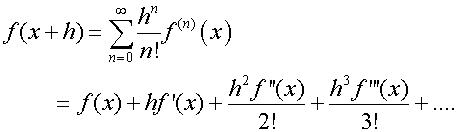Infinite Series
An infinite series has an infinite number of terms.
The sum of the first n terms, Sn , is called a partial sum.
If Sn tends to a limit as n tends to infinity, the limit is called the sum to infinity of the series.
Arithmetic series
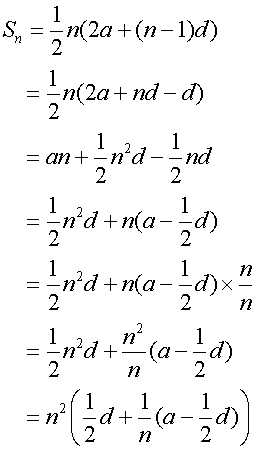
As n tends to infinity, Sn tends to ![]()
The sum to infinity for an arithmetic series is undefined.
Geometric series
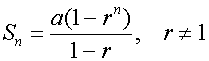
When r > 1, rn tends to infinity as n tends to infinity.
When r < 1, rn tends to zero as n tends to infinity.
The sum to infinity for a geometric series is undefined
when ![]()
The sum to infinity for a geometric series
when ![]()
is 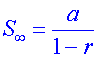
Example
Find the sum to infinity for the series
96 +48 +24…… if it exists.
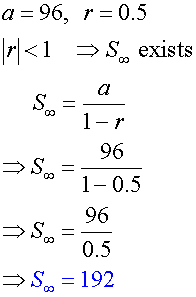
Example
Express the recurring decimal 0.242424…. as a vulgar fraction
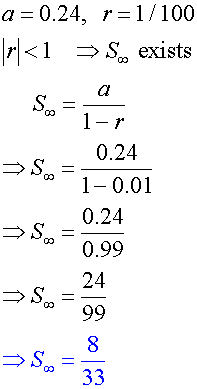
Example
Given that 12 and 6 are two adjacent terms of an infinite
geometric series with a sum to infinity of 192,
a) Find the first term.
b) Find the partial sum S6
Solution
a)
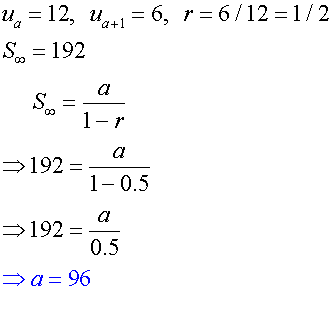
b)
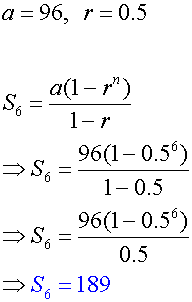
Sigma notation - Rules
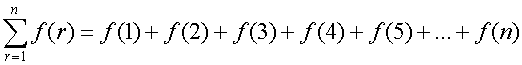
Constant multiplier
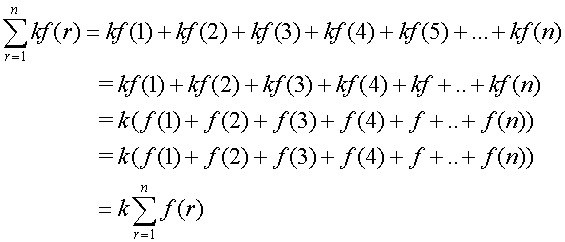
Adding series
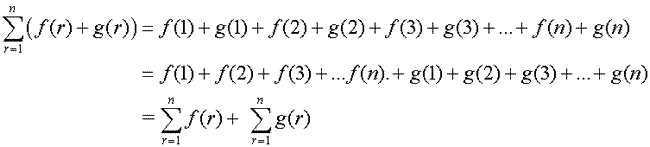
Binomial theorem refresher
Sum of first n natural numbers
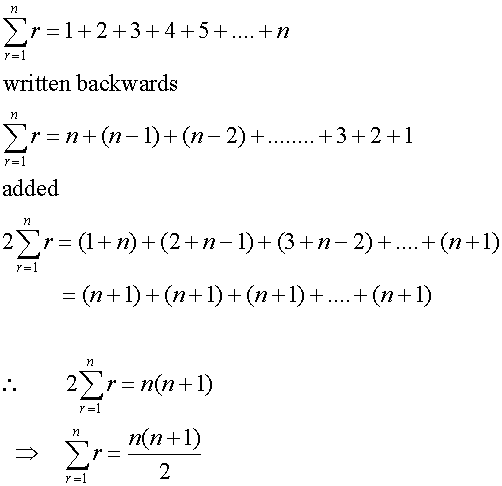
