Integers
Integers are whole numbers, which can be positive or negative.
The Set of Integers
The set of integers includes all whole numbers and their negatives.
\[ \mathbb{Z} = \{ \ldots, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, \ldots \} \]
Integers are used when counting forwards and backwards, measuring changes, or describing positions relative to zero.
- Temperature: \( -3^\circ \text{C}, 0^\circ \text{C}, 7^\circ \text{C} \)
- Money: \( -£12 \) (debt), \( £0 \), \( £45 \)
- Elevation: \( -20 \text{ m} \) (below sea level), \( 0 \), \( 120 \text{ m} \)
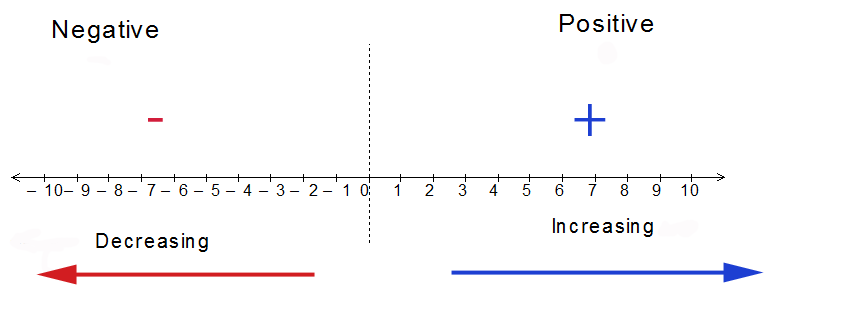
Polarity
The polarity of a number tells you whether it is positive or negative.
Numbers greater than zero are positive,
numbers less than zero are negative.
Zero itself is neutral.
A negative number is written with a minus sign in front of it.
It is good practice to put negative numbers in brackets, e.g. (−6).
If you have an account at the bank and you have arranged an overdraft facility then:
If you are £6 overdrawn, you have less money available than if you had £12.
If you are £125 overdrawn, you owe the bank more than if you were £5 overdrawn.
If you have £5 in your account, you have more money available than if you were £50,000 overdrawn.
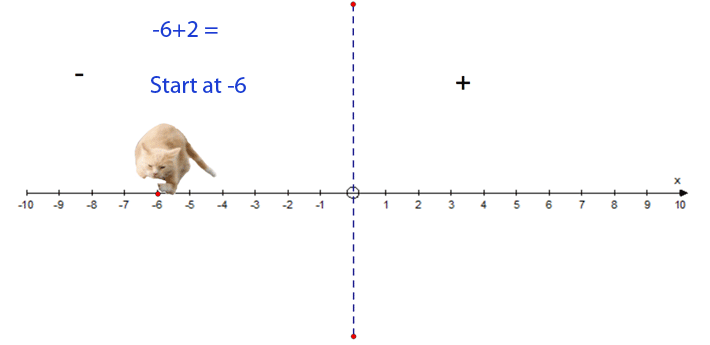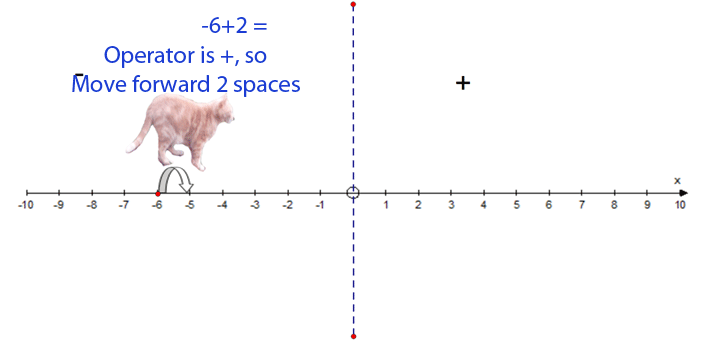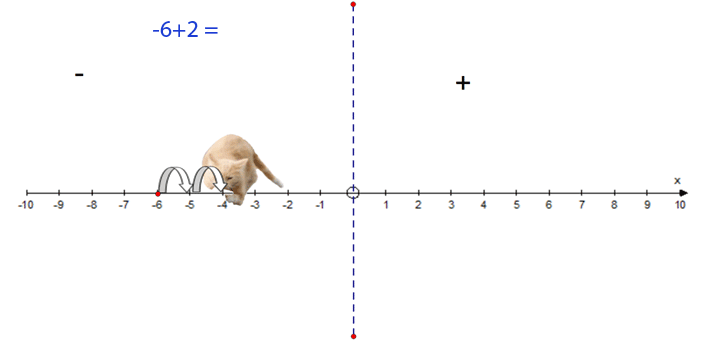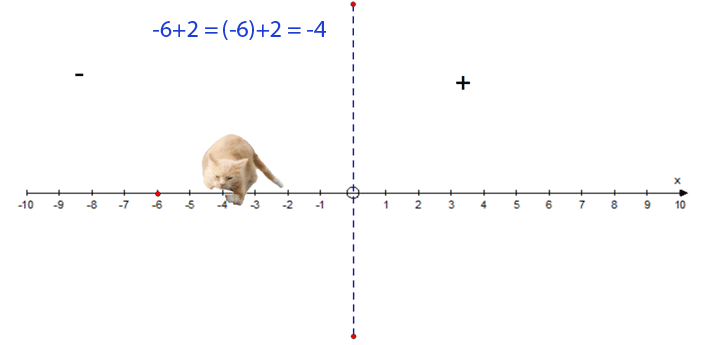
Addition / Subtraction
- Start at the first number
- Face the polarity of the second number
- The operator between the numbers is important
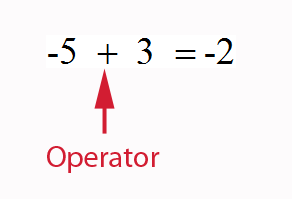
+ means go forwards − means go backwards.
