Circles, Arcs and Sectors
The Circle
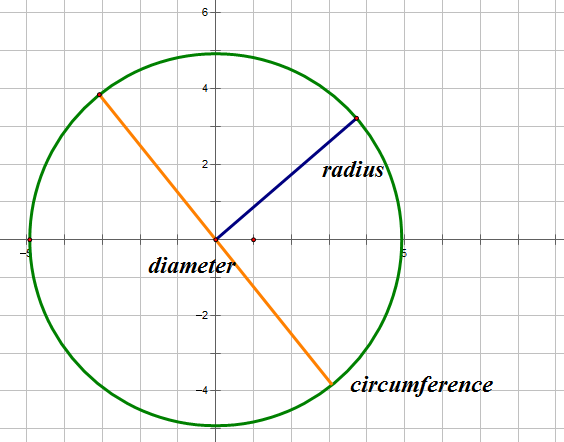
A circle has three main components:
- The circumference, which is the outside edge of the circle.
- The radius, which goes from any point on the circumference to the centre of the circle.
- The diameter, which joins the circumference through the centre of the circle.
Calculating the Circumference
A relationship exists between all circles: the circumference divided by the diameter is always the same.
This ratio is called pi, the 16th letter of the Greek alphabet. It is an irrational number and has the symbol $\pi$.
By definition:
$$ \frac{C}{d} = \pi $$
Re‑arranging gives the formula:
$$ C = \pi d $$
Very often, $\pi$ is taken to 2 decimal places and we use the value $3.14$.
Find the circumference of a circle which has a diameter of $4\text{ cm}$.
Use the $\pi$ button on your calculator and give your answer correct to two decimal places.
$$ C = \pi d = \pi \times 4 \approx 12.57\text{ cm} $$
Since the diameter of a circle is twice its radius, $d = 2r$.
Substituting into $C = \pi d$ gives:
$$ C = \pi (2r) = 2\pi r $$
Find the circumference of a circle which has a radius of $4\text{ cm}$.
Use the $\pi$ button on your calculator and give your answer correct to two decimal places.
$$ C = 2\pi r = 2\pi \times 4 \approx 25.13\text{ cm} $$
Area of a Circle
To find the area of a circle, you could attempt to count the number of squares inside it.
This would give an approximation of the area.
You could also cut the circle into segments and lay them out next to each other.
Here, the circle is cut into 8 equal parts.
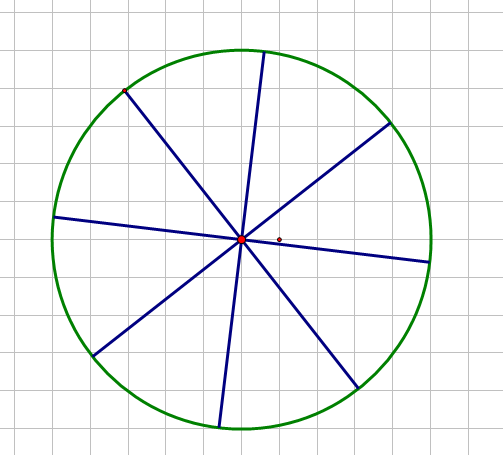

As the circle is cut into smaller and smaller parts, a rectangle is formed.
Using the equation $\text{Area} = \text{length} \times \text{breadth}$, we obtain:
$$ A = \pi r^2 $$
Find the area of a circle which has a radius of $4\text{ cm}$.
Use the $\pi$ button on your calculator and give your answer correct to two decimal places.
$$ A = \pi r^2 = \pi \times 4^2 = 16\pi \approx 50.27\text{ cm}^2 $$
Find the area of a circle which has a diameter of $4\text{ cm}$.
Use the $\pi$ button on your calculator and give your answer correct to two decimal places.
Since $d = 4\text{ cm}$, the radius is $r = 2\text{ cm}$.
$$ A = \pi r^2 = \pi \times 2^2 = 4\pi \approx 12.57\text{ cm}^2 $$
Interactive Circle Explorer
Use the slider to change the radius. The circle and calculations update instantly.
