Areas on graphs
Example
In the following graph, a vehicle is travelling
at a constant speed of 4m/s for
a time duration of 5 seconds.
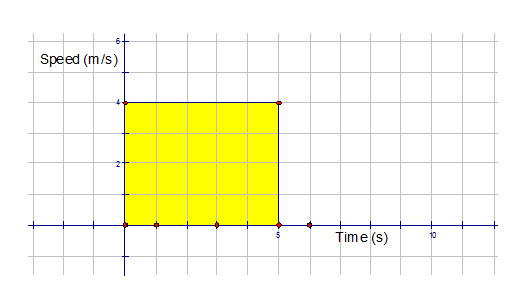
What distance is travelled by the vehicle ?
Distance = Speed x Time
so D = 4 m/s x 5 s
= 20 m
If we calculate the area of the graph,
then A = LB
A =5 x 4
A = 20 units2
Example
In the following graph, a vehicle starts at rest,
accelerates to a speed of 4m/s after 3 seconds,
maintains this speed for 3 seconds then decelerates
to a standstill over a time duration of 45 seconds.
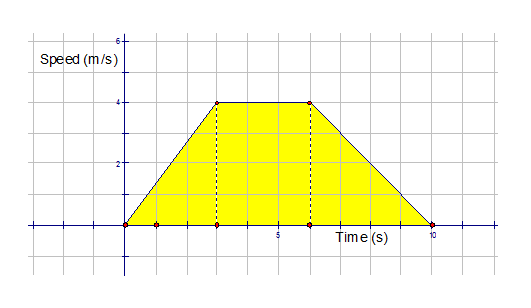
What distance is travelled by the vehicle ?
This time, there are 3 distinct areas to consider:-
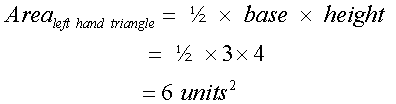
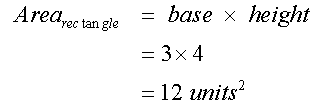
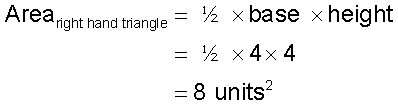
Total area = 26 units2
The vehicle travels 26 m.
How can this be checked ?
Newton’s equations of Motion:-
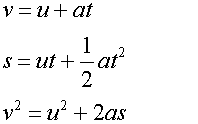
where
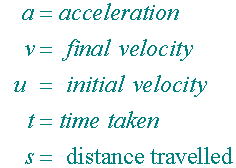
For the left hand triangle
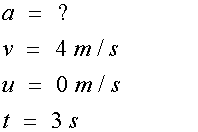
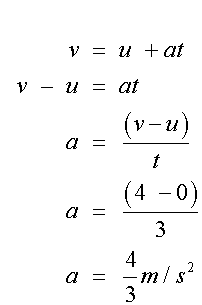
so
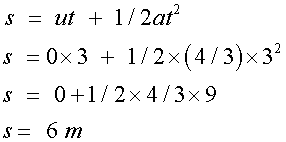
For the rectangle
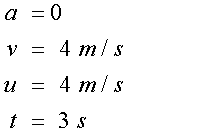
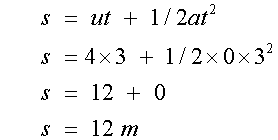
For the right hand triangle
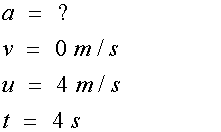
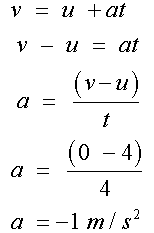
so
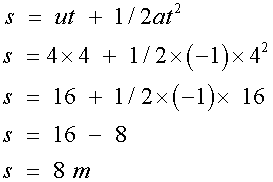
The vehicle does indeed travel 26 m.
Areas under curves
Example
In the following graph, a vehicle starts at rest
and accelerates :
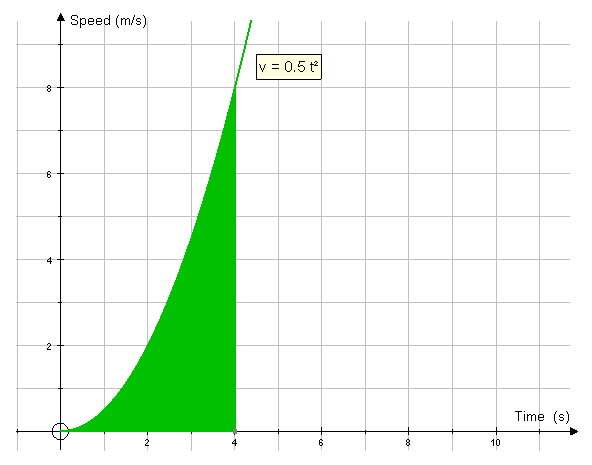
What distance is travelled by the vehicle during the first 4 seconds ?
This is more of a challenge.
