The modulus function y =│x│
The absolute value of x is defined as
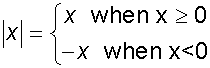
This always gives a positive result.
Example
y=3x2+6x-2 has graph
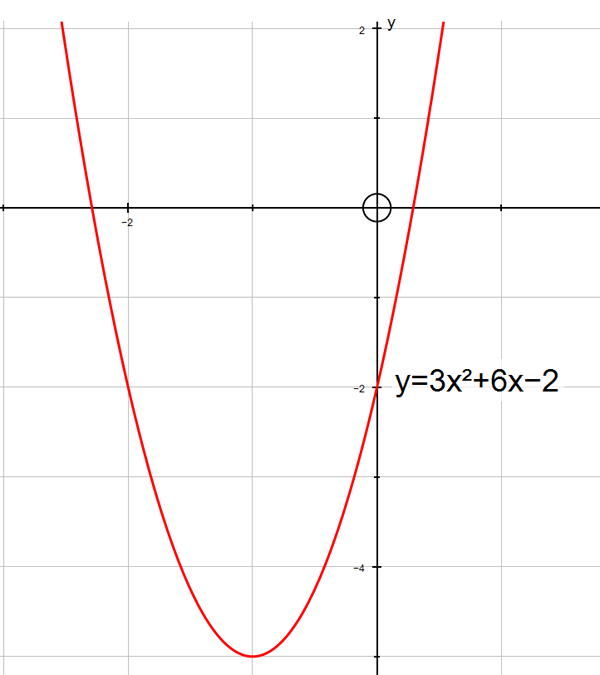
Whereas
y=|3x²+6x−2| has graph
Note how the negative portions have been
reflected in the x-axis.
Examples
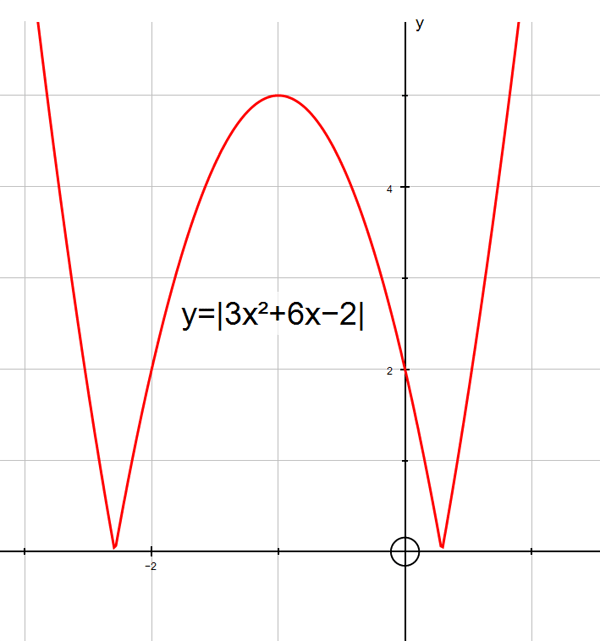
