Time Dependent Graphs
Example
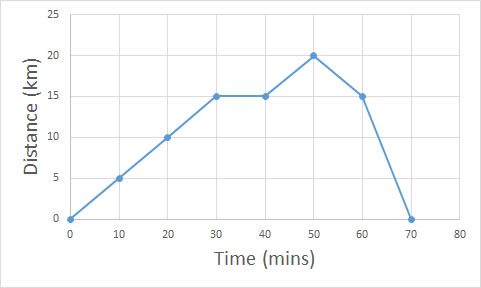
What is the average speed and average velocity for this trip ?
The trip covers a total of 40 km in 70 minutes.

Overall, the average speed for the trip is 34.3 km/h (1dp)
Average velocity is the rate of change of displacement with time.
Velocity is the gradient of a displacement-time graph.
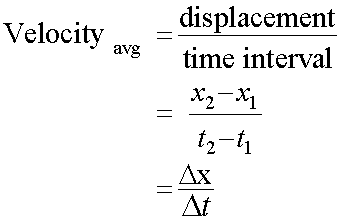
The total displacement is zero km, so the average velocity is zero km/h.
Does the average speed reflect the activity that took place ?
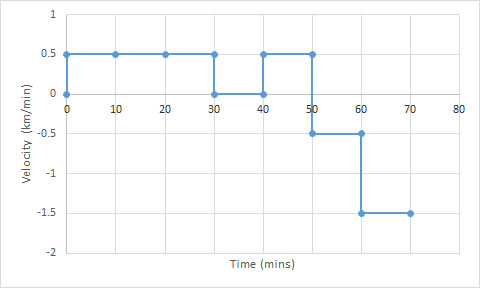
Looking at the graph, it can be seen that 15km was covered in the first 30 minutes.

A 10 minute rest took place.
.The furthest point was reached after a further 10 minutes, then the resting point was revisited.

Finally, a quick return was made with 15km being covered in 10 minutes.

What about the instantaneous speed and instantaneous velocity ?
The instantaneous velocity is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time.
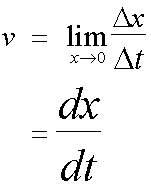