Split the curve into intervals of ½ seconds and draw
rectangles to find upper and lower bounds of the area.
v = 0.5t2
Time (s) |
t |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
3 |
3.5 |
4 |
Speed (m/s) |
v |
0.125 |
0.5 |
1.125 |
2 |
3.125 |
4.5 |
6.125 |
8 |
The lower bound of the area under the curve
is the sum of the areas of the rectangles drawn to
the right of the curve.
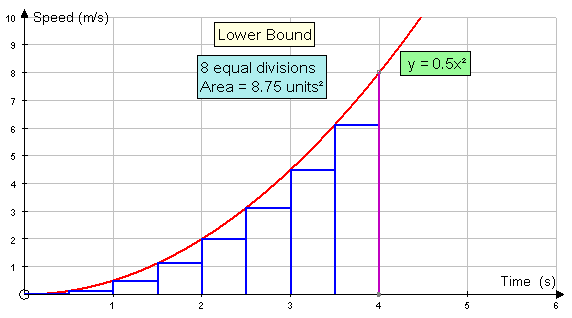
Area = 0.5(0+0.125+0.5+1.125+2+3.125+4.5+6.125)
Area = 0.5 x 17.5 = 8.75 units2
The upper bound of the area under the curve
is the sum of the areas of the rectangles drawn to
the left of the curve.
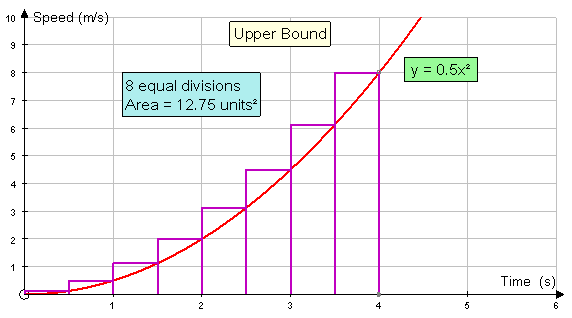
Area = 0.5(0.125+0.5+1.125+2+3.125+4.5+6.125+8)
Area = 0.5 x 25.5 = 12.75 units2
The true area under the graph lies somewhere
between these two values.
Increasing the number of rectangles helps:-
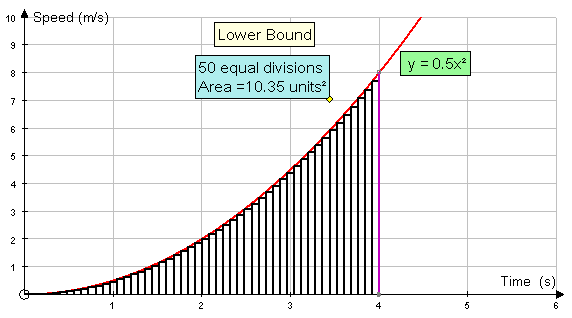
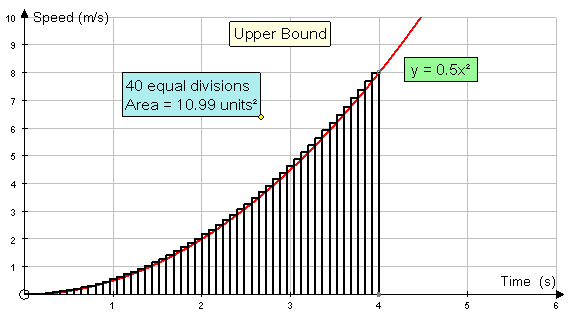
Eventually, both the upper and lower bounds converge to a limit.
This limit is the area under the graph.
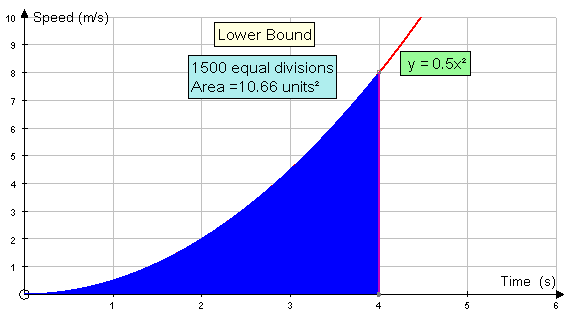
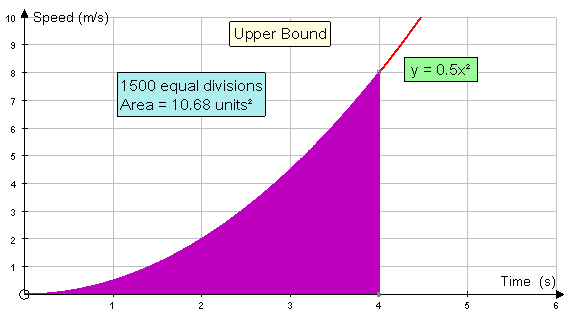
Here, the area is converging to 10.67 units2
The Area Function
The area between the graph of the function y = f(x)
and the x-axis, starting at x = 0 is called the area function A(x)