Radius:
Diameter:
Circumference:
Area:
Arcs and Sectors – Terminology
An arc is a part of a curve. It is a fraction of the circumference of the circle.
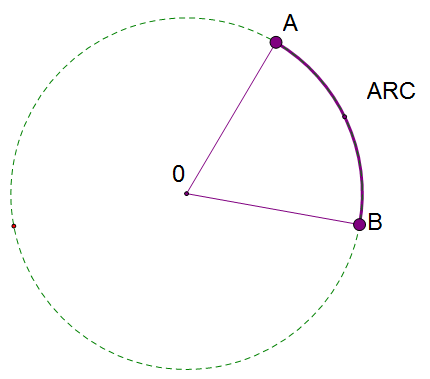
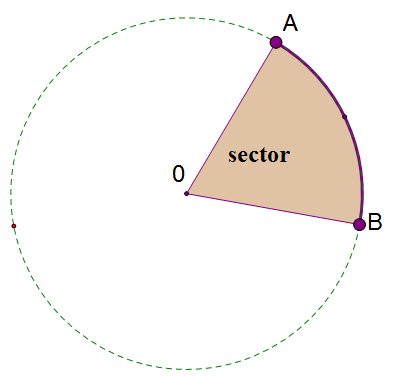
A sector is part of a circle enclosed between two radii.
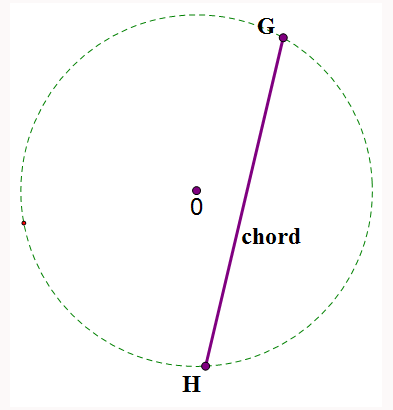
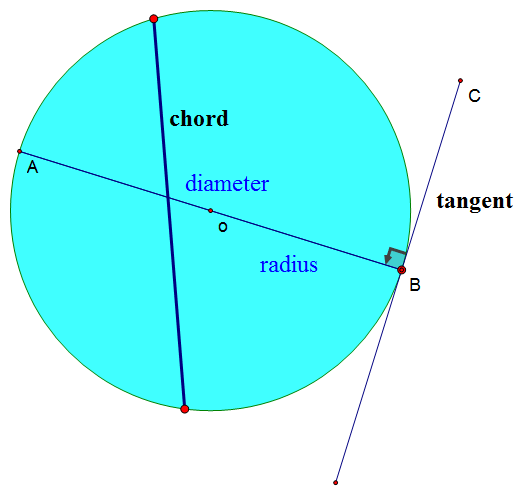
A chord is a line joining two points on a curve.
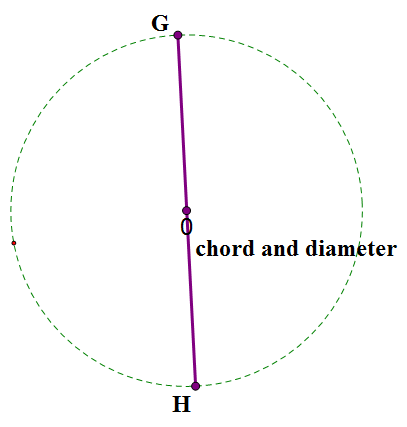
A chord can be a diameter.
Arcs and Sectors – Equations
If a sector has angle $\theta^\circ$ at the centre, then:
$$ \frac{\theta}{360} = \frac{\text{arc length}}{2\pi r} = \frac{\text{sector area}}{\pi r^2} $$
So:
$$ \text{Arc length} = \frac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r $$
$$ \text{Sector area} = \frac{\theta}{360} \times \pi r^2 $$
Arcs
What is the length of arc $AB$?