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of velocity.
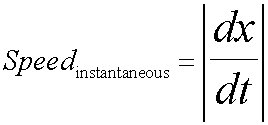
For the journey,
Firstly
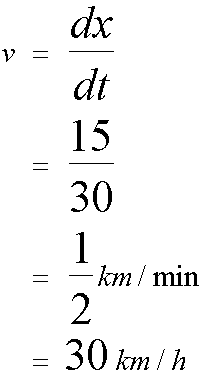
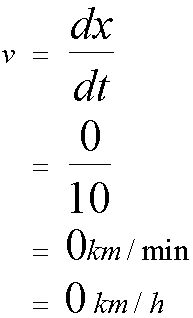
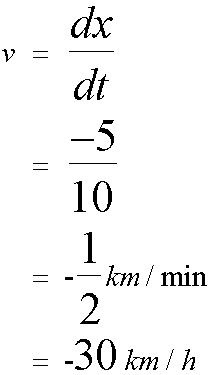
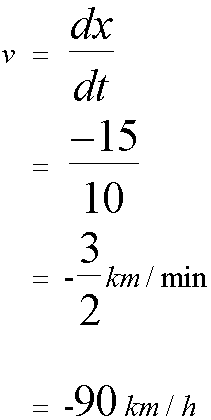
Graph of velocity against time
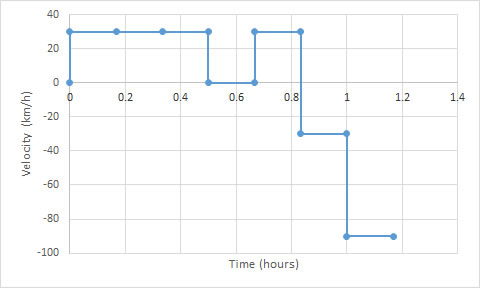
Notice how the area under the graph gives the displacement:
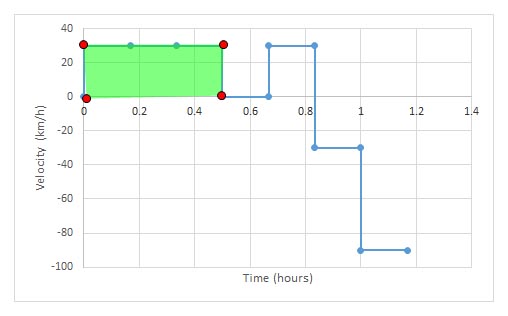
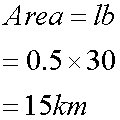
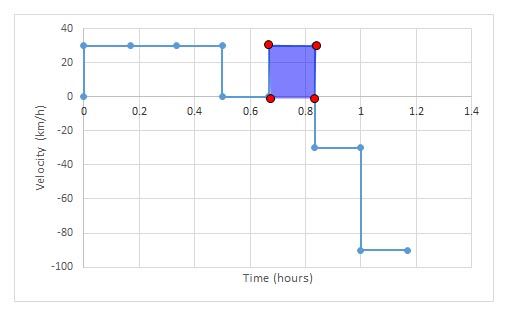
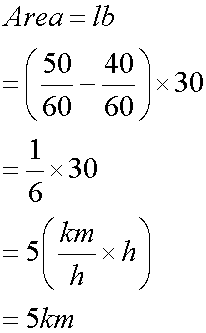
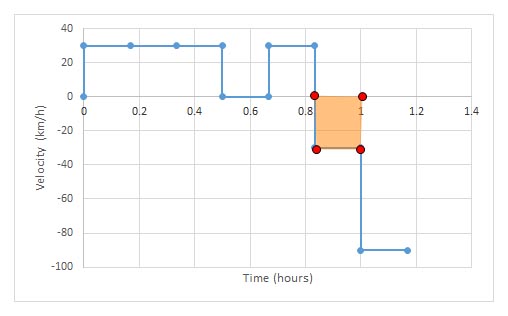
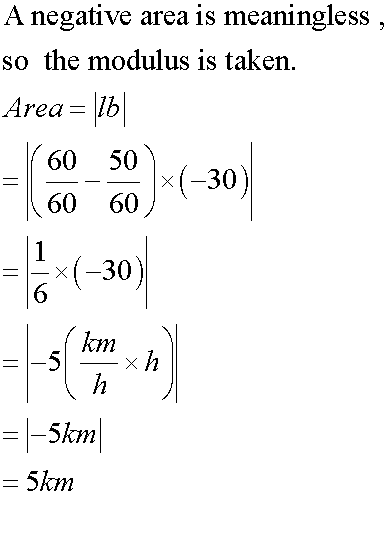
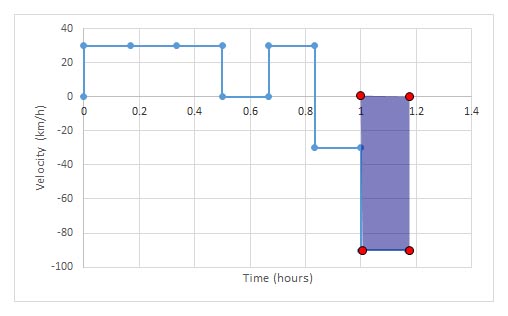
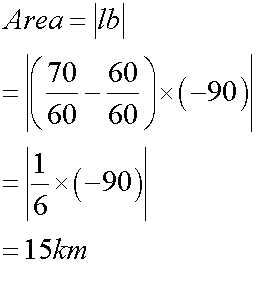
the area under a velocity- time graph is displacement:
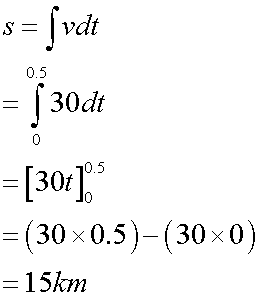
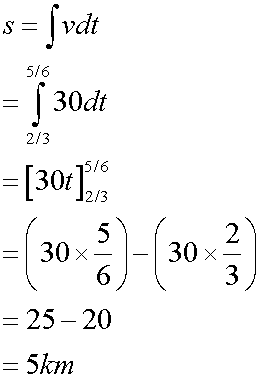
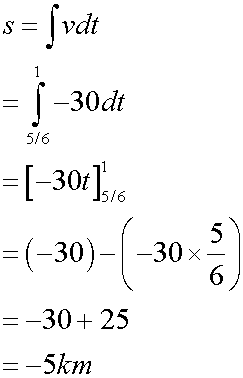
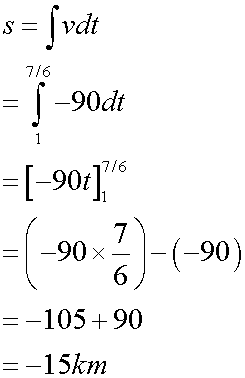
Average acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time.
