Project Management
Precedence Tables
These are used to map out the steps needed to complete a project. A list of tasks is completed, along with their completion time.
Example
An outhouse is being repurposed as a workshop. The earth floor is to be replaced with concrete, which is being mixed and poured onsite.
Here is a list of tasks:
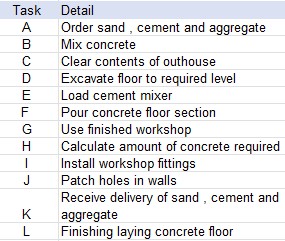
Nothing can happen before the outhouse has been cleared and the floor excavated !
Here is the order of tasks :
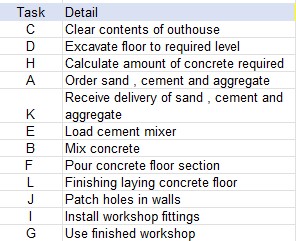
Some steps - called dependencies - can only be started after others immediately before have been already been started or completed.
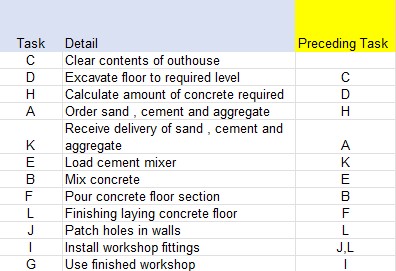
Before any concrete mixing takes place, the materials must have been delivered. The sub activitites of loading, mixing and pouring must be repeated until laying the floor is finished. Installing the workshop fittings can only happen once the floor and walls have been sorted.
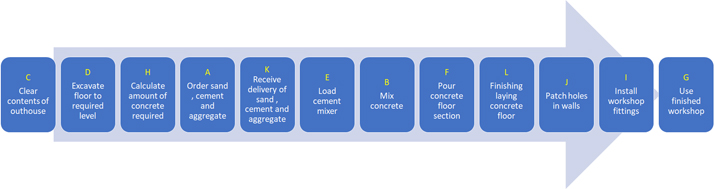
As well as knowing the order of tasks, their timings must also be known.
It is estimated that 5 days should be allocated to clearing the outhouse, a further 5 for excavating the floor. Then the calculation and ordering of materials should be given a day. The delivery of materials are expected a week after ordering. Five days are allocated to laying the floor, 2 for patching up holes in the wall and 3 for installing the workshop fittings.
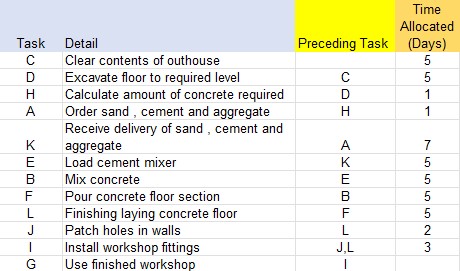
If all the timings in the table are added up, the total is 44 days.
However, the table includes the subactivites associated with making concrete for laying the floor and ignores the fact that activities H and A are completed on the same day.
The critical path is the longest time to go from start to finish.
It is shown as the large arrow in this network diagram :
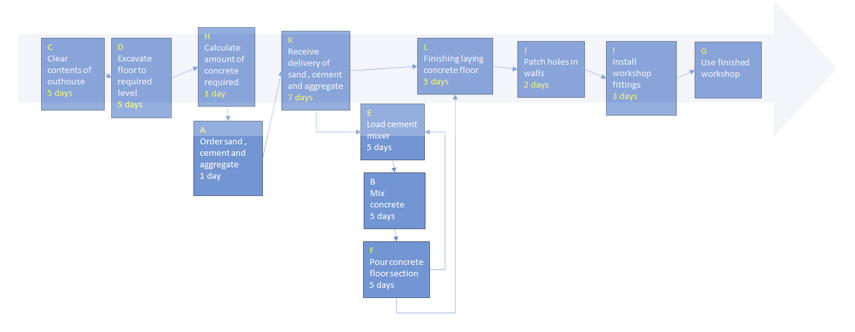
5+5+1+7+5+2+3 = 28 days are required to do the work.
The workshop can be used on the 29th day.
Example
Find the critical path for the following precedence table :
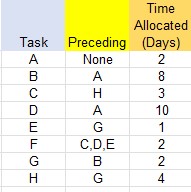
First, complete a network diagram.