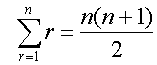
Useful result
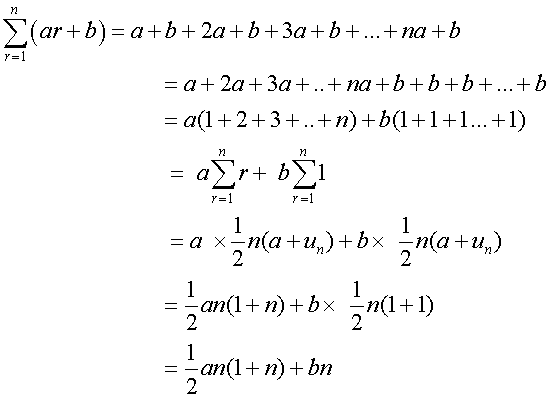
Example
Find the value of
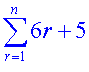
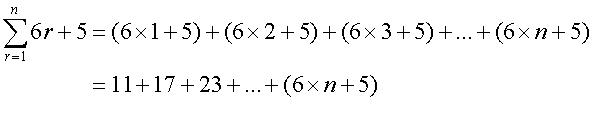
From the rules above,
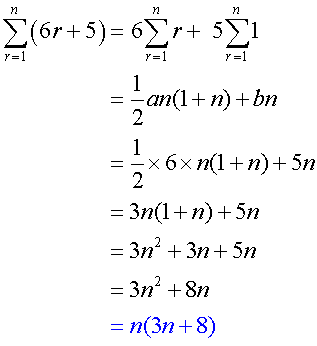
Common series - Sigma notation
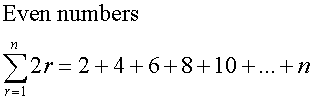
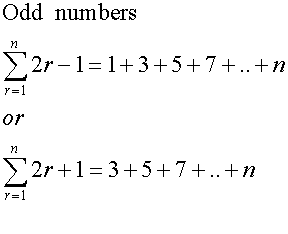
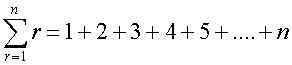
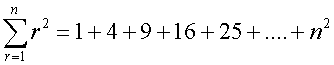
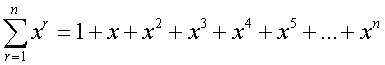
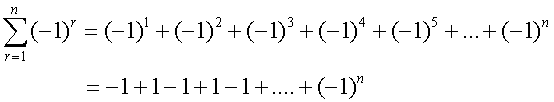
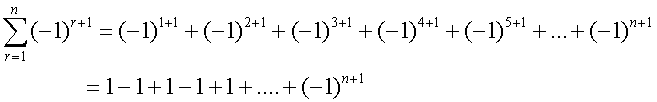
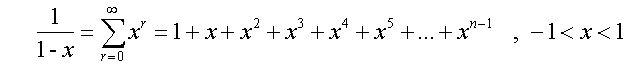
Power Series
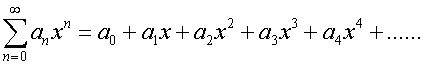
where a0,a1,a2…an are constants.
The series always converges when x = 0
It will possibly converge for other values of x.
A series cannot be convergent unless its terms
tend to zero
![]()
D’Alembert’s ratio test
For a series of positive terms
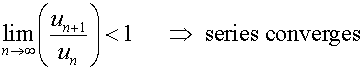
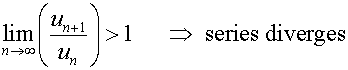
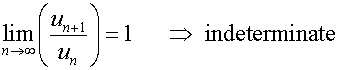
Example
Use d’Alembert’s ratio test to test for convergence
of the following series :-
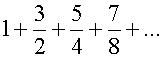
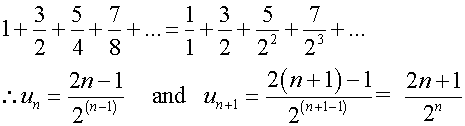
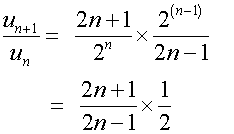
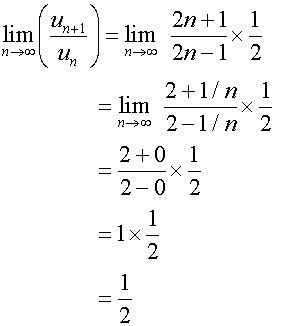

Absolute convergence
If
![]()
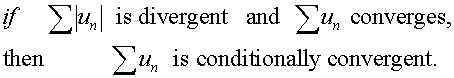

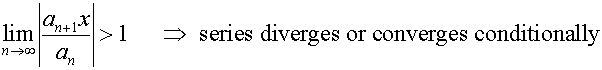
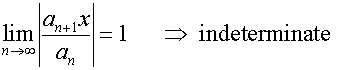
Example
Find the sum to infinity of the series
4 + 7x +10x2+13x3+…
and the region of valid values of x.