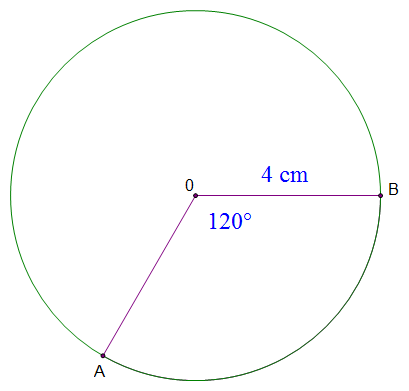
Use $\text{Arc length} = \dfrac{\theta}{360} \times 2\pi r$.
Length of arc AB.
Find the radius of the following circle:
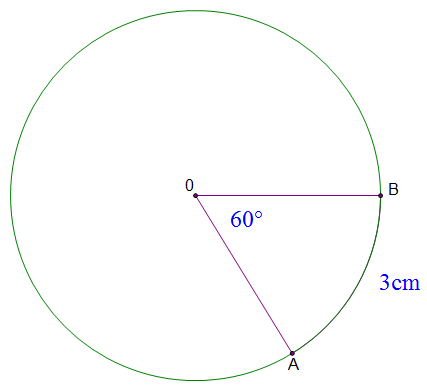
Finding the radius from arc length and angle.
Sectors
What is the area of sector $AOB$?
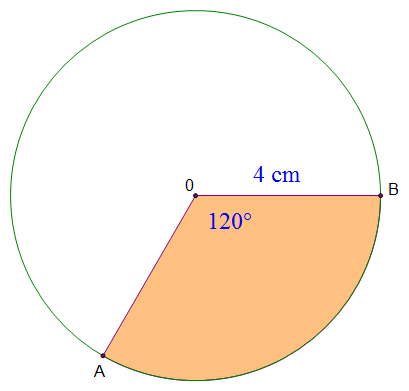
Use $\text{Sector area} = \dfrac{\theta}{360} \times \pi r^2$.
Find the radius of the following circle:
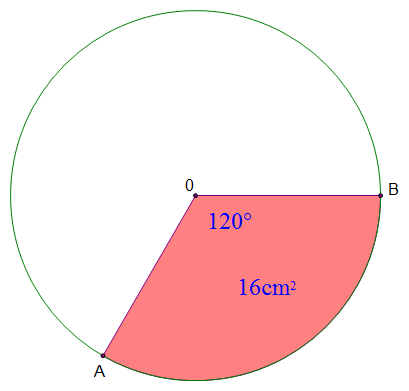
Rearrange $\text{Sector area} = \dfrac{\theta}{360} \times \pi r^2$ to solve for $r$.
Substituting to find solution
What is the length of arc $AB$?
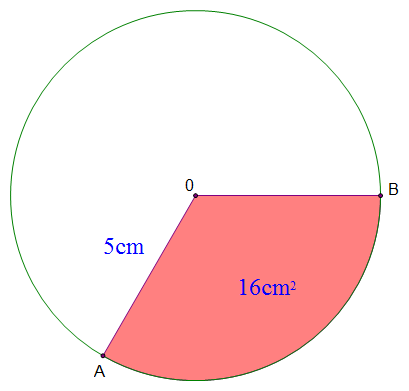
Relating arc length to sector area.
