Periodic Table of the elements
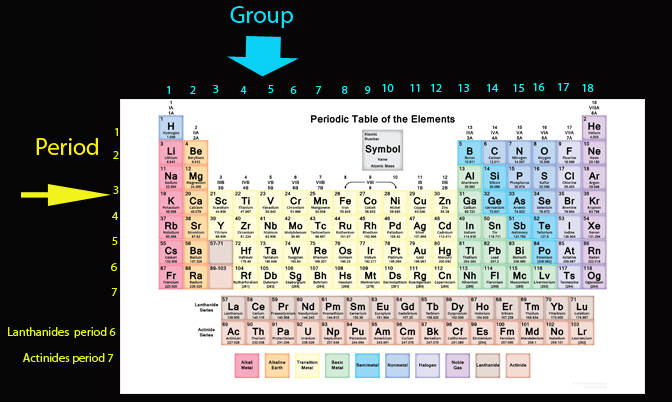
In 1864 Julius Lothar Meyer started to organize the elements by atomic mass and grouped them according to their chemical properties . In 1869 Dmitrii Mendeleev then organised the known elements by their properties and predicted that there were undiscovered ones. This started what is now known as the periodic table
Henry Moseley's discovery that an element’s atomic number is identical to the number of protons it has led to the realization the periodic table should be ordered by atomic number (called Z )- and not atomic mass ( called A)
The atomic number gave both the number of protons and electrons, since the atom has an overall charge of zero.The atomic mass gave the number of nucleons - the total number of neutrons and protons. So to find the number of neutrons, A - Z , subtract Z from A.
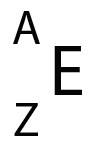


The Pauli exclusion principle affects how the electrons fill the shells.
Shell 1 holds a maximum of 2 electrons, shell 2 holds a maximum of 8 electrons, like so : 2, 8 , 8 , 18, 18, 32
Each shell has subshells - s,p,d and fStructure of Atoms
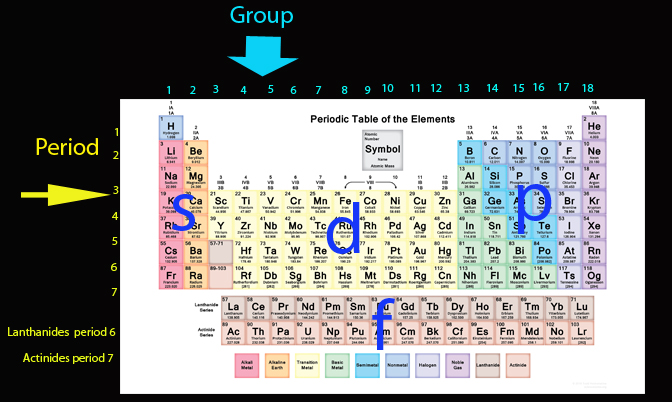
The s block covers the first two columns, groups 1 and 2. The p block is the right hand 6, so groups 13,14,15,16,17 and 18.
These subshells are filled in a particular way : filling subshells
Isotopes of an element are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. The atoms share the same chemical properties, but will have different physical properties, like hardness or boiling point.
Example
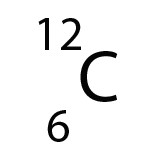
- The atomic number (Z) is 6, so Carbon has 6 protons.
- There are 12 nucleons (A) , so there are A - Z = 12-6 = 6 neutrons.
- There are 6 electrons, since A = 6
- Carbon is in period 2, so has two electron shells and the electron arrangement can be written as 2,4
- Carbon is in group 14 so the electron arrangement can be written as 1s22s22p2
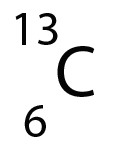
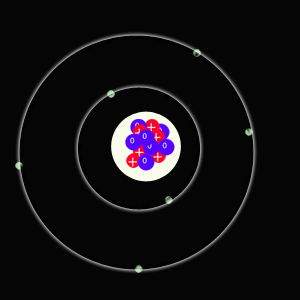
- The atomic number (Z) is 6, so Carbon has 6 protons.
- There are 13 nucleons (A) , so there are A - Z = 13-6 = 7 neutrons.
- There are 6 electrons, since A = 6
The Royal Society of Chemistry Interactive Periodic Table
Valence, Lewis Symbols, Atomic size and Ionization energy :The periodic trends