Acceleration is the gradient of a velocity-time graph.
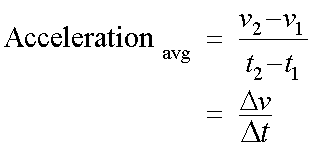
The instantaneous acceleration is the rate of change of velocity at that particular time.
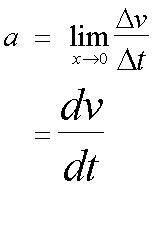
Example
The velocity-time graph of an item is plotted.
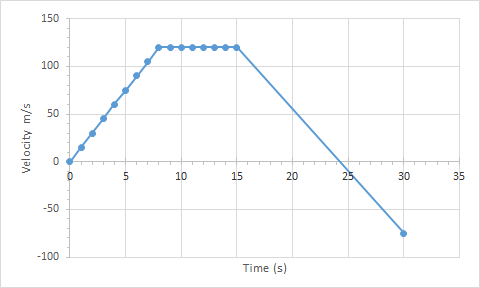
The item starts from rest.
After 8 seconds, the item is travelling at a velocity of 120m/s, which is maintained for a further 7 seconds.
After 30 seconds, the item is travelling at -75m/s.
Find the acceleration for each part of the journey.
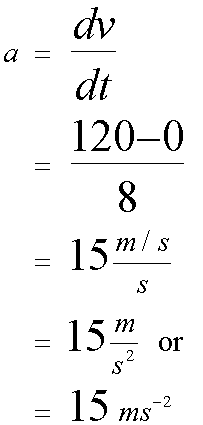
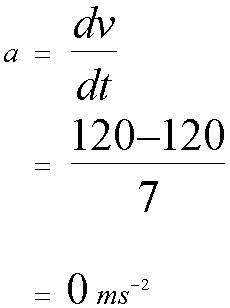
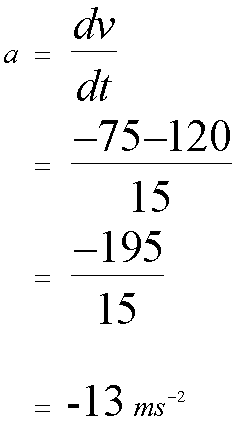
Deriving the Equations of Motion
Since acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time,
for UNIFORM ACCELERATION
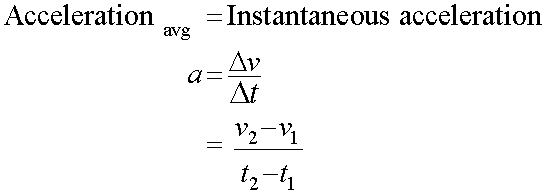
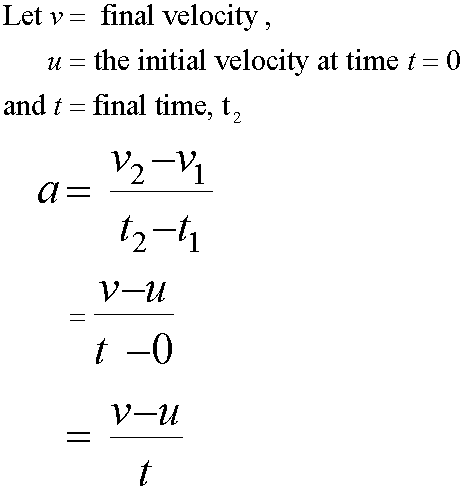
Where v = final velocity and u = initial velocity.