$$ \frac{\text{length of arc}}{\pi d} = \frac{\text{area of sector}}{\pi r^2} $$ $$ \text{length of arc} \times \pi r^2 = \text{area of sector} \times \pi d $$ $$ \text{length of arc} = \frac{ \text{area of sector} \times \pi d }{ \pi r^2 } $$Chords, Bisectors and Tangents
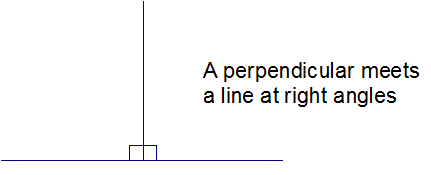

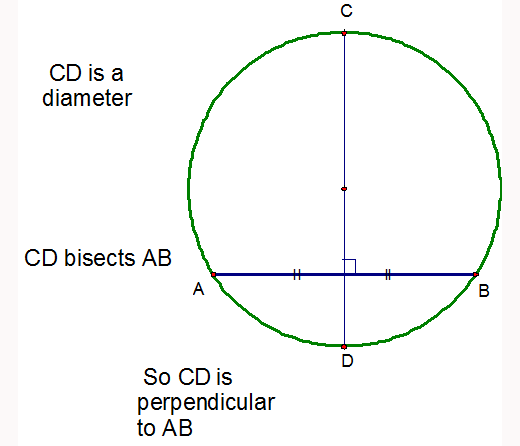
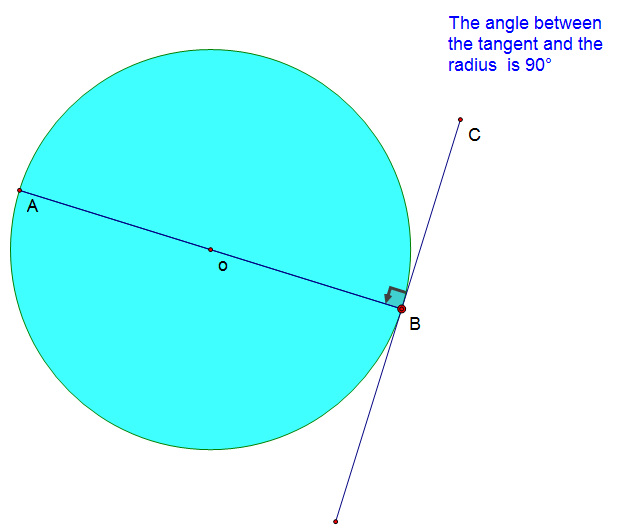
A tangent touches the circle at one point only.
Pythagoras in a Circle
Drag the point on the circle. The right triangle updates and you can see $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$ and $x^2 + y^2 = r^2$ in action.
Coordinates of point: (x, y) = (, )
Radius: r =
Pythagoras in the triangle:
$a = |x|,\; b = |y|,\; c = r$
$a^2 + b^2 = $
$c^2 = r^2 = $
Because the point lies on the circle, $x^2 + y^2 = r^2$ and that’s exactly $a^2 + b^2 = c^2$.
What is the value of $x$?
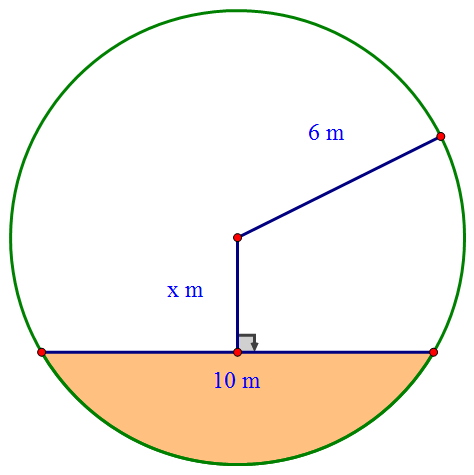
Move the radius down:
$$ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 $$
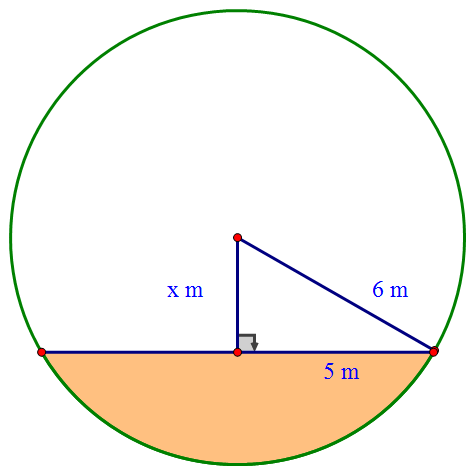
Using Pythagoras’ theorem to find the missing side.
$$ \text{hypotenuse}^2 = \text{short side}^2 + \text{other side}^2 $$ $$ 6^2 = 5^2 + x^2 $$ $$ 6^2 - 5^2 = x^2 $$ $$ 36 - 25 = x^2 $$ $$ x^2 = 11 $$ $$ x = \sqrt{11} $$ $$ x = 3.3166\ \text{m} $$ $$ x = 3.3\ \text{m (1 dp)} $$The Angle in a Semi‑Circle
A famous result in geometry says that any angle drawn in a semi‑circle is a right angle. This is sometimes called Thales’ Theorem.
Angle in a semi‑circle = $90^\circ$