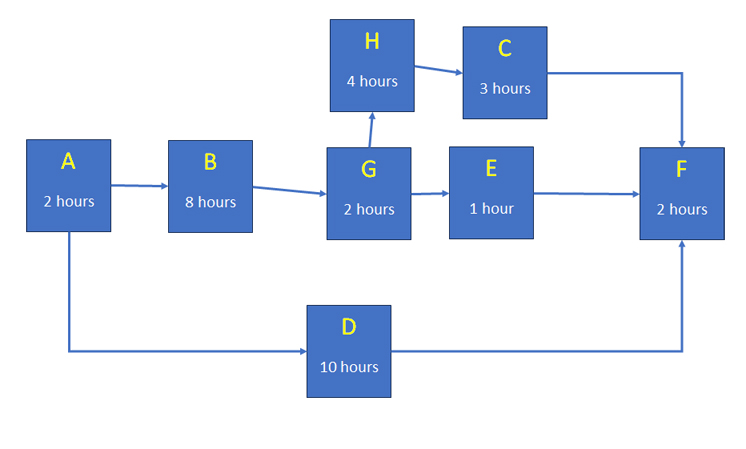
There are 3 paths to follow
A,B,G,E,F takes 2+8+2+1+2 = 15 hours
A,B,G,H,C,F takes 2+8+2+4+3+2 = 21 hours
A,D,F takes 2+10+2 = 14 hours
The critical path is A,B,G,H,C,F and takes 21 hours.
Examples at CIMT.org.uk
Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart ( named after Henry Gantt) is a bar chart which shows tasks on the y-axis and time on the x-axis.
Example
Basic Gantt chart for data given above
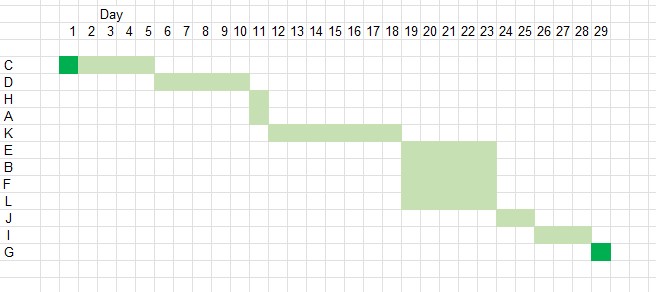
The workshop can be used on the 29th day.
PERT Chart
Program evaluation and review technique
Developed by The US Navy in 1957, PERT charts are used by project managers to create realistic schedules by coordinating tasks and estimating their duration by assigning three time estimates for each; optimistic, most likely and pessimistic.
Each task is shown as a seperate box in a network diagram. Dependencies and the critical path can be seen.
Optimistic time (o) : Minimum possible time to complete an activity or path.
Most likely time (m) : Best estimate to complete an activity or path.
Pessimistic time (p) : Maximum possible time to complete an activity or path.
Expected time (te) : Best estimate of average time to complete an activity or path.
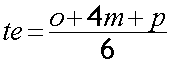
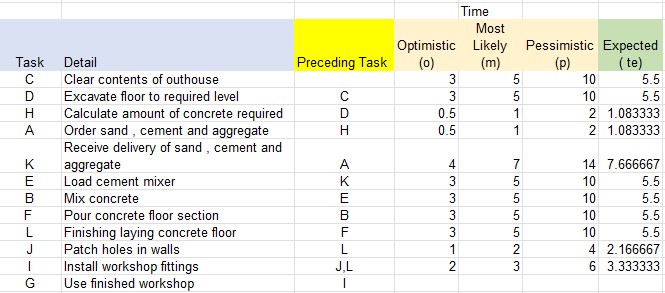
Example
Expected time calculation for data given above
In the basic diagram, the nodes (boxes containing the activities and milestones) are connected by arrows. Some PERT charts contain extra data such as start/finish dates.
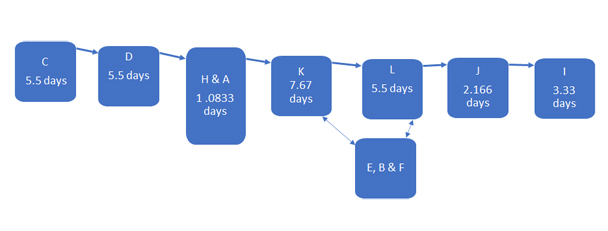
The critical path is 30.7493 days.
Learn more at Simplilearn.com