Pythagoras’ Theorem
The longest side of a right‑angled triangle is called the hypotenuse, which is always opposite the right angle.
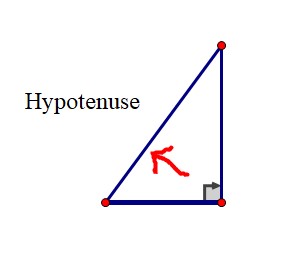
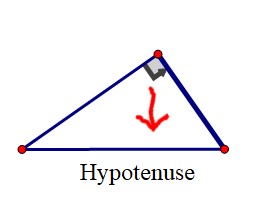
In any right‑angled triangle, the area of the square on the hypotenuse
= the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.

For any right‑angled triangle, this rule can be used to calculate the length of the hypotenuse if the lengths of the smaller sides are known.
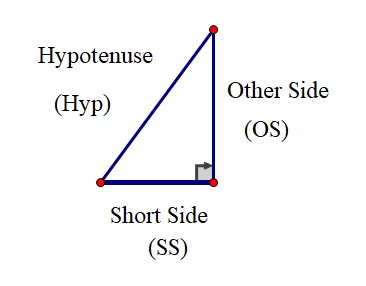
$$
(\text{Hypotenuse})^2 = (\text{Shortest side})^2 + (\text{Other side})^2
$$
To find the length of the hypotenuse
- Sketch the triangle
- Mark the hypotenuse
- Write out Pythagoras’ Theorem
- Solve
- Write out the solution
Example
Find the length of the hypotenuse:
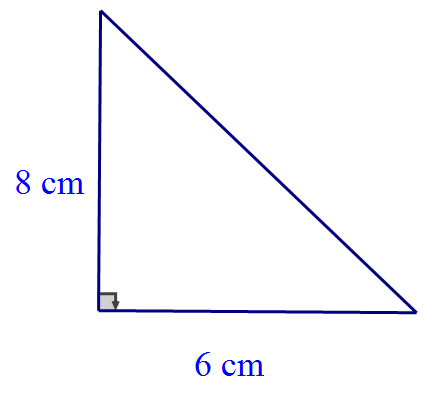
$$
c^2 = 8^2 + 6^2
$$
$$
c^2 = 64 + 36
$$
$$
c^2 = 100
$$
$$
c = 10
$$
To find the length of a shorter side
- Sketch the triangle
- Mark the hypotenuse
- Write out Pythagoras’ Theorem
- Solve
- Write out the solution
Example
Find the length of the missing side:
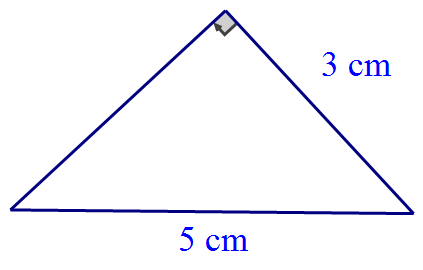
$$
13^2 = x^2 + 5^2
$$
$$
169 = x^2 + 25
$$
$$
x^2 = 144
$$
$$
x = 12
$$
The converse of Pythagoras
$$
(\text{Hypotenuse})^2 = (\text{Shortest side})^2 + (\text{Other side})^2
$$
$$
\Rightarrow \text{The triangle is right‑angled.}
$$
Example
Is this a right‑angled triangle?
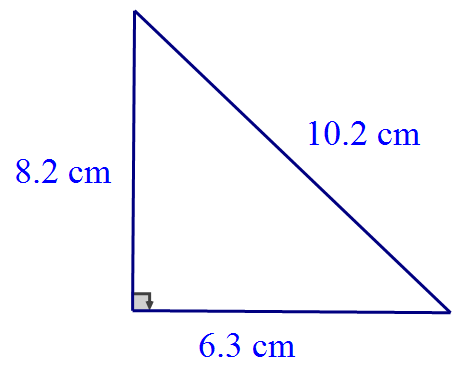
Make separate calculations for hypotenuse and sides.
$$
10^2 = 100
$$
$$
6^2 + 8^2 = 36 + 64 = 100
$$
$$
\Rightarrow \text{Yes, it is right‑angled.}
$$
Hidden Pythagoras
Sometimes Pythagoras’ Theorem is needed even when it is not obvious at first.
Example
Calculate the perimeter of triangle ABD.
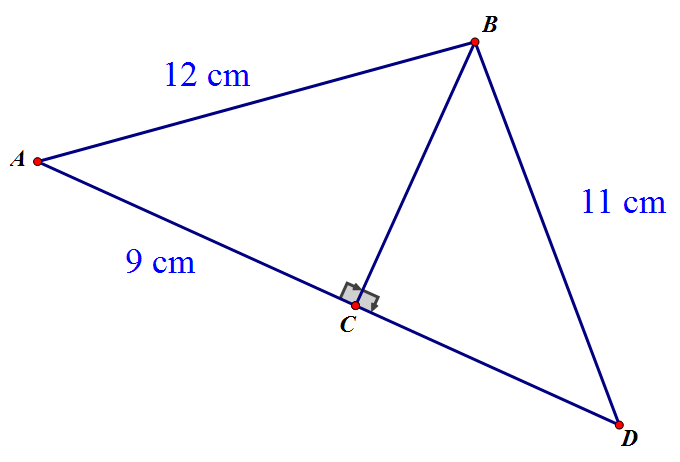
Find BC using triangle ACB, then use triangle BCD to find CD.
$$
BC^2 = 10^2 - 6^2 = 100 - 36 = 64
$$
$$
BC = 8
$$
$$
CD^2 = 11^2 - 8^2 = 121 - 64 = 57
$$
$$
CD = 7.6
$$
Perimeter = 12 + 11 + 9 + 7.6 = 39.6 cm
Pythagoras with co‑ordinates
Example
Calculate the distance between A(-5, 10) and B(3, 0).
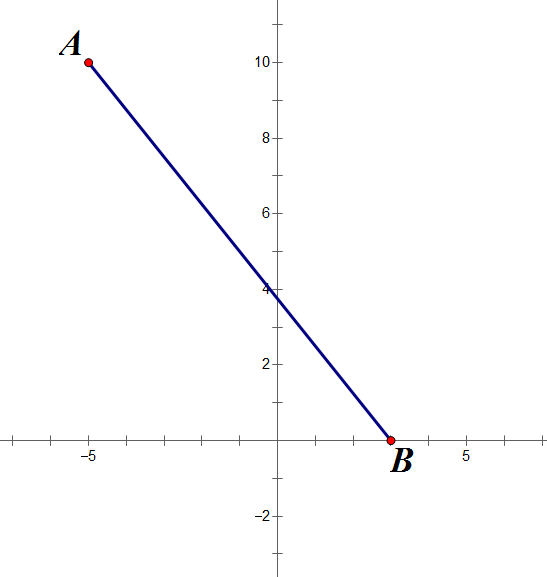
$$
d^2 = (3 - (-5))^2 + (0 - 10)^2
$$
$$
d^2 = 8^2 + (-10)^2 = 64 + 100 = 164
$$
$$
d = \sqrt{164} \approx 12.8
$$
This is the basis of the distance formula.