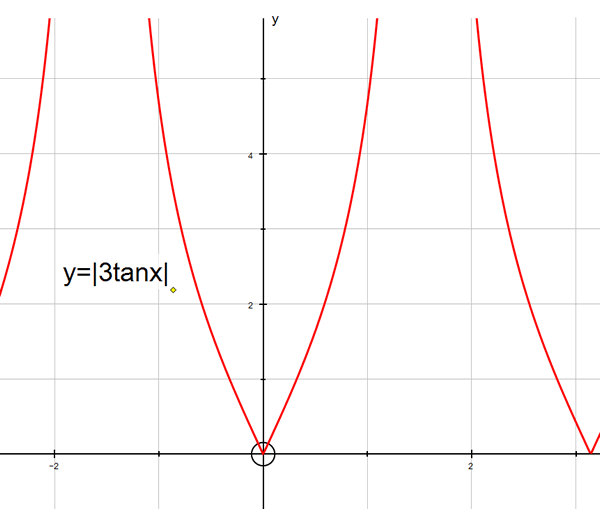
y =| 3tanx|
y =| 3x + 2|
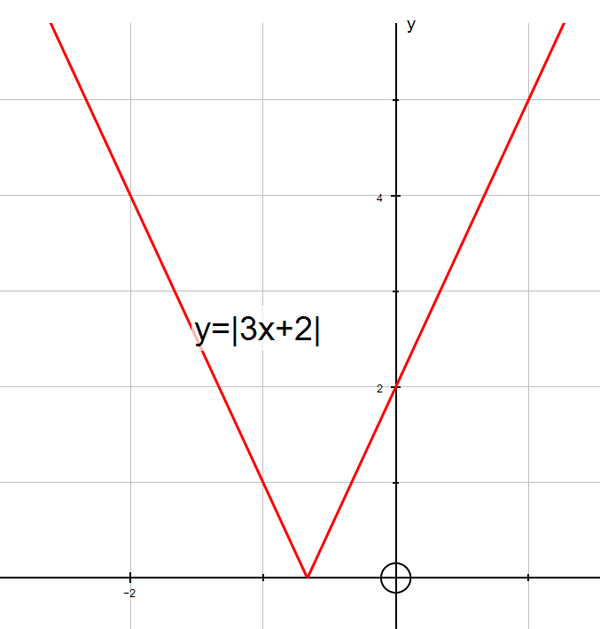
Odd and Even functions
Odd functions have half-turn symmetry about the origin,
so f(-x) = - f(x)
Example
y=x3
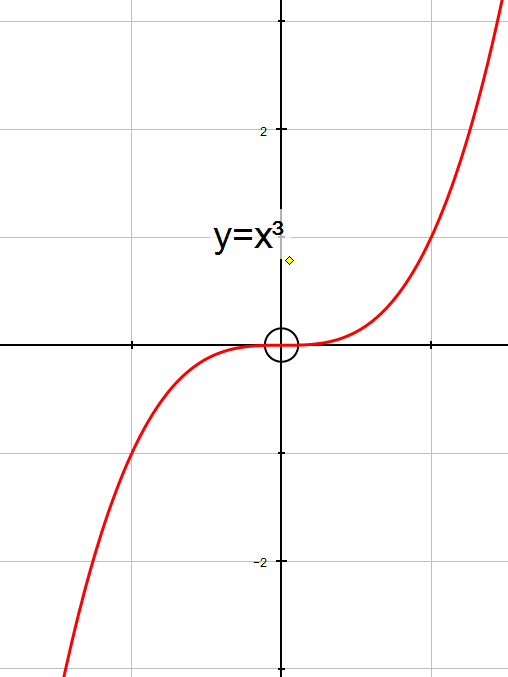
y=x5−3x
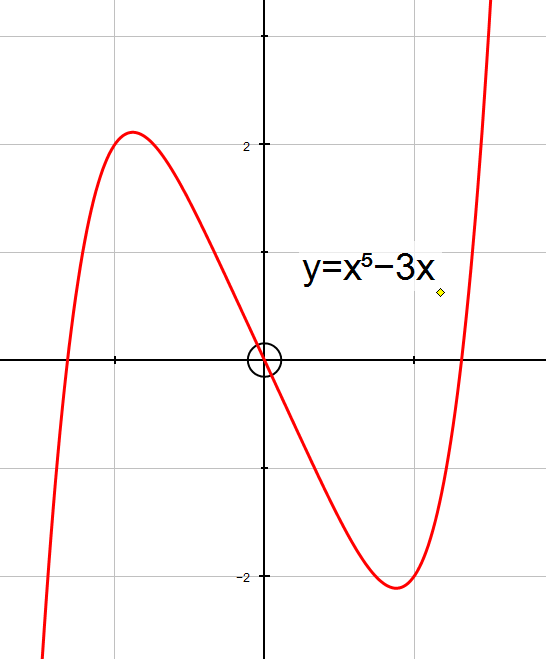
Example
Show that x5+ 3x3 is an odd function.
