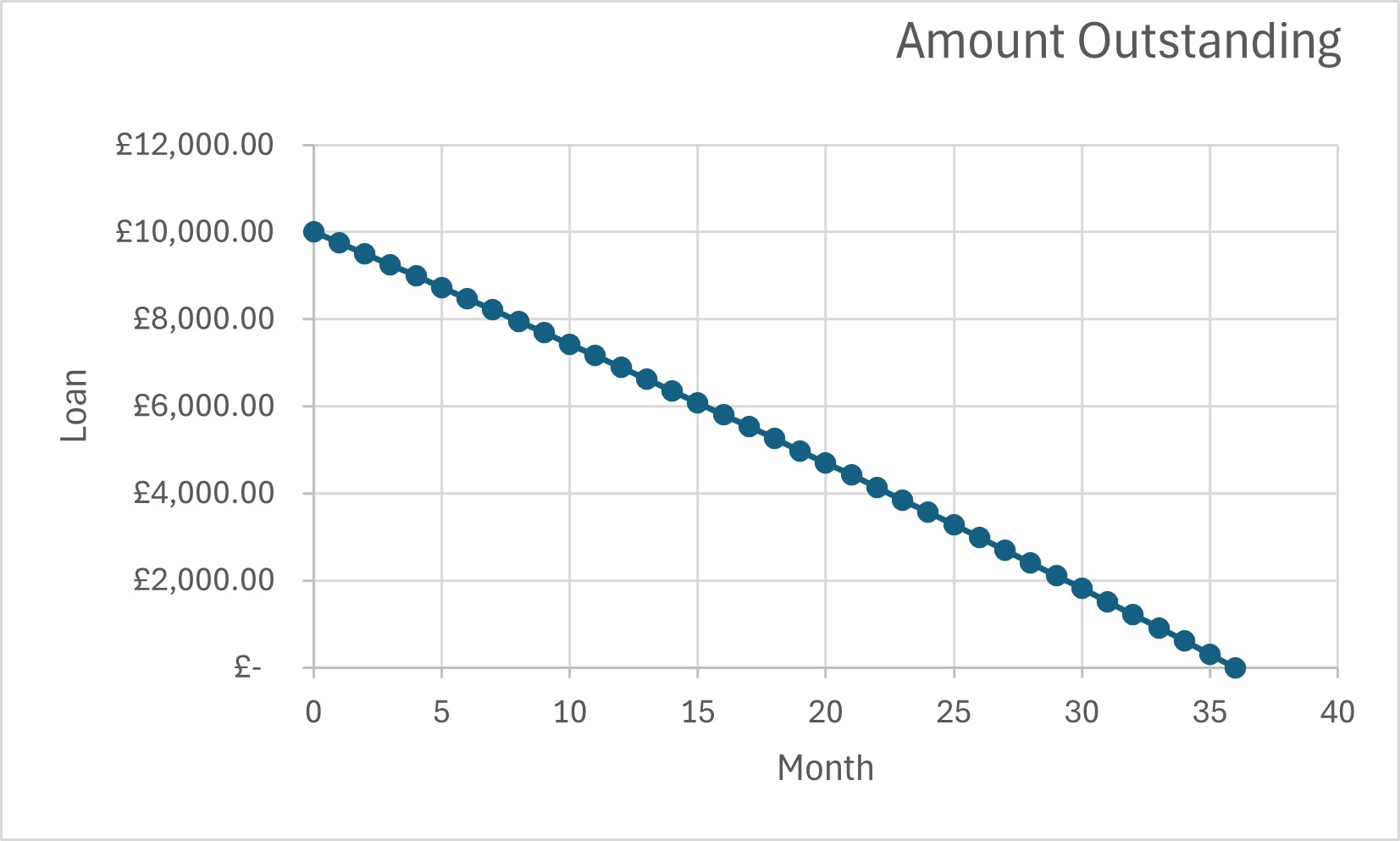
From the graph, after 15 months the outstanding loan is approximately £6,000.
Comparing Loans
The effective monthly rate can be used to compare loan offers quickly.
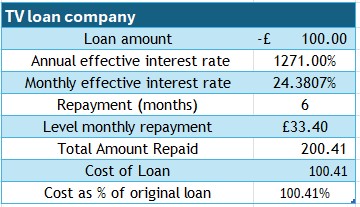
A TV advert offers short‑term loans with a typical annual interest rate of 1271%.
- Create a loan schedule for £100 over 6 months.
- Calculate the cost of the loan.
- Express the cost as a percentage of the original loan.
- Comment on your findings.
