Strategy for factorising quadratics ax2 + bx + c
Warning : Not all quadratics factorise !
- Write down the factor pairs of the coefficient of x2 in the expression , a.
- Write down the factor pairs of the constant term, c.
- List all possible combinations of these factor pairs.
- Pick the correct combination by cross multiplying, adding and comparing with the coefficient of x in the expression, b.
- Read across to get the contents of the brackets.
- Check by expanding brackets and comparing all terms with the original expression.
- Write out solution
Worked examples
Factorise x2 + 4x + 3
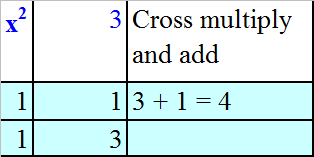
Read across,
so (x+1) in one bracket, (x+3) in the other.
x2 + 4x + 3 = (x + 1 )( x + 3)
Factorise x2 + x - 6
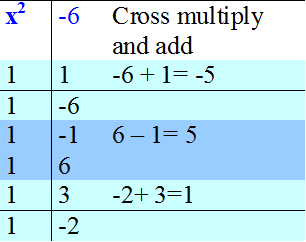
Read across,
so (x+3) in one bracket, (x-2) in the other.
x2 + x - 6 = (x - 2 )( x + 3)
Factorise x2 - 3x - 10
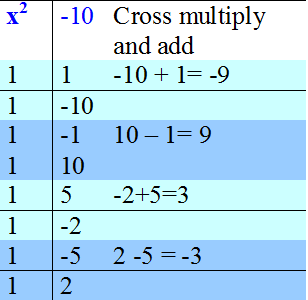
x2 - 3x - 10 = (x - 5 )( x + 2)
Factorise x2 - 7x - 8
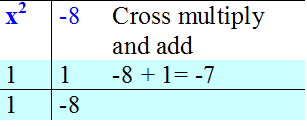
x2 - 7x - 8 = (x - 8 )( x + 1)
Factorise 1 - x - 2x2
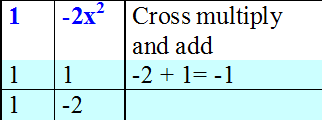
1 - x - 2x2 = (1+ x ) (1 - 2x)
Factorise 6x2 + 23x + 10
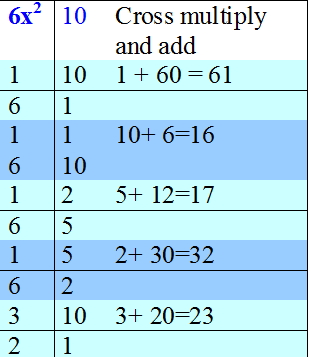
6x2 + 23x + 10 = (2x + 1 )( 3x + 10)
Factorise 3x2 + 7x + 2
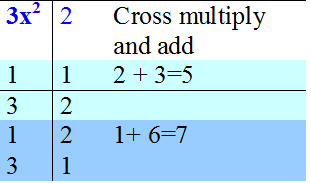
3x2 + 7x + 2 = (x + 2 )( 3x + 1)
Factorise 4x2 - 21x + 5
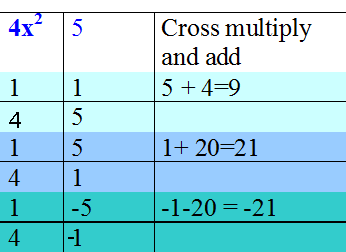
4x2 - 21x + 5 = (x - 5 )( 4x - 1)
- ax2 + bx + c factorises into the form ( + )( + )
- ax2 - bx + c factorises into the form ( - )( - )
- ax2 + bx - c factorises into the form ( - )( + )
- ax2 - bx - c factorises into the form ( - )( + )