Re-arranging gives
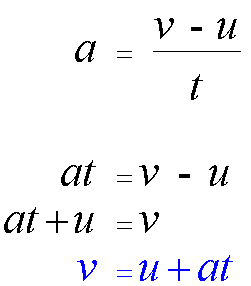
For uniform acceleration, the average velocity is the mean of the intitial and final velocity:
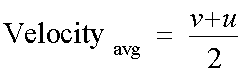
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement with time.
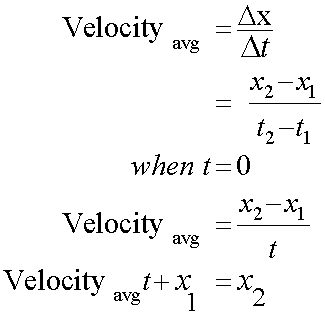
Taking atwo of the equations
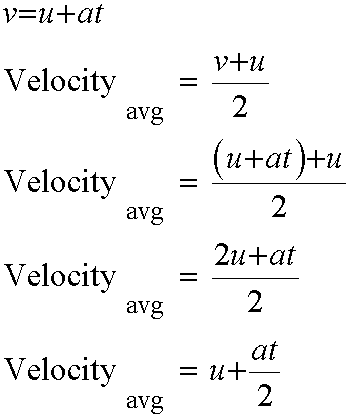
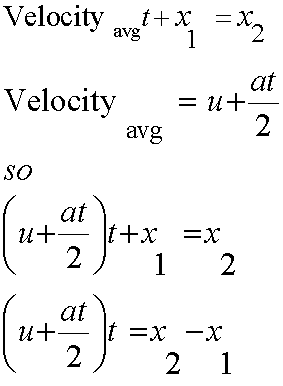
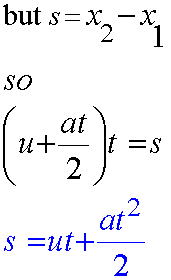
Finally,
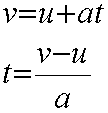
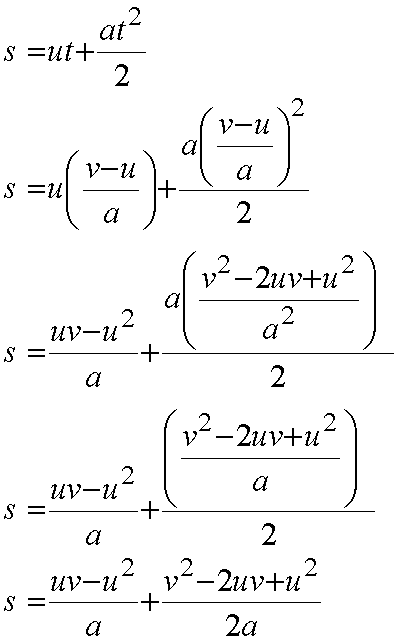
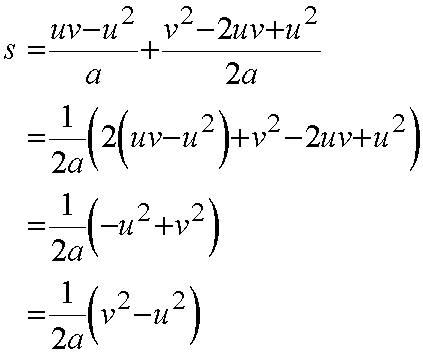
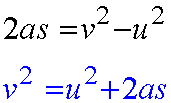
Free -Fall Acceleration
Direction is vertical, y direction, not horizontal x direction.
Positive direction is upwards.
The free-fall acceleration is negative, since it is towards the Earth's centre.
The free-fall acceleration near Earth's surface is
![]()
The magnitude of the acceleration is g = 9.8 m/s2
Do not substitute -9.8 m/s2 for g