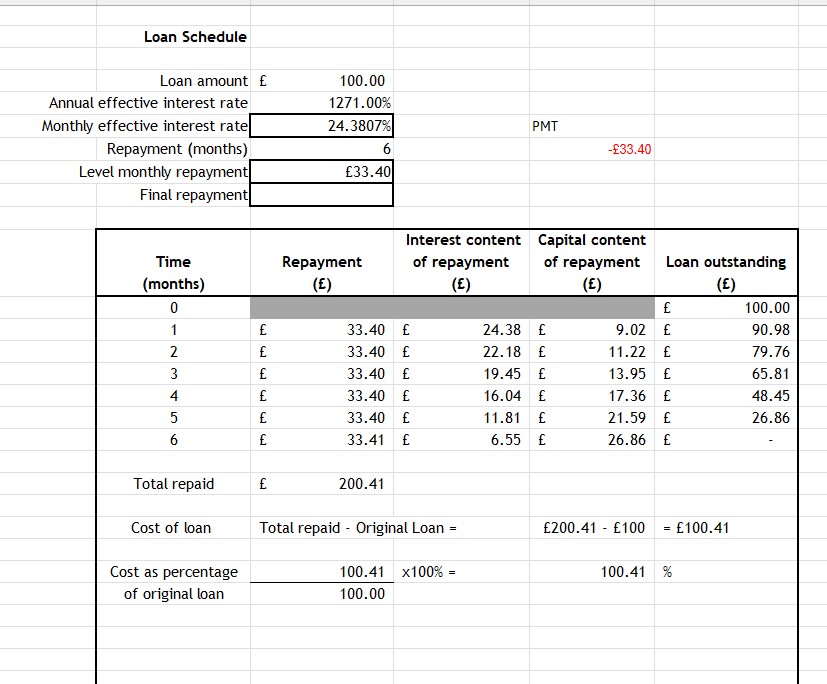
1. Total repaid = £200.41
2. Cost = £200.41 − £100 = £100.41
3. Percentage = (£100.41 ÷ £100) × 100% = 100.41%
4. The cost of borrowing exceeds the original loan!
Excel formula view:
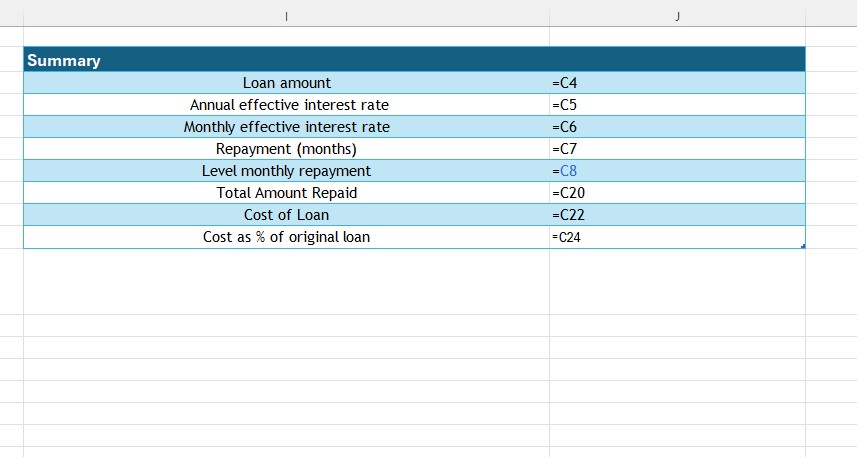
£10,000 loan over 3 years. Compare providers:
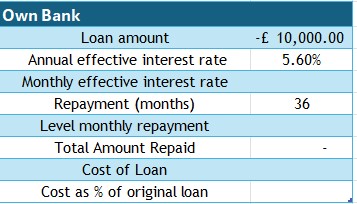
- Own Bank: AER 5.6%
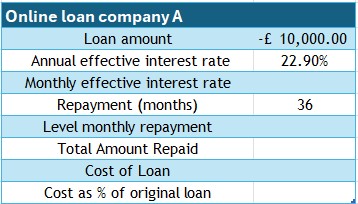
- Internet Bank A: AER 22.9%
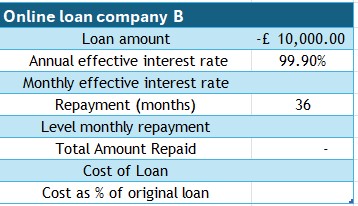
- Internet Bank B: AER 99.9%
Loan information boxes:
Comment on findings:
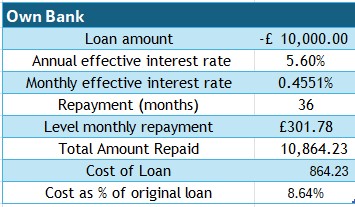
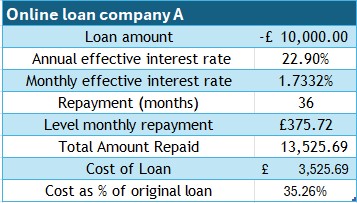
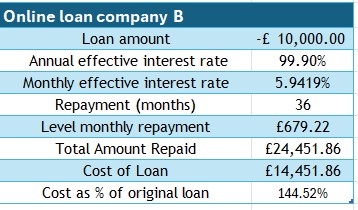
Clearly, the loan from Own Bank is cheapest.