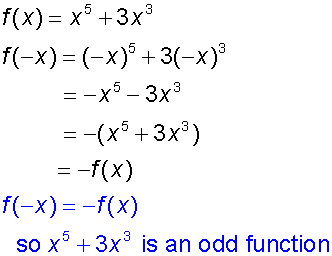
Even functions are symmetrical about the y – axis
so f(-x) = f(x)
Example
y=x4 - 1
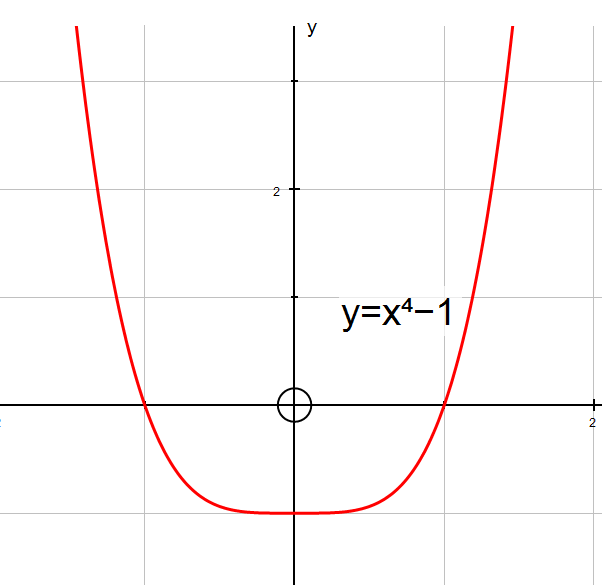
Example
Is x6+ 3x2 an even function ?
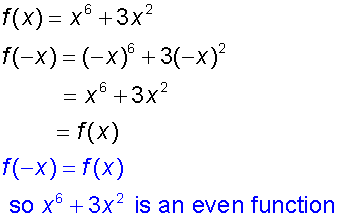
Asymptotes
An asymptote to a curve is a straight line which
the curve approaches but never reaches.
Example
f(x) = 1/x
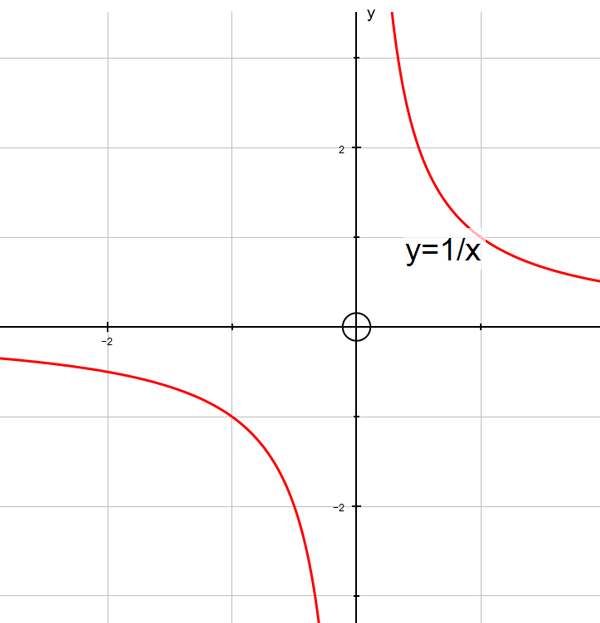
The graph y=1/x has vertical asymptote x=0
and horizontal asymptote y = 0.
To the left of the line x=0, f(x) tends to - ∞
as x tends to zero.
To the right of the line x=0, f(x) tends to ∞
as x tends to zero.