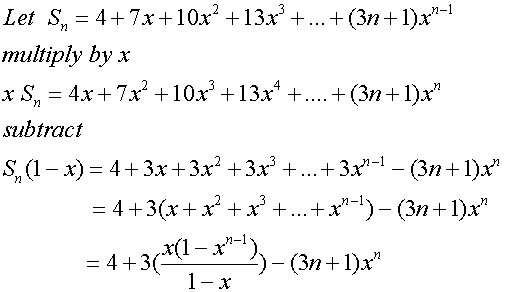
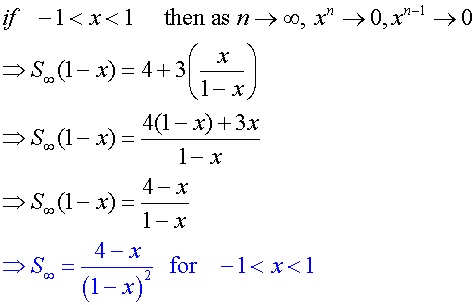
Fibonacci series
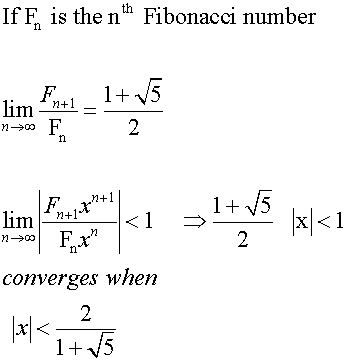
Centre of convergence
The power series can be written
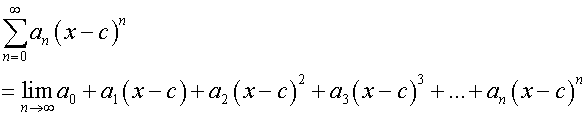
where c is the centre of convergence.
This is the middle of the interval of convergence,
the interval for which the limit exists.
The radius of convergence is called R.
If R = ∞ , the series converges for all x.
Otherwise,
the series converges for ![]()
and diverges for ![]()
![]()
To find a0, set x = c , since the remaining terms will
become zero.
differentiate
![]()
To find a1, evaluate f’(c)
go again
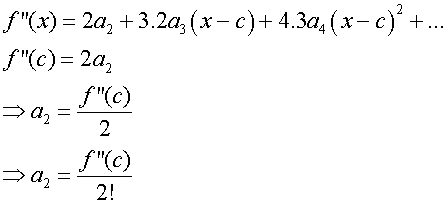
Continuing gives the following
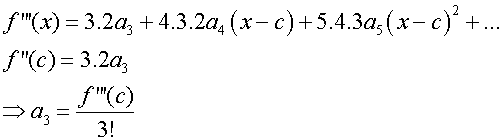
and
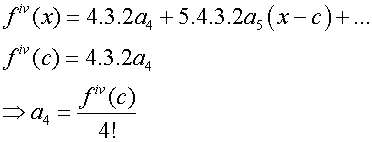
so that
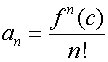
Substituting back into the original series
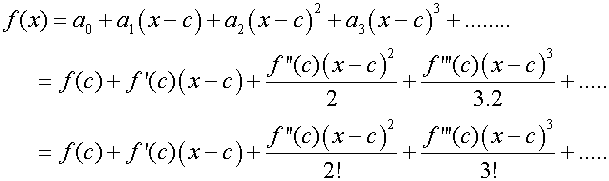
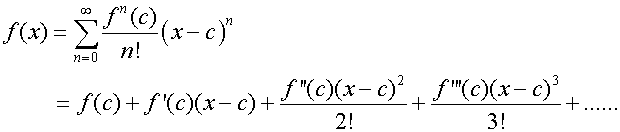
In the interval (-R+c,R+c)
Taylor’s series