- Move the number of steps given by the second number
- Finish
3 + 4 = 7
- Start at 3
- Face towards the positive
- Go 4 steps forwards
- Finish at 7
3 − 4 = −1
- Start at 3
- Face towards the positive
- Go 4 steps backwards
- Finish at −1
−6 + 2 = −4
−1 − 4 = −5
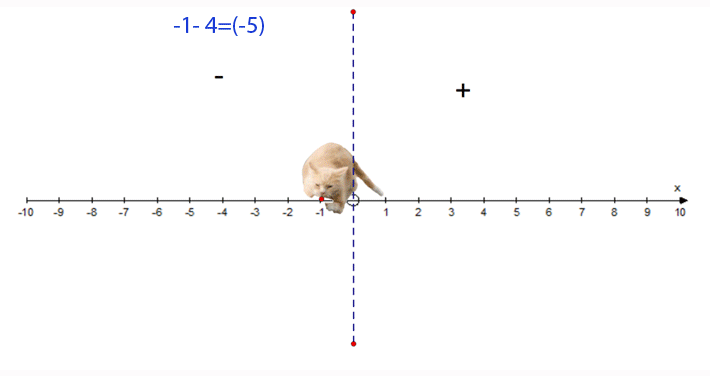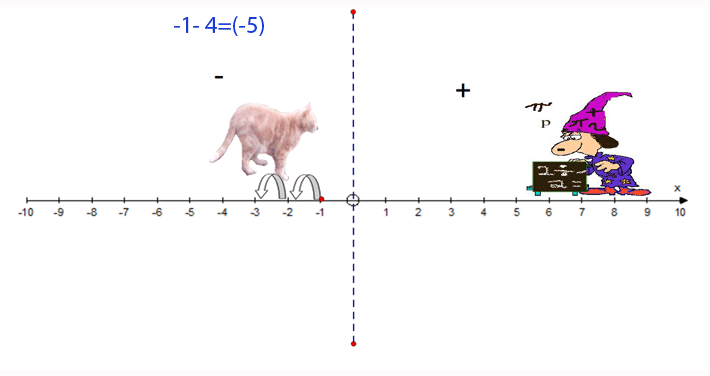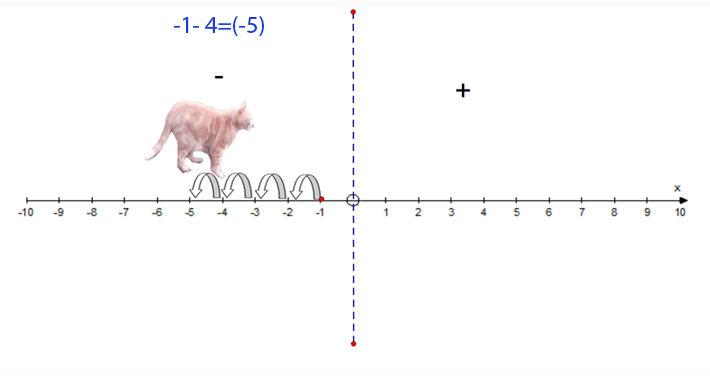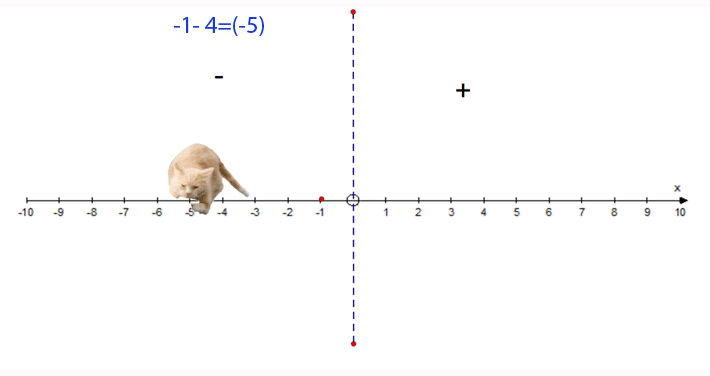
- Start at −1
- Face towards the positive
- Go 4 steps backwards
- Finish at −5
Adding a negative number is the same as subtracting its positive counterpart.