Example
f(x) = (x-3) /(x3+1)
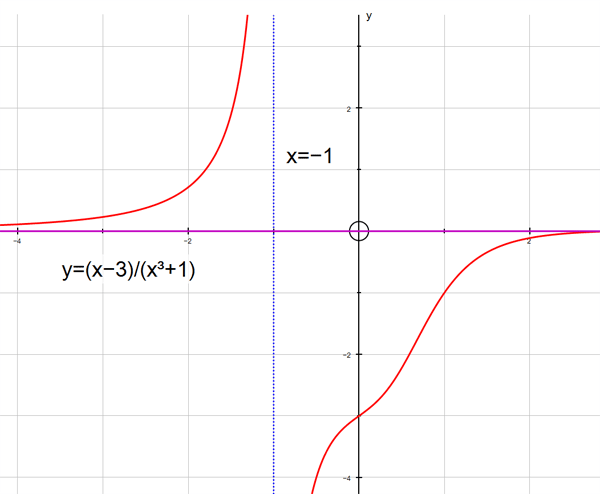
The graph y= (x-3) /(x3+1) has vertical asymptote x=-1
and horizontal asymptote y = 0.
To the left of the line x=-1, f(x) tends to ∞
as x tends to -1.
To the right of the line x=-1, f(x) tends to -∞
as x tends to -1.
Example
f(x) = (x+1)(x−3)/(x+3)(x−4)
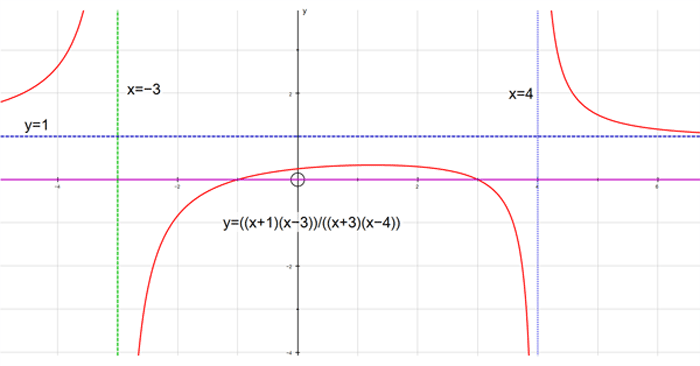
The graph has vertical asymptotes x=-3 and x=4
and horizontal asymptote y = 1
Finding asymptotes
Vertical asymptotes are found by considering what makes the denominator zero.
Horizontal and oblique asymptotes need a little further action.
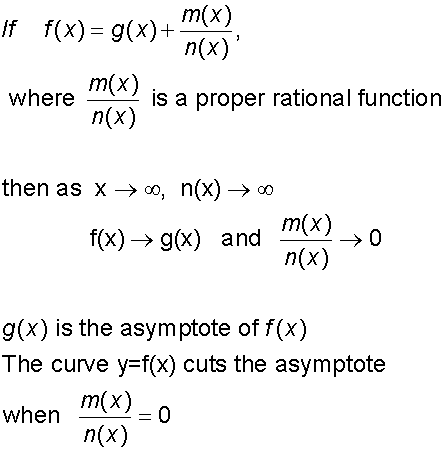
Use algebraic division to reduce the function.
The quotient becomes the asymptote.
Example
Find the asymptotes of the function
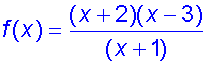
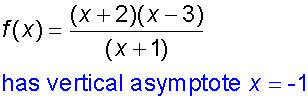
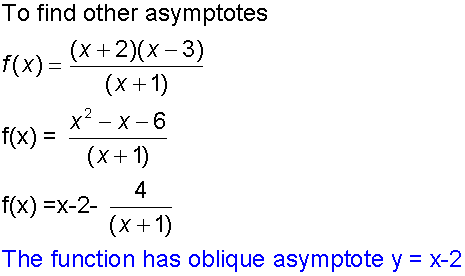
Alternatively:-
Asymptotes parallel to the x-axis can be found
by equating the co-efficient of the highest power
of x to zero. Those parallel to the y-axis can be found by equating the co-efficient of the highest power
of y to zero.
To find oblique asymptotes, substitute y=mx+c into the equation and equate the co-efficients of the two highest powers of x to zero.