Internet Bank B’s monthly effective rate is higher than Own Bank’s
annual rate!
Nominal interest rate from effective rate
If given EAR/AER, the nominal rate can be found by changing the subject of the formula .
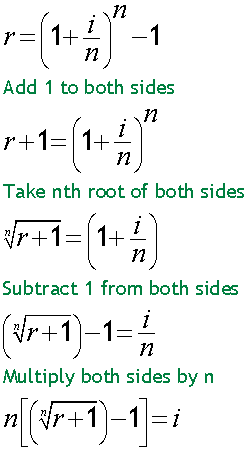
So:
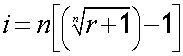
where i = nominal rate, r = effective annual rate, n = compounding periods.
EAR = 9%, compounded monthly. Find nominal rate.
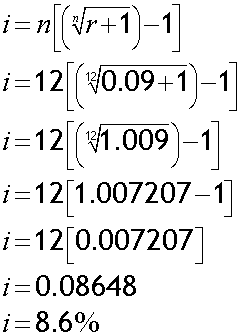
Alternatively:
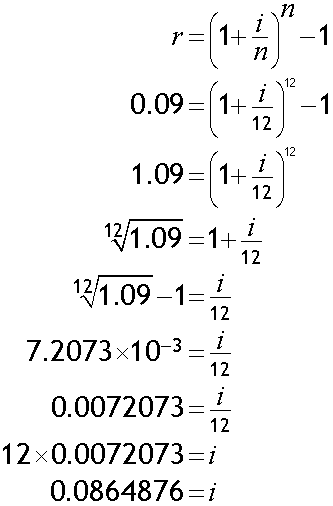
Nominal rate = 8.6% (1 d.p.)
Annual rate = 61.94%. Find effective monthly rate.
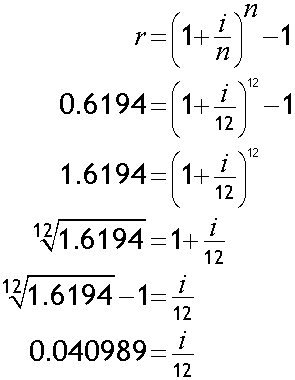
Effective monthly rate = 4.1% (1 d.p.)
Alternatively:
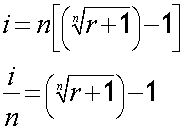
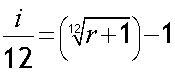
Substituting:
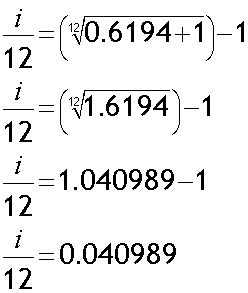
APR (Annual Percentage Rate)
APR is the interest rate paid each year on a loan. It includes fees and charges but does not include compounding.
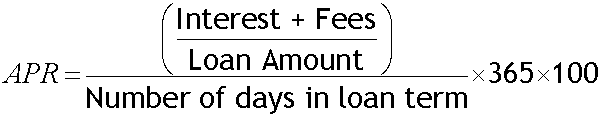
Foreign Exchange
Converting currency is an application of ratio .
Converting into another currency
Example
Fred converts £150 into US dollars.
Rate: £1 = $1.67.
How many dollars does he get?
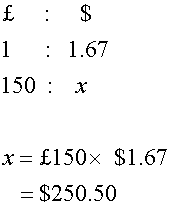
£150 × 1.67 = $250.50
Using the rule of 3:
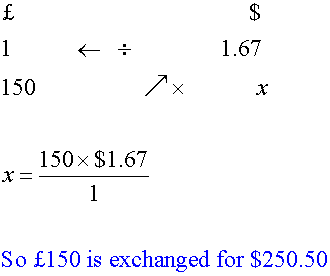
Converting back
Fred converts $75 back into pounds.
Rate: £1 = $1.67.
How many pounds?
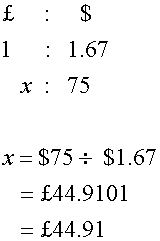
$75 ÷ 1.67 = £44.91
Using rule of 3:
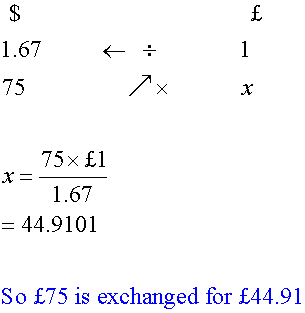
Joe converts $150 into Euros and receives €108.09.
No commission. What was the exchange rate?
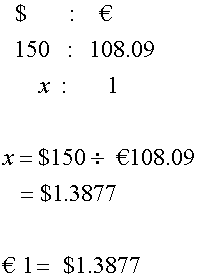
or