(This is like making a purchase with a
debit card
.)
−5 + (−3) = −8
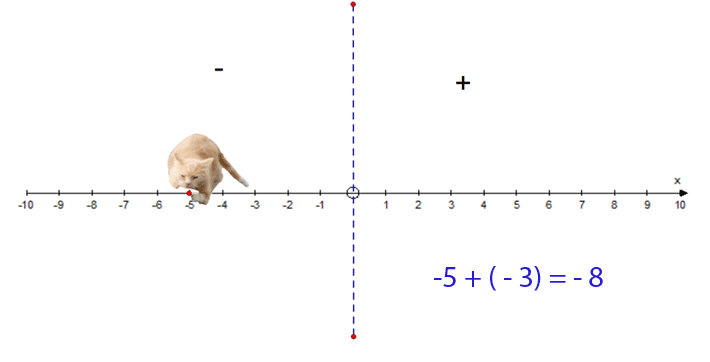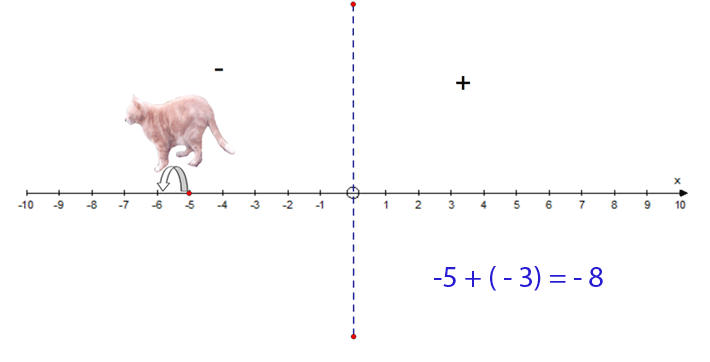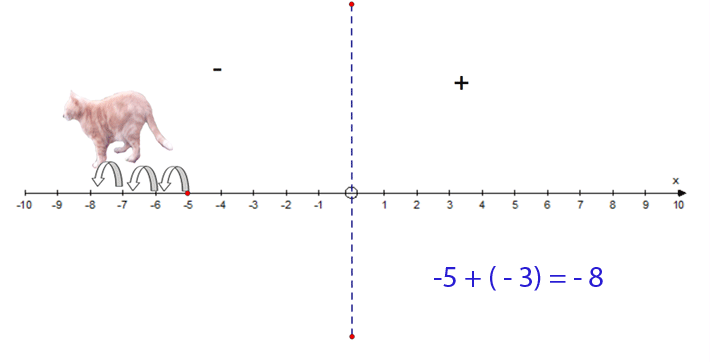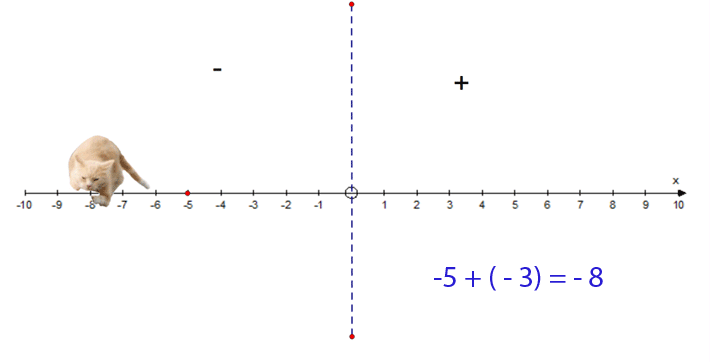
- Start at −5
- Face towards the negative
- Go 3 steps forwards
- Finish at −8
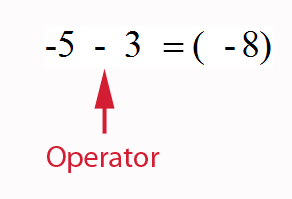
Subtracting a negative number is the same as adding its positive counterpart.