Example
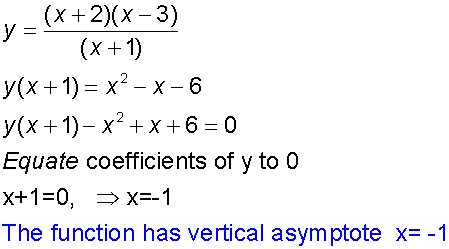
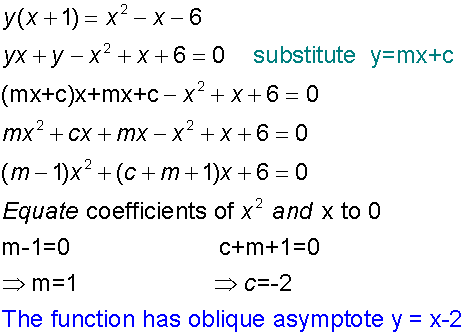
Sketching Asymptotes
To sketch a function which has asymptotes,follow these steps :-
- Identify any vertical asymptotes
- Identify any horizontal or oblique asymptotes
- Identify the y – intercept
- Identify the x – intercept
- Find stationary points
- Identify nature of stationary points
- Investigate what happens as values approach infinity
- Sketch and annotate
Example
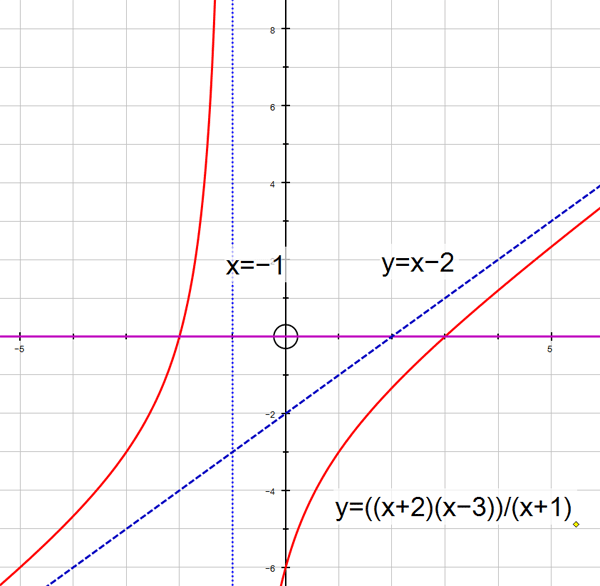
Using the example above, sketch the function
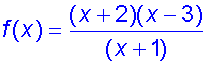
Vertical asymptotes are found by setting the denominator to zero:
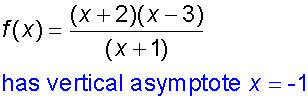
Horizontal and oblique asymptotes are found by dividing through the fraction:
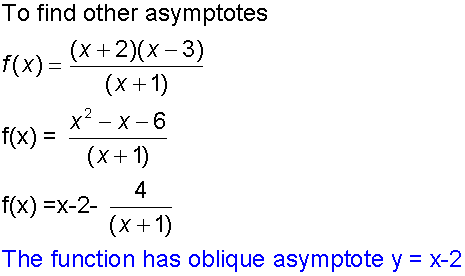
The y - intercept occurs when x = 0
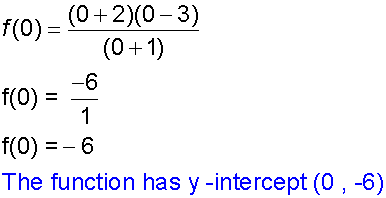
The x - intercept occurs when y = 0
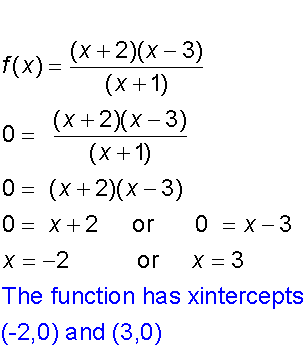
To find the stationary points, set the first derivative
of the function to zero, then factorise and solve.
