Newton’s equations of Motion:-
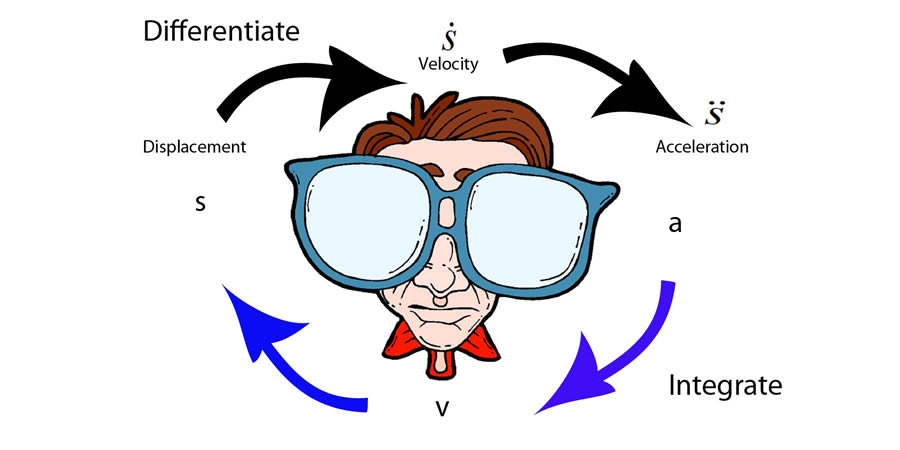
Deriving the equations of motion
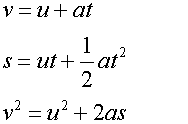
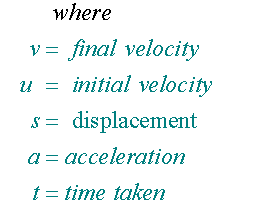
Re-arranged
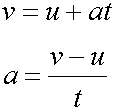
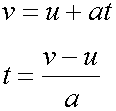
When starting from rest u = 0
giving
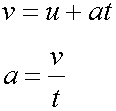
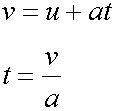
Rearranging the second formula:
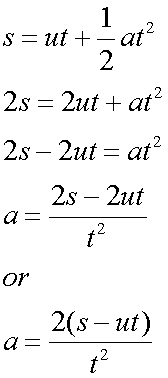
When u = 0,
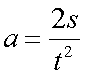
Rearranging the second formula for time :
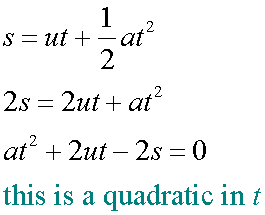
When u = 0 ,
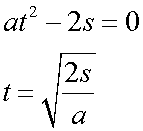
Otherwise
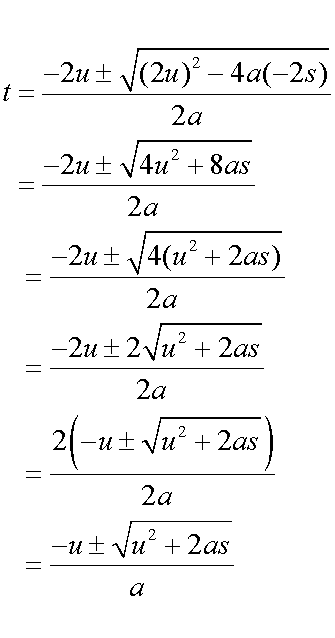
Rearranging the third formula:
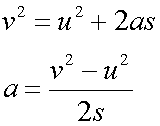
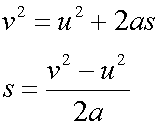
When u = 0 ,
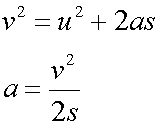
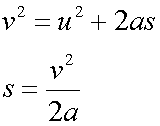
Notice that
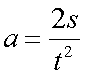
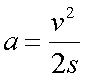
so when u = 0
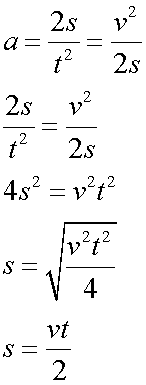
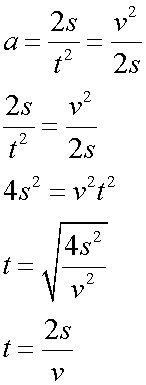
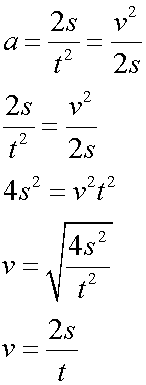
Integrating methods
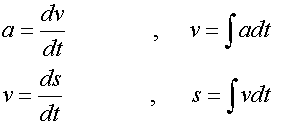
Displacement , s, is the vector quantity of the distance travelled from a fixed point.
After time ,t, the displacement from the origin
can be written as the function s(t).
A particle in motion on a plane at position (x(t),y(t)) at time t
can be represented by the position vector
![]()
where i and j are unit vectors in the x and y directions.
The distance from the origin is the magnitude
of the displacement
![]()
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time .
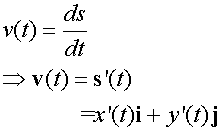
This is often shortened to
![]()
![]()
The speed of the particle at time t is found using the equation
![]()
The direction of motion at time t is
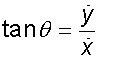
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time .
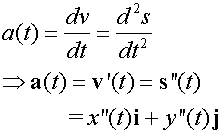
This is often shortened to
![]()
![]()
The magnitude of acceleration at time t
is found using the equation
![]()
The direction of acceleration at time t is
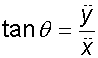
Example
A particle moving in a plane such that its displacement
is given by the equations
x = 3t3 + 2t2 and y = 4t2 + 5t
(x and y are measured in metres , time is in seconds)
Find, when t = 2,
- the position of the particle.
- the magnitude and direction of its velocity
- the magnitude and direction of its acceleration
Solution
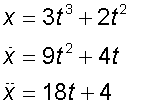
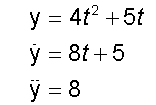
1. when t = 2,
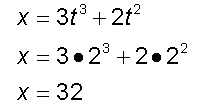
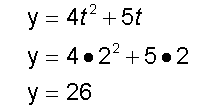
The particle is at (32,26)
2. when t = 2,
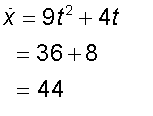
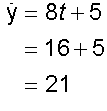
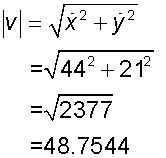
The speed is 48.8m/s
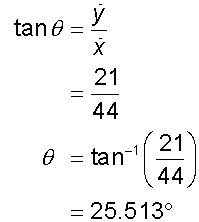
The velocity is 48.8 m/s at a direction
of 25.5° from the horizontal.
3.
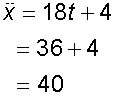 and
and ![]()
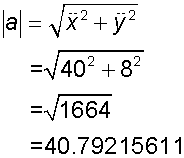
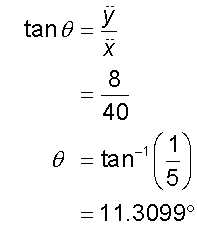
The acceleration is 40.8 m/s2
at a direction of 11.3° from the horizontal.