(Like buying something and then returning it for a refund.)
−5 − (−8) = 3
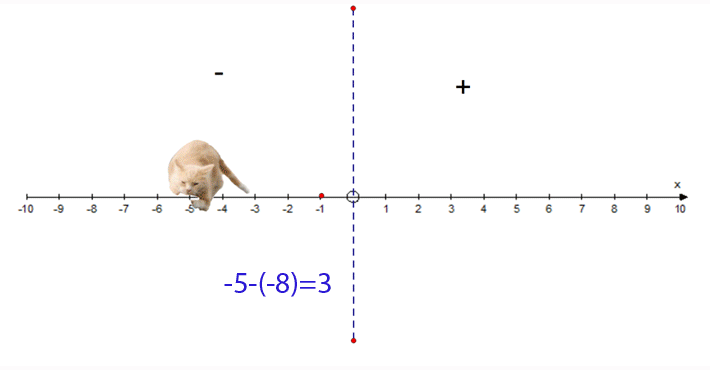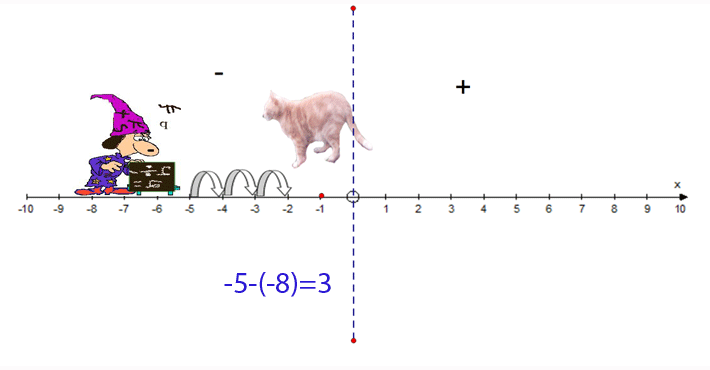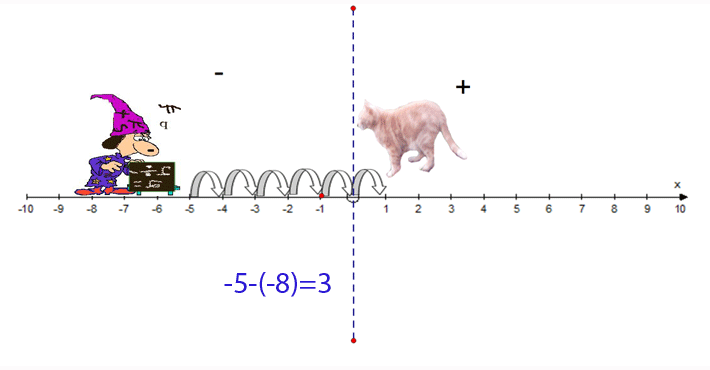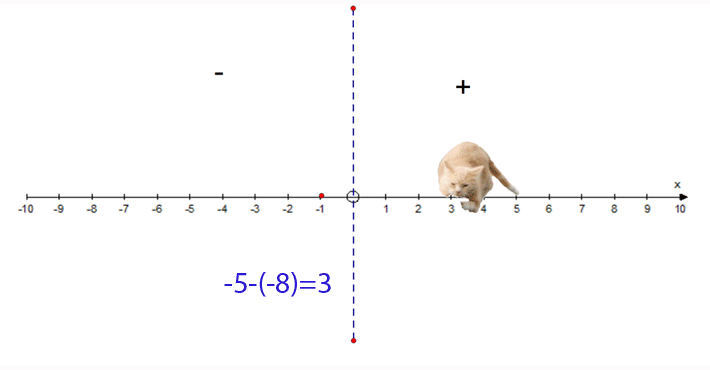
- Start at −5
- Face towards the negative
- Go 8 steps backwards
- Finish at 3
Multiplying Integers
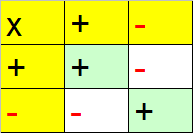
Like signs produce a positive answer.
Mixed signs produce a negative answer.
5 × 8 = 40
(−5) × (−8) = 40
(−5) × 8 = −40
5 × (−8) = −40
Dividing Integers
Like signs produce a positive answer.
Mixed signs produce a negative answer.
40 ÷ 8 = 5
(−40) ÷ (−8) = 5
(−40) ÷ 8 = −5
40 ÷ (−8) = −5