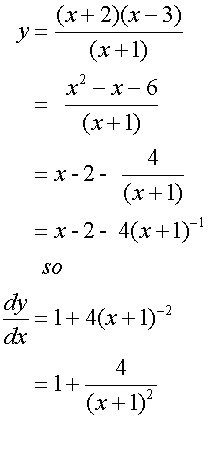
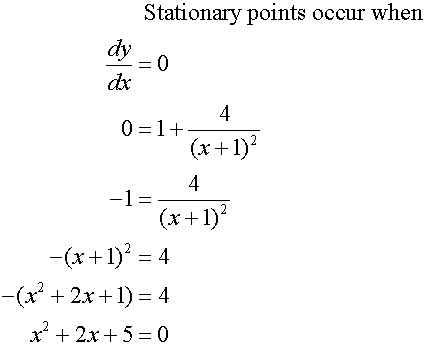
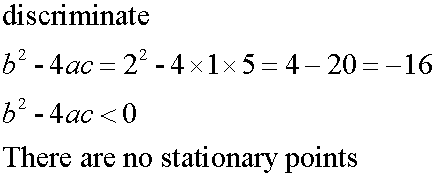
Sketch the graph
Example
sketch the function
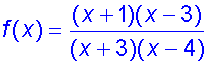
Vertical asymptotes:
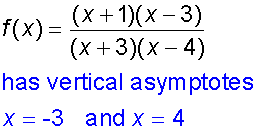
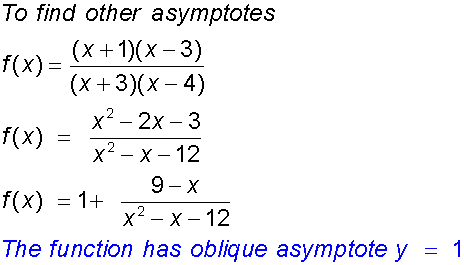
The y - intercept :

The x - intercept:
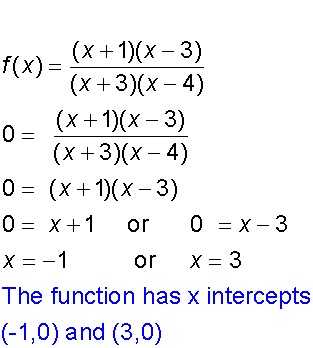
Stationary points :
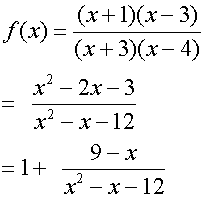
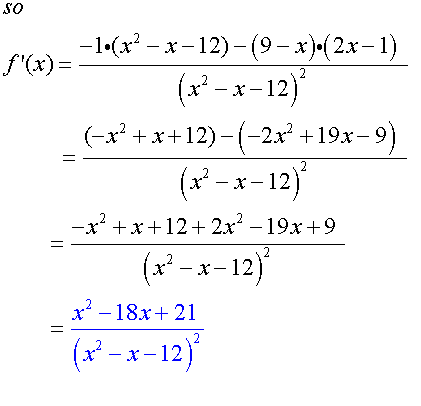
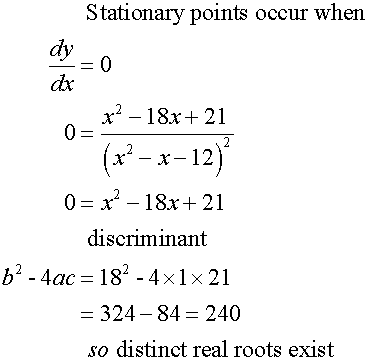
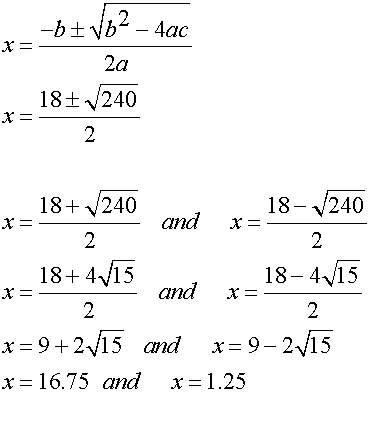
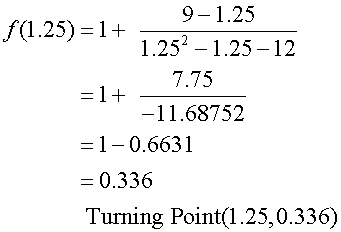
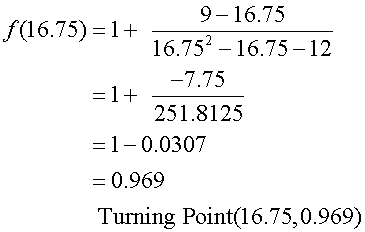
Find nature of turning points
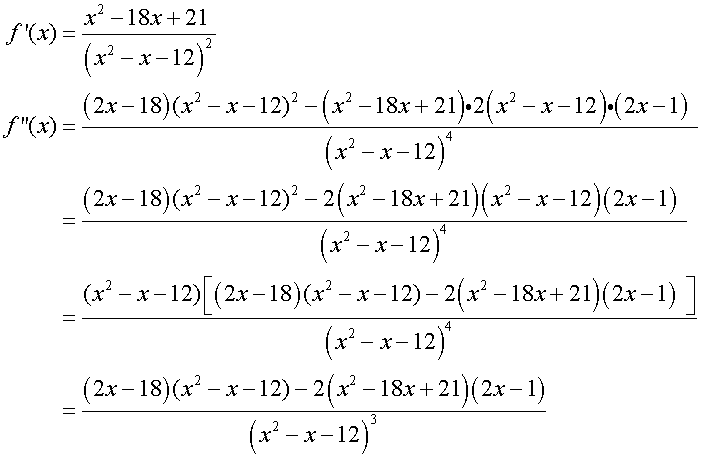
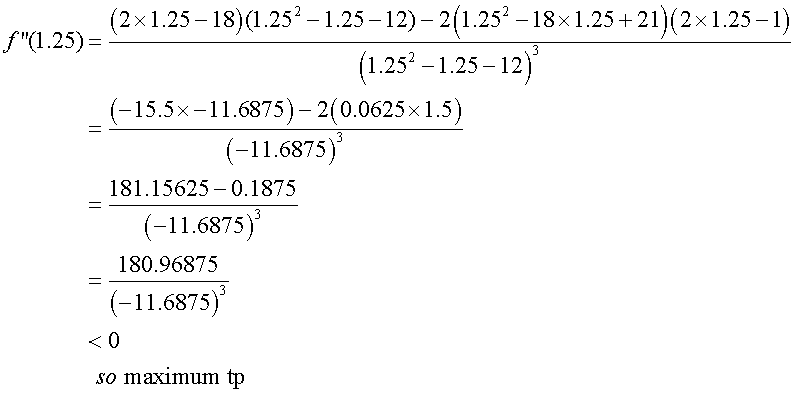
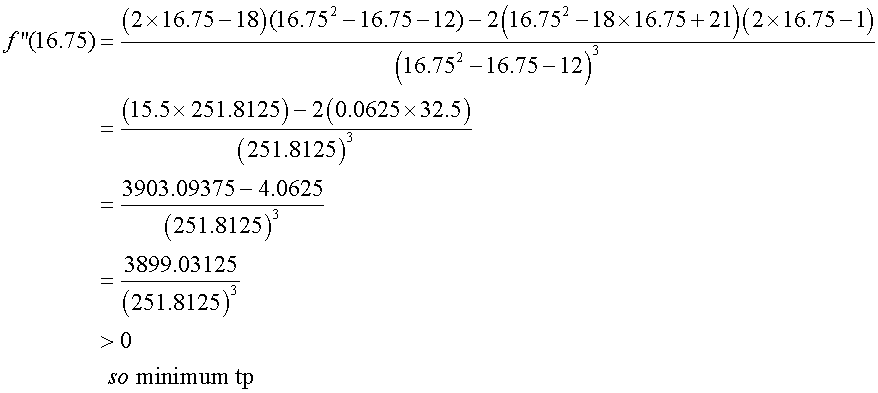
